SLLS516E August 2002 – July 2015 SN65LVDS100 , SN65LVDS101 , SN65LVDT100 , SN65LVDT101
UNLESS OTHERWISE NOTED, this document contains PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description (Continued)
- 6 Device Options
- 7 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 8 Specifications
- 9 Parameter Measurement Information
- 10Detailed Description
-
11Application and Implementation
- 11.1 Application Information
- 11.2
Typical Application
- 11.2.1 PECL to LVDS Translation
- 11.2.2 LVDS to 3.3-V PECL Translation
- 11.2.3 5-V PECL to 3.3-V PECL Translation
- 11.2.4 CML to LVDS or 3.3-V PECL Translation
- 11.2.5 Single-Ended 3.3-V PECL to LVDS Translation
- 11.2.6 Single-Ended CMOS to LVDS Translation
- 11.2.7 Single-Ended CMOS to 3.3-V PECL Translation
- 11.2.8 Receipt of AC-Coupled Signals
- 12Power Supply Recommendations
- 13Layout
- 14Device and Documentation Support
- 15Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- D|8
- DGK|8
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
1 Features
- Designed for Signaling Rates ≥ 2 Gbps
- Total Jitter < 65 ps
- Low-Power Alternative for the MC100EP16
- Low 100-ps (Maximum) Part-to-Part Skew
- 25 mV of Receiver Input Threshold Hysteresis
Over 0-V to 4-V Input Voltage Range - Inputs Electrically Compatible With LVPECL,
CML, and LVDS Signal Levels - 3.3-V Supply Operation
- LVDT Integrates 110-Ω Terminating Resistor
- Offered in SOIC and MSOP
2 Applications
- Wireless Infrastructure
- Telecom Infrastructure
- Printers
3 Description
The SN65LVDS100, SN65LVDT100, SN65LVDS101, and SN65LVDT101 are high-speed differential receivers and drivers connected as repeaters. The receiver accepts low-voltage differential signaling (LVDS), positive-emitter-coupled logic (PECL), or current-mode logic (CML) input signals at rates up to 2 Gbps and repeats it as either an LVDS or PECL output signal. The signal path through the device is differential for low radiated emissions and minimal added jitter.
Device Information(1)
| PART NUMBER | PACKAGE | BODY SIZE (NOM) |
|---|---|---|
| SN65LVDS100 | SOIC (8) | 4.90 mm × 3.91 mm |
| VSSOP (8) | 3.00 mm × 3.00 mm | |
| SN65LVDT100 | SOIC (8) | 4.90 mm × 3.91 mm |
| VSSOP (8) | 3.00 mm × 3.00 mm | |
| SN65LVDS101 | SOIC (8) | 4.90 mm × 3.91 mm |
| VSSOP (8) | 3.00 mm × 3.00 mm | |
| SN65LVDT101 | SOIC (8) | 4.90 mm × 3.91 mm |
| VSSOP (8) | 3.00 mm × 3.00 mm |
- For all available packages, see the orderable addendum at the end of the data sheet.
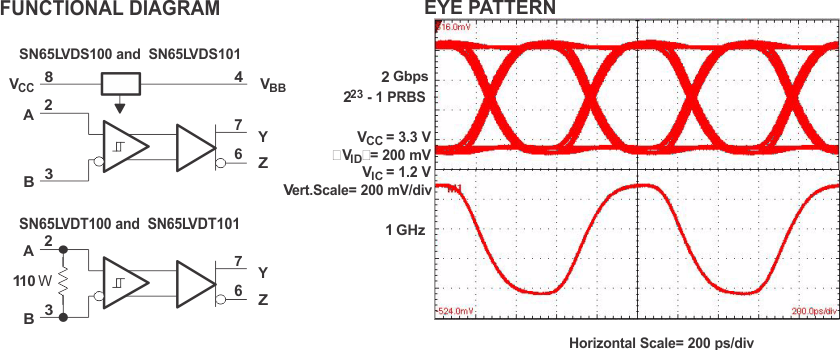
Dual Eye Diagram