SCLS099I December 1982 – September 2024 SN54HC112 , SN74HC112
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
- 6 Parameter Measurement Information
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Revision History
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- N|16
- D|16
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
6 Parameter Measurement Information
Phase relationships between waveforms were chosen arbitrarily. All input pulses are supplied by generators having the following characteristics: PRR ≤ 1MHz, ZO = 50Ω, tt < 6ns.
For clock inputs, fmax is measured when the input duty cycle is 50%.
The outputs are measured one at a time with one input transition per measurement.
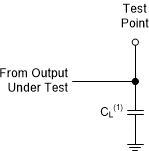
(1) CL includes probe
and test-fixture capacitance.
Figure 6-1 Load Circuit for Push-Pull
Outputs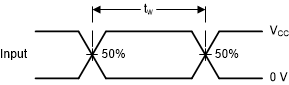 Figure 6-2 Voltage Waveforms,
Standard CMOS Inputs Pulse Duration
Figure 6-2 Voltage Waveforms,
Standard CMOS Inputs Pulse Duration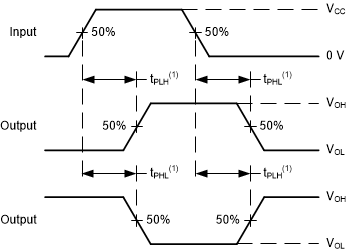
(1) The
greater between tPLH and tPHL is the same as
tpd.
Figure 6-4 Voltage Waveforms,
Propagation Delays for Standard CMOS Inputs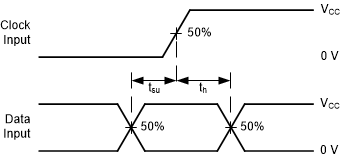 Figure 6-3 Voltage Waveforms,
Standard CMOS Inputs Setup and Hold Times
Figure 6-3 Voltage Waveforms,
Standard CMOS Inputs Setup and Hold Times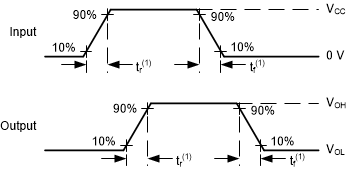
(1) The greater between
tr and tf is the same as tt.
Figure 6-5 Voltage Waveforms, Input
and Output Transition Times for Standard CMOS Inputs