SLAS638A January 2009 – October 2015 SN65HVS885
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PWP|28
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- PWP|28
Orderable Information
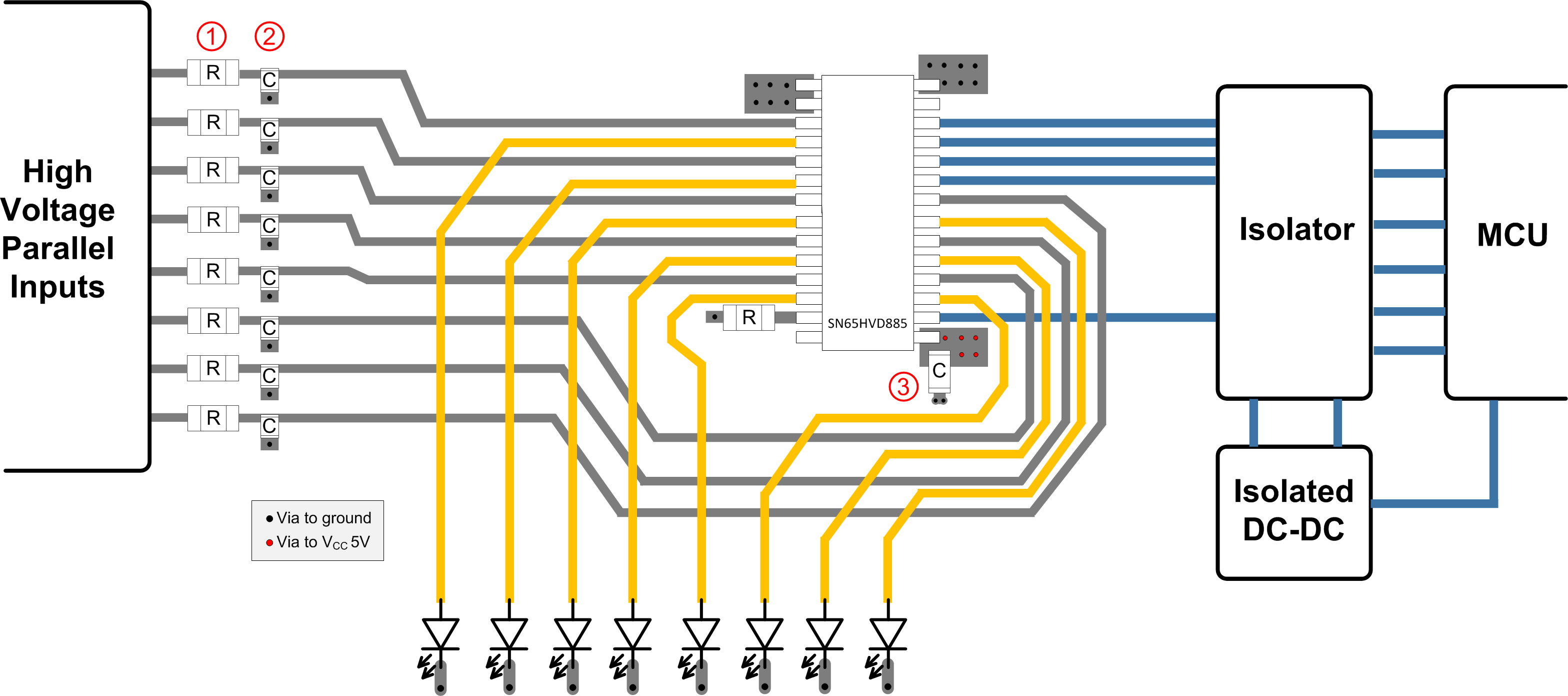
11 Layout
11.1 Layout Guidelines
- Place series MELF resistors between the field inputs and the device input pins.
- Place small ~22 nF capacitors close to the field input pins to reduce noise.
- Place a supply buffering 0.1-µF capacitor around as close to the VCC pin as possible.
11.2 Layout Example