SBASB80 October 2024 TAA3040
ADVANCE INFORMATION
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
5 Specifications
- 5.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 5.2 ESD Ratings
- 5.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 5.4 Thermal Information
- 5.5 Electrical Characteristics
- 5.6 Timing Requirements: I2C Interface
- 5.7 Switching Characteristics: I2C Interface
- 5.8 Timing Requirements: SPI Interface
- 5.9 Switching Characteristics: SPI Interface
- 5.10 Timing Requirements: TDM, I2S or LJ Interface
- 5.11 Switching Characteristics: TDM, I2S or LJ Interface
- 5.12 Timing Requirements: PDM Digital Microphone Interface
- 5.13 Switching Characteristics: PDM Digial Microphone Interface
- 5.14 Timing Diagrams
-
6 Detailed Description
- 6.1 Overview
- 6.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 6.3
Feature Description
- 6.3.1 Serial Interfaces
- 6.3.2 Phase-Locked Loop (PLL) and Clock Generation
- 6.3.3 Input Channel Configurations
- 6.3.4 Reference Voltage
- 6.3.5 Programmable Microphone Bias
- 6.3.6
Signal-Chain Processing
- 6.3.6.1 Programmable Channel Gain and Digital Volume Control
- 6.3.6.2 Programmable Channel Gain Calibration
- 6.3.6.3 Programmable Channel Phase Calibration
- 6.3.6.4 Programmable Digital High-Pass Filter
- 6.3.6.5 Programmable Digital Biquad Filters
- 6.3.6.6 Programmable Channel Summer and Digital Mixer
- 6.3.6.7
Configurable Digital Decimation Filters
- 6.3.6.7.1
Linear Phase Filters
- 6.3.6.7.1.1 Sampling Rate: 8 kHz or 7.35 kHz
- 6.3.6.7.1.2 Sampling Rate: 16 kHz or 14.7 kHz
- 6.3.6.7.1.3 Sampling Rate: 24 kHz or 22.05 kHz
- 6.3.6.7.1.4 Sampling Rate: 32 kHz or 29.4 kHz
- 6.3.6.7.1.5 Sampling Rate: 48 kHz or 44.1 kHz
- 6.3.6.7.1.6 Sampling Rate: 96 kHz or 88.2 kHz
- 6.3.6.7.1.7 Sampling Rate: 192 kHz or 176.4 kHz
- 6.3.6.7.1.8 Sampling Rate: 384 kHz or 352.8 kHz
- 6.3.6.7.1.9 Sampling Rate 768 kHz or 705.6 kHz
- 6.3.6.7.2 Low-Latency Filters
- 6.3.6.7.3
Ultra-Low-Latency Filters
- 6.3.6.7.3.1 Sampling Rate: 16 kHz or 14.7 kHz
- 6.3.6.7.3.2 Sampling Rate: 24 kHz or 22.05 kHz
- 6.3.6.7.3.3 Sampling Rate: 32 kHz or 29.4 kHz
- 6.3.6.7.3.4 Sampling Rate: 48 kHz or 44.1 kHz
- 6.3.6.7.3.5 Sampling Rate: 96 kHz or 88.2 kHz
- 6.3.6.7.3.6 Sampling Rate 192 kHz or 176.4 kHz
- 6.3.6.7.3.7 Sampling Rate 384 kHz or 352.8 kHz
- 6.3.6.7.1
Linear Phase Filters
- 6.3.7 Automatic Gain Controller (AGC)
- 6.3.8 Digital PDM Microphone Record Channel
- 6.3.9 Interrupts, Status, and Digital I/O Pin Multiplexing
- 6.4 Device Functional Modes
- 6.5 Programming
-
7 Register Maps
- 7.1
Device Configuration Registers
- 7.1.1
Register Descriptions
- 7.1.1.1 PAGE_CFG Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x00) [reset = 0h]
- 7.1.1.2 SW_RESET Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x01) [reset = 0h]
- 7.1.1.3 SLEEP_CFG Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x02) [reset = 0h]
- 7.1.1.4 SHDN_CFG Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x05) [reset = 5h]
- 7.1.1.5 ASI_CFG0 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x07) [reset = 30h]
- 7.1.1.6 ASI_CFG1 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x08) [reset = 0h]
- 7.1.1.7 ASI_CFG2 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x09) [reset = 0h]
- 7.1.1.8 ASI_CH1 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x0B) [reset = 0h]
- 7.1.1.9 ASI_CH2 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x0C) [reset = 1h]
- 7.1.1.10 ASI_CH3 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x0D) [reset = 2h]
- 7.1.1.11 ASI_CH4 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x0E) [reset = 3h]
- 7.1.1.12 ASI_CH5 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x0F) [reset = 4h]
- 7.1.1.13 ASI_CH6 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x10) [reset = 5h]
- 7.1.1.14 ASI_CH7 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x11) [reset = 6h]
- 7.1.1.15 ASI_CH8 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x12) [reset = 7h]
- 7.1.1.16 MST_CFG0 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x13) [reset = 2h]
- 7.1.1.17 MST_CFG1 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x14) [reset = 48h]
- 7.1.1.18 ASI_STS Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x15) [reset = FFh]
- 7.1.1.19 CLK_SRC Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x16) [reset = 10h]
- 7.1.1.20 PDMCLK_CFG Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x1F) [reset = 40h]
- 7.1.1.21 PDMIN_CFG Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x20) [reset = 0h]
- 7.1.1.22 GPIO_CFG0 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x21) [reset = 22h]
- 7.1.1.23 GPO_CFG0 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x22) [reset = 0h]
- 7.1.1.24 GPO_CFG1 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x23) [reset = 0h]
- 7.1.1.25 GPO_CFG2 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x24) [reset = 0h]
- 7.1.1.26 GPO_CFG3 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x25) [reset = 0h]
- 7.1.1.27 GPO_VAL Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x29) [reset = 0h]
- 7.1.1.28 GPIO_MON Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x2A) [reset = 0h]
- 7.1.1.29 GPI_CFG0 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x2B) [reset = 0h]
- 7.1.1.30 GPI_CFG1 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x2C) [reset = 0h]
- 7.1.1.31 GPI_MON Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x2F) [reset = 0h]
- 7.1.1.32 INT_CFG Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x32) [reset = 0h]
- 7.1.1.33 INT_MASK0 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x33) [reset = FFh]
- 7.1.1.34 INT_LTCH0 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x36) [reset = 0h]
- 7.1.1.35 BIAS_CFG Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x3B) [reset = 0h]
- 7.1.1.36 CH1_CFG0 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x3C) [reset = 0h]
- 7.1.1.37 CH1_CFG1 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x3D) [reset = 0h]
- 7.1.1.38 CH1_CFG2 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x3E) [reset = C9h]
- 7.1.1.39 CH1_CFG3 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x3F) [reset = 80h]
- 7.1.1.40 CH1_CFG4 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x40) [reset = 0h]
- 7.1.1.41 CH2_CFG0 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x41) [reset = 0h]
- 7.1.1.42 CH2_CFG1 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x42) [reset = 0h]
- 7.1.1.43 CH2_CFG2 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x43) [reset = C9h]
- 7.1.1.44 CH2_CFG3 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x44) [reset = 80h]
- 7.1.1.45 CH2_CFG4 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x45) [reset = 0h]
- 7.1.1.46 CH3_CFG0 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x46) [reset = 0h]
- 7.1.1.47 CH3_CFG1 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x47) [reset = 0h]
- 7.1.1.48 CH3_CFG2 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x48) [reset = C9h]
- 7.1.1.49 CH3_CFG3 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x49) [reset = 80h]
- 7.1.1.50 CH3_CFG4 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x4A) [reset = 0h]
- 7.1.1.51 CH4_CFG0 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x4B) [reset = 0h]
- 7.1.1.52 CH4_CFG1 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x4C) [reset = 0h]
- 7.1.1.53 CH4_CFG2 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x4D) [reset = C9h]
- 7.1.1.54 CH4_CFG3 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x4E) [reset = 80h]
- 7.1.1.55 CH4_CFG4 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x4F) [reset = 0h]
- 7.1.1.56 CH5_CFG2 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x52) [reset = C9h]
- 7.1.1.57 CH5_CFG3 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x53) [reset = 80h]
- 7.1.1.58 CH5_CFG4 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x54) [reset = 0h]
- 7.1.1.59 CH6_CFG2 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x57) [reset = C9h]
- 7.1.1.60 CH6_CFG3 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x58) [reset = 80h]
- 7.1.1.61 CH6_CFG4 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x59) [reset = 0h]
- 7.1.1.62 CH7_CFG2 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x5C) [reset = C9h]
- 7.1.1.63 CH7_CFG3 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x5D) [reset = 80h]
- 7.1.1.64 CH7_CFG4 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x5E) [reset = 0h]
- 7.1.1.65 CH8_CFG2 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x61) [reset = C9h]
- 7.1.1.66 CH8_CFG3 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x62) [reset = 80h]
- 7.1.1.67 CH8_CFG4 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x63) [reset = 0h]
- 7.1.1.68 DSP_CFG0 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x6B) [reset = 1h]
- 7.1.1.69 DSP_CFG1 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x6C) [reset = 40h]
- 7.1.1.70 AGC_CFG0 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x70) [reset = E7h]
- 7.1.1.71 IN_CH_EN Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x73) [reset = F0h]
- 7.1.1.72 ASI_OUT_CH_EN Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x74) [reset = 0h]
- 7.1.1.73 PWR_CFG Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x75) [reset = 0h]
- 7.1.1.74 DEV_STS0 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x76) [reset = 0h]
- 7.1.1.75 DEV_STS1 Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x77) [reset = 80h]
- 7.1.1.76 I2C_CKSUM Register (page = 0x00, address = 0x7E) [reset = 0h]
- 7.1.1
Register Descriptions
- 7.2 Programmable Coefficient Registers
- 7.1
Device Configuration Registers
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Revision History
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RTW|24
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RTW|24
Orderable Information
6.5.1.1.1 General I2C Operation
The I2C bus employs two signals, SDA (data) and SCL (clock), to communicate between integrated circuits in a system using serial data transmission. The address and data 8-bit bytes are transferred MSB first. In addition, each byte transferred on the bus is acknowledged by the receiving device with an acknowledge bit. Each transfer operation begins with the master device driving a start condition on the bus and ends with the master device driving a stop condition on the bus. The bus uses transitions on the data pin (SDA) while the clock is at logic high to indicate start and stop conditions. A high-to-low transition on SDA indicates a start, and a low-to-high transition indicates a stop. Normal data-bit transitions must occur within the low time of the clock period.
The master device drives a start condition followed by the 7-bit slave address and the read/write (R/W) bit to open communication with another device and then waits for an acknowledgment condition. The slave device holds SDA low during the acknowledge clock period to indicate acknowledgment. When this occurs, the master device transmits the next byte of the sequence. Each slave device is addressed by a unique 7-bit slave address plus the R/W bit (1 byte). All compatible devices share the same signals via a bidirectional bus using a wired-AND connection.
There is no limit on the number of bytes that can be transmitted between start and stop conditions. When the last word transfers, the master device generates a stop condition to release the bus. Figure 6-66 shows a generic data transfer sequence.
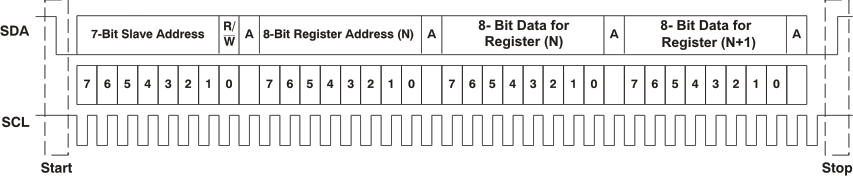 Figure 6-66 Typical I2C Sequence
Figure 6-66 Typical I2C SequenceIn the system, use external pullup resistors for the SDA and SCL signals to set the logic high level for the bus. The SDA and SCL voltages must not exceed the device supply voltage, IOVDD.