SLLS378E May 2000 – January 2023 SN65LBC180A , SN75LBC180A
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1Features
- 2Description
- 3Revision History
- 4Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5Reference
- 6Detailed Description
- 7Application Information
- 8Device and Documentation Support
- 9Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- N|14
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.1 Typical Application Circuit
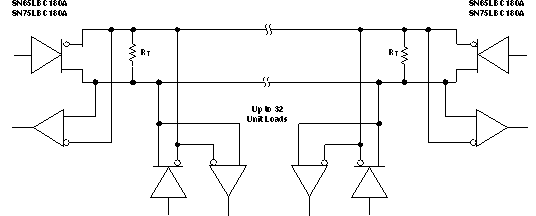
A. The line should be terminated at
both ends in its characteristic impedance (RT = ZO). Stub
lengths off the main line should be kept as short as possible. One SN65LBC180A
typically represents less than one unit load.