SLOS795F September 2013 – October 2017 TAS5414C-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PHD|64
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- PHD|64
Orderable Information
7 Detailed Description
7.1 Overview
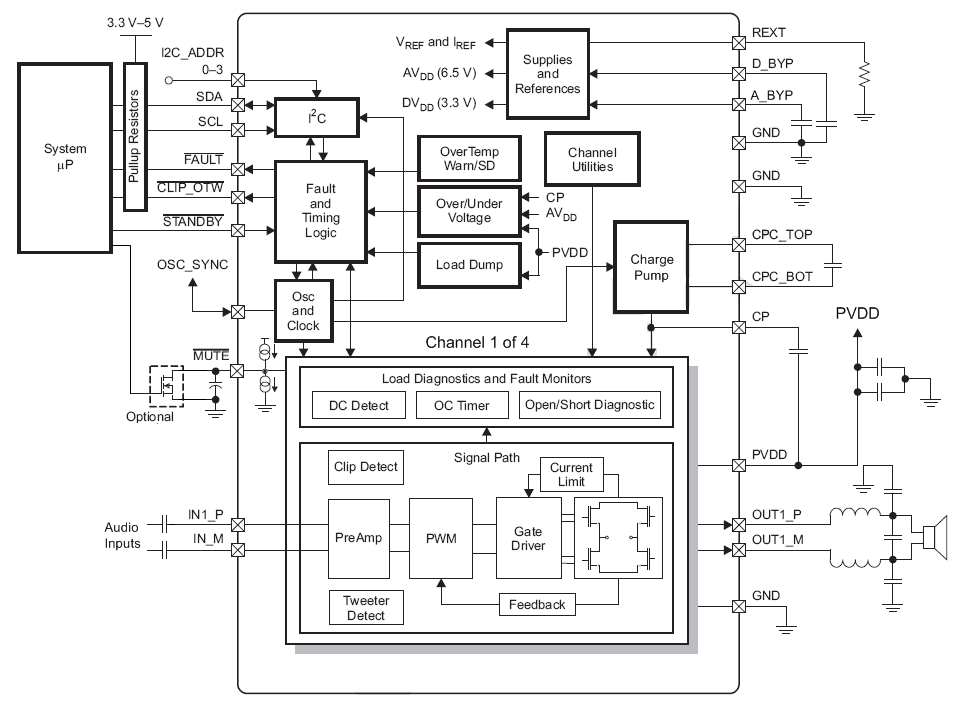
The TAS5414C-Q1 and TAS5424C-Q1 are single-chip, four-channel, analog-input audio amplifiers for use in the automotive environment. The design uses an ultra-efficient class-D technology developed by Texas Instruments, but with changes needed by the automotive industry. This technology allows for reduced power consumption, reduced heat, and reduced peak currents in the electrical system. The device realizes an audio sound system design with smaller size and lower weight than traditional class-AB solutions.
There are eight core design blocks:
- Preamplifier
- PWM
- Gate drive
- Power FETs
- Diagnostics
- Protection
- Power supply
- I2C serial communication bus
7.2 Functional Block Diagram
7.3 Feature Descption
7.3.1 Preamplifier
The preamplifier is a high-input-impedance, low-noise, low-offset-voltage input stage with adjustable gain. The high input impedance allows the use of low-cost input capacitors while still achieving extended low-frequency response. A dedicated, internally regulated supply pwoers the preamplifier, giving it excellent noise immunity and channel separation. The preamplifier also includes:
- Mute Pop-and-Click Control — The device ramps the gain gradually when ib receiving a mute or play command. The start or stopping of switching in a class-D amplifier can cause another form of click and pop. The TAS5414C-Q1 and TAS5424C-Q1 incorporate a patented method to reduce the pop energy during the switching startup and shutdown sequence. Fault conditions require rapid protection response by the TAS5414C-Q1 and the TAS5424C-Q1, which do not have time to ramp the gain down in a pop-free manner. The device transitions into Hi-Z mode when encountering an OV, UV, OC, OT, or dc fault. Also, activation of the STANDBY pin may not be pop-free.
- Gain Control — Setting of gains for the four channels occurs in the preamplifier via I2C control registers, outside of the global feedback resistors of the device, thus allowing for stability of the system at all gain settings with properly loaded conditions.
7.3.2 Pulse-Width Modulator (PWM)
The PWM converts the analog signal from the preamplifier into a switched signal of varying duty cycle. This is the critical stage that defines the class-D architecture. In the TAS5414C-Q1 and TAS5424C-Q1, the modulator is an advanced design with high bandwidth, low noise, low distortion, excellent stability, and full 0–100% modulation capability. The patented PWM uses clipping recovery circuitry to eliminate the deep saturation characteristic of PWMs when the input signal exceeds the modulator waveform.
7.3.3 Gate Drive
The gate driver accepts the low-voltage PWM signal and level-shifts it to drive a high-current, full-bridge, power FET stage. The device uses proprietary techniques to optimize EMI and audio performance.
7.3.4 Power FETs
The BTL output for each channel comprises four rugged N-channel 30-V 65-mΩ FETs for high efficiency and maximum power transfer to the load. These FETs can handle large voltage transients during load dump.
7.3.5 Load Diagnostics
The device incorporates load diagnostic circuitry designed to help pinpoint the nature of output misconnections during installation. The TAS5414C-Q1 and the TAS5424C-Q1 include functions for detecting and determining the status of output connections. The devices support the following diagnostics:
- Short to GND
- Short to PVDD
- Short across load
- Open load
- Tweeter detection
Reporting to the system of the presence of any of the short or open conditions occurs via I2C register read. One can read the tweeter-detect status from the CLIP_OTW pin when properly configured.
- Output Short and Open Diagnostics — The device contains circuitry designed to detect shorts and open conditions on the outputs. Invocation of the load diagnostic function can only occur when the output is in the Hi-Z mode. There are four phases of test during load diagnostics and two levels of test. In the full level, all channels must be in the Hi-Z state. Testing covers all four phases on each channel, all four channels at the same time. When fewer than four channels are in Hi-Z, the reduced level of test is the only available option. In the reduced level, the only tests available are short to PVDD and short to GND. Load diagnostics can occur at power up before moving the amplifier out of Hi-Z mode. If the amplifier is already in play mode, it must Mute and then Hi-Z before performing the load diagnostic. By performing the mute function, the normal pop- and click-free transitions occur before the diagnostics begin. Performance of the diagnostics is as shown in Figure 11. Figure 12 shows the impedance ranges for the open-load and shorted-load diagnostics. Reading the results of the diagnostics is from the diagnostic register via I2C for each channel. With the default settings and MUTE capacitor, the S2G and S2P phase take approximately 20 ms each, the OL phase takes approximately 100 ms, and the SL takes approximately 230 ms. In I2C register 0x10, bit D4 can extend the test time for S2P and S2G to 80 ms each. To prevent false S2G and S2P faults, this time extension is necessary if the output pins have a capacitance higher than 680 nF to ground .
-
Tweeter Detection — Tweeter detection is an alternate operating mode used to determine the proper connection of a frequency-dependent load (such as a speaker with a crossover). Invoking of weeter detection is via I2C, with individual testing of all four channels recommended. Tweeter detection uses the average cycle-by-cycle current limit circuit (see CBC section) to measure the current delivered to the load. The proper implementation of this diagnostic function depends on the amplitude of a user-supplied test signal and on the impedance-versus-frequency curve of the acoustic load. The system (external to the TAS5414C-Q1 and TAS5424C-Q1) must generate a signal to which the load responds. The frequency and amplitude of this signal must be calibrated by the user to result in a current draw that is greater than the tweeter detection threshold when the load under test is present, and less than the detection threshold if the load is unconnected. The current level for the tweeter detection threshold, as well as the maximum current that can safely be delivered to a load when in tweeter-detection mode, is in the Electrical Characteristics section of the data sheet. Reporting of the tweeter-detection results is on the CLIP_OTW pin during the application of the test signal. With tweeter detection activated (indicating that the tested load is present), pulses on the CLIP_OTW pin begin to toggle. The pulses on the CLIP_OTW pins report low whenever the current exceeds the detection threshold, and the pin remains low until the current no longer exceeds the threshold. The minimum low-pulse period that one can expect is equal to one period of the switching frequency. Having an input signal that increases the duration of detector activation (for example, increasing the amplitude of the input signal) increases the amount of time for which the pin reports low.
NOTE: Because tweeter detection is an alternate operating mode, place the channels to be tested in Play mode (via register 0x0C) after tweeter detection has been activated in order to commence the detection process. Additionally, set up the CLIP_OTW pin via register 0x0A to report the results of tweeter detection.
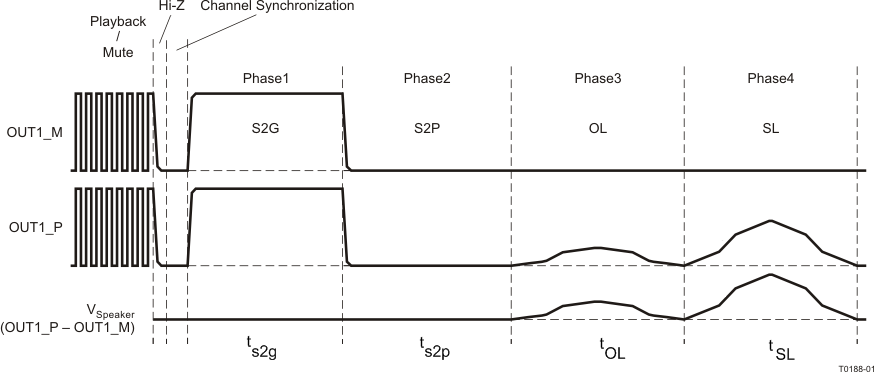 Figure 11. Load Diagnostics Sequence of Events
Figure 11. Load Diagnostics Sequence of Events
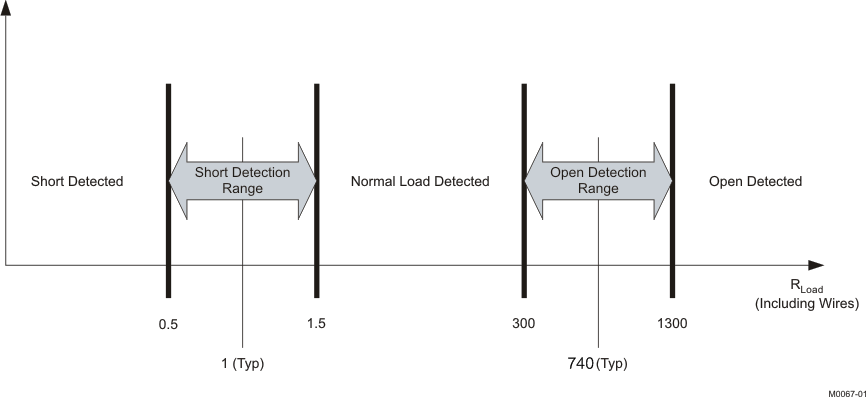 Figure 12. Open- and Shorted-Load Detection
Figure 12. Open- and Shorted-Load Detection
7.3.6 Protection and Monitoring
- Cycle-By-Cycle Current Limit (CBC) — The CBC current-limiting circuit terminates each PWM pulse to limit the output current flow to the average current limit (ILIM) threshold. The overall effect on the audio in the case of a current overload is quite similar to a voltage-clipping event, temporarily limiting power at the peaks of the musical signal and normal operation continues without disruption on removal of the overload. The TAS5414C-Q1 and TAS5424C-Q1 do not prematurely shut down in this condition. All four channels continue in play mode and pass signal.
- Overcurrent Shutdown (OCSD) — Under severe short-circuit events, such as a short to PVDD or ground, the device uses a peak-current detector, and the affected channel shuts down in 200 μs to 390 μs if the conditions are severe enough. The shutdown speed depends on a number of factors, such as the impedance of the short circuit, supply voltage, and switching frequency. Only the shorted channels shut down in such a scenario. The user may restart the affected channel via I2C. An OCSD event activates the fault pin, and the I2C fault register saves a record of the affected channels. If the supply or ground short is strong enough to exceed the peak current threshold but not severe enough to trigger the OCSD, the peak current limiter prevents excess current from damaging the output FETs, and operation returns to normal after the short is removed.
- DC Detect—This circuit detects a dc offset at the output of the amplifier continuously during normal operation. If the dc offset reaches the level defined in the I2C registers for the specified time period, the circuit triggers. By default, a dc detection event does not shut the output down. Disabling and enabling the shutdown function is via I2C. If enabled, the triggered channel shuts down, but the others remain playing, but with the FAULT pin asserted. The I2C registers define the dc level.
- Clip Detect—The clip detect circuit alerts the user to the presence of a 100% duty-cycle PWM due to a clipped waveform. When this occurs, a signal passed to the CLIP_OTW pin asserts it until the 100% duty-cycle PWM signal is no longer present. All four channels connect to the same CLIP_OTW pin. Through I2C, one can change the CLIP_OTW signal clip-only, OTW-only, or both. A fourth mode, used only during diagnostics, is the option to report tweeter detection events on this pin (see the Tweeter Detection section). The microcontroller in the system can monitor the signal at the CLIP_OTW pin, and may have a configuration that reduces the volume to all four channels in an active clipping-prevention circuit.
- Overtemperature Warning (OTW), Overtemperature Shutdown (OTSD) and Thermal Foldback — By default, the CLIP_OTW pin setting indicates an OTW. One can make changes via I2C commands. If selected to indicate a temperature warning, CLIP_OTW pin assertion occurs when the die temperature reaches warning level 1 as shown in the electrical specifications. The OTW has three temperature thresholds with a 10°C hysteresis. I2C register 0x04 indicates each threshold in bits 5, 6, and 7. The device still functions until the temperature reaches the OTSD threshold, at which time the outputs go into Hi-Z mode and the device asserts the FAULT pin. I2C is still active in the event of an OTSD, and one can read the registers for faults, but all audio ceases abruptly. After the OTSD resets, one can turn the device back on through I2C. The OTW indication remains until the temperature drops below warning level 1. The thermal foldback decreases the channel gain.
- Undervoltage (UV) and Power-on-Reset (POR) — The undervoltage (UV) protection detects low voltages on PVDD, AVDD, and CP. In the event of an undervoltage, the device asserts the FAULT pin and updates the I2C registerd, depending on which voltage caused the event. Power-on reset (POR) occurs when PVDD drops low enough. A POR event causes the I2C to go into a high-impedance state. After the device recovers from the POR event, the device re-initialization occur via I2C.
- Overvoltage (OV) and Load Dump — The OV protection detects high voltages on PVDD. If PVDD reaches the overvoltage threshold, the device asserts the FAULT pin iand updates the I2C register. The device can withstand 50-V load-dump voltage spikes.
7.3.7 I2C Serial Communication Bus
The device communicates with the system processor via the I2C serial communication bus as an I2C slave-only device. The processor can poll the device via I2C to determine the operating status. All reports of fault conditions and detections are via I2C. There are also numerous features and operating conditions that one can set via I2C.
The I2C bus allows control of the following configurations:
- Independent gain control of each channel. The gain can be set to 12 dB, 20 dB, 26 dB, and 32 dB.
- Select the AM non-interference switching frequency
- Select the functionality of the OTW_CLIP pin
- Enable or disable the dc-detect function with selectable threshold
- Place a channel in Hi-Z (switching stopped) mode (mute)
- Select tweeter detect, set the detection threshold, and initiate the function
- Initiate the open- and shorted-load diagnostic
- Reset faults and return to normal switching operation from Hi-Z mode (unmute)
In addition to the standard SDA and SCL pins for the I2C bus, the TAS5414C-Q1 and the TAS5424C-Q1 include a single pin that allows up to four devices to work together in a system with no additional hardware required for communication or synchronization. The I2C_ADDR pin sets the device in master or slave mode and selects the I2C address for that device. Tie I2C_ADDR to DGND for master, to 1.2 Vdc for slave 1, to 2.4 Vdc for slave 2, and to D_BYP for slave 3. The OSC_SYNC pin is for synchronizing the internal clock oscillators, thereby avoid beat frequencies. One can apply an external oscillator to this pin for external control of the switching frequency.
Table 1. Table 7. I2C_ADDR Pin Connection
| I2C_ADDR VALUE | I2C_ADDR PIN CONNECTION | I2C ADDRESSES |
|---|---|---|
| 0 (OSC MASTER) | To SGND pin | 0xD8/D9 |
| 1 (OSC SLAVE1) | 35% DVDD (resistive voltage divider between D_BYP pin and SGND pin)(1) | 0xDA/DB |
| 2 (OSC SLAVE2) | 65% DVDD (resistive voltage divider between D_BYP pin and SGND pin)(1) | 0xDC/DD |
| 3 (OSC SLAVE3) | To D_BYP pin | 0xDE/DF |
7.3.8 I2C Bus Protocol
The TAS5414C-Q1 and TAS5424C-Q1 have a bidirectional serial control interface that is compatible with the Inter IC (I2C) bus protocol and supports 400-kbps data transfer rates for random and sequential write and read operations. This is a slave-only device that does not support a multimaster bus environment or wait-state insertion. The control interface programs the registers of the device and reads device status.
The I2C bus employs two signals, SDA (data) and SCL (clock), to communicate between integrated circuits in a system. Data transfer on the bus is serial, one bit at a time. The transfer of address and data is in byte (8-bit) format with the most-significant bit (MSB) transferred first. In addition, the receiving device acknowledges each byte transferred on the bus with an acknowledge bit. Each transfer operation begins with the master device driving a start condition on the bus and ends with the master device driving a stop condition on the bus. The bus uses transitions on the data terminal (SDA) while the clock is HIGH to indicate a start and stop conditions. A HIGH-to-LOW transition on SDA indicates a start, and a LOW-to-HIGH transition indicates a stop. Normal data-bit transitions must occur within the low time of the clock period. Figure 13 shows these conditions. The master generates the 7-bit slave address and the read/write bit to open communication with another device and then wait for an acknowledge condition. The TAS5414C-Q1 and TAS5424C-Q1 hold SDA LOW during the acknowledge-clock period to indicate an acknowledgment. When this occurs, the master transmits the next byte of the sequence. Each device is addressed by a unique 7-bit slave address plus R/W bit (1 byte). All compatible devices share the same signals via a bidirectional bus using a wired-AND connection. There must be an external pullup resistor for the SDA and SCL signals to set the HIGH level for the bus. There is no limit on the number of bytes that one can transmit between start and stop conditions. When the last word transfers, the master generates a stop condition to release the bus.
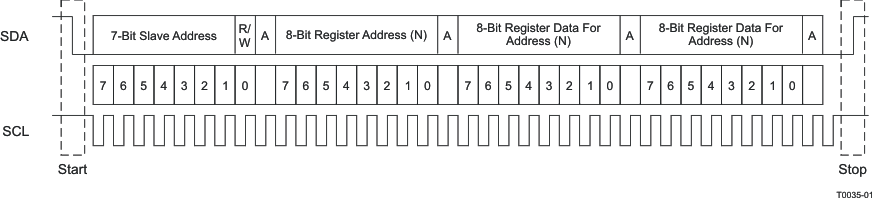 Figure 13. Typical I2C Sequence
Figure 13. Typical I2C Sequence
Use the I2C_ADDR pin (pin 2) to program the device for one of four addresses. These four addresses are licensed I2C addresses and do not conflict with other licensed I2C audio devices. To communicate with the TAS5414C-Q1 and the TAS5424C-Q1, the I2C master uses addresses shown in Figure 13. Transmission of read and write data can be via single-byte or multiple-byte data transfers.
7.3.9 Hardware Control Pins
There are four discrete hardware pins for real-time control and indication of device status.
- FAULT pin: This active-low open-drain output pin indicates the presence of a fault condition that requires the device to go into the Hi-Z mode or standby mode. On assertion of this pin, the device has protected itself and the system from potential damage. One can read the exact nature of the fault via I2C with the exception of PVDD undervoltage faults below POR, in which case the I2C bus is no longer operational. However, the fault is still indicated due to FAULT pin assertion.
- CLIP_OTW pin: Configured via I2C, this active-low open-drain pin\ indicates one of the following conditions: overtemperature warning, the detection of clipping, or the logical OR of both of these conditions. During tweeter detect diagnostics, assertion of this pin also occurs when a tweeter is present. If overtemperature warning is set, the device can also indicate thermal foldback on this pin.
- MUTE pin: This active-low pin is used for hardware control of the mute-unmute function for all four channels. Capacitor CMUTE controls the time constant for the gain ramp needed to produce a pop- and click-free mute function. For pop- and click-free operation, implementation of the mute function should be through I2C commands. The use of a hard mute with an external transistor does not ensure pop- and click-free operation, and TI does not recommended it except as an emergency hard mute function in case of a loss of I2C control. Sharing the CMUTE capacitor between multiple devices is disallowed.
- STANDBY pin: On assertion of this active-low pin, the device goes into a complete shutdown, and the typical current-draw limit is 2 μA, typical. STANDBY can be used to shut down the device rapidly. If all channels are in Hi-Z, the device enters standby in approximately 1 ms. All I2C register content is lost and the I2C bus goes into the high-impedance state on assertion of the STANDBY pin.
7.3.10 AM Radio Avoidance
To reduce interference in the AM radio band, the device has the ability to change the switching frequency via I2C commands. Table 2 lists the recommended frequencies. The fundamental frequency and its second harmonic straddle the AM radio band listed. This eliminates the tones that can be present due to demodulation of the switching frequency by the AM radio.
Table 2. Recommended Switching Frequencies for AM Mode Operation
| US | EUROPEAN | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| AM FREQUENCY (kHz) |
SWITCHING FREQUENCY (kHz) |
AM FREQUENCY (kHz) |
SWITCHING FREQUENCY (kHz) |
| 540–670 | 417 | 522–675 | 417 |
| 680–980 | 500 | 676–945 | 500 |
| 990–1180 | 417 | 946–1188 | 417 |
| 1190–1420 | 500 | 1189–1422 | 500 |
| 1430–1580 | 417 | 1423–1584 | 417 |
| 1590–1700 | 500 | 1585–1701 | 500 |
7.4 Device Functional Modes
Table 3 through Table 5 depict the operating modes and faults.
Table 3. Operating Modes
| STATE NAME | OUTPUT FETS | CHARGE PUMP | OSCILLATOR | I2C | AVDD and DVDD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| STANDBY | Hi-Z, floating | Stopped | Stopped | Stopped | OFF |
| Hi-Z | Hi-Z, weak pulldown | Active | Active | Active | ON |
| Mute | Switching at 50% | Active | Active | Active | ON |
| Normal operation | Switching with audio | Active | Active | Active | ON |
Table 4. Global Faults and Actions
| FAULT OR EVENT |
FAULT OR EVENT CATEGORY |
MONITORING MODES |
REPORTING METHOD |
ACTION TYPE |
ACTION RESULT |
LATCHED OR SELF- CLEARING |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| POR | Voltage fault | All | FAULT pin | Hard mute (no ramp) | Standby | Self-clearing |
| UV | Hi-Z, mute, normal | I2C + FAULT pin | Hi-Z | Latched | ||
| CP UV | ||||||
| OV | ||||||
| Load dump | All | FAULT pin | Standby | Self-clearing | ||
| OTW | Thermal warning | Hi-Z, mute, normal | I2C + CLIP_OTW pin | None | None | Self-clearing |
| OTSD | Thermal fault | Hi-Z, mute, normal | I2C + FAULT pin | Hard mute (no ramp) | Standby | Latched |
Table 5. Channel Faults and Actions
| FAULT/ EVENT |
FAULT OR EVENT CATEGORY |
MONITORING MODES |
REPORTING METHOD |
ACTION TYPE |
ACTION RESULT |
LATCHED OR SELF- CLEARING |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Open-short diagnostic | Diagnostic | Hi-Z (I2C activated) | I2C | None | None | Latched |
| Clipping | Warning | Mute / Play | CLIP_OTW pin | None | None | Self-clearing |
| CBC load current limit | Online protection | Current Limit | Start OC timer | Self-clearing | ||
| OC fault | Output channel fault | I2C + FAULT pin | Hard mute | Hi-Z | Latched | |
| DC detect | Hard mute | Hi-Z | Latched | |||
| OT Foldback | Warning | I2C + CLIP_OTW pin | Reduce Gain | None | Self-clearing |
7.4.1 Audio Shutdown and Restart Sequence
The gain ramp of the filtered output signal and the updating of the I2C registers correspond to the MUTE pin voltage during the ramping process. The value of the external capacitor on the MUTE pin dictates the length of time that the MUTE pin takes to complete its ramp. With the default 220-nF capacitor, the turnon common-mode ramp takes approximately 26 ms and the gain ramp takes approximately 76 ms.
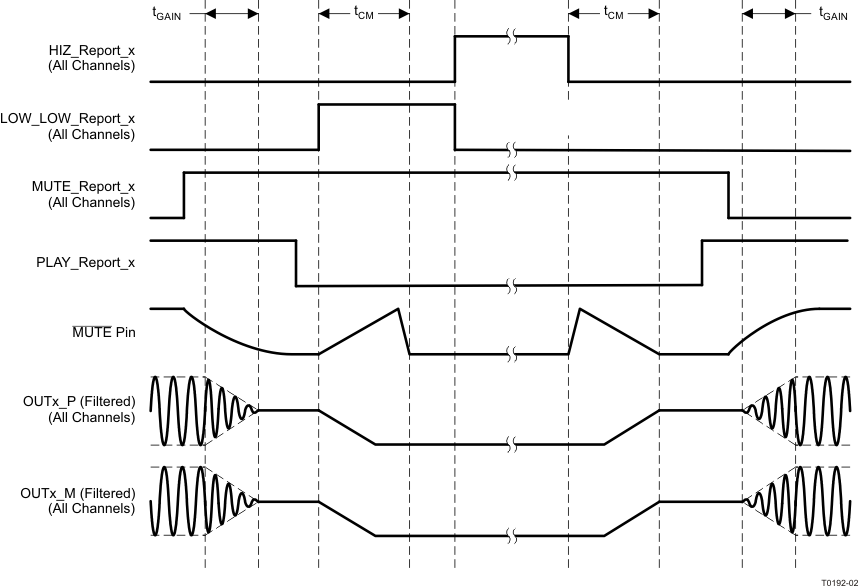 Figure 14. Timing Diagram for Click- and Pop-Free Shutdown and Restart Sequence
Figure 14. Timing Diagram for Click- and Pop-Free Shutdown and Restart Sequence7.4.2 Latched-Fault Shutdown and Restart Sequence Control
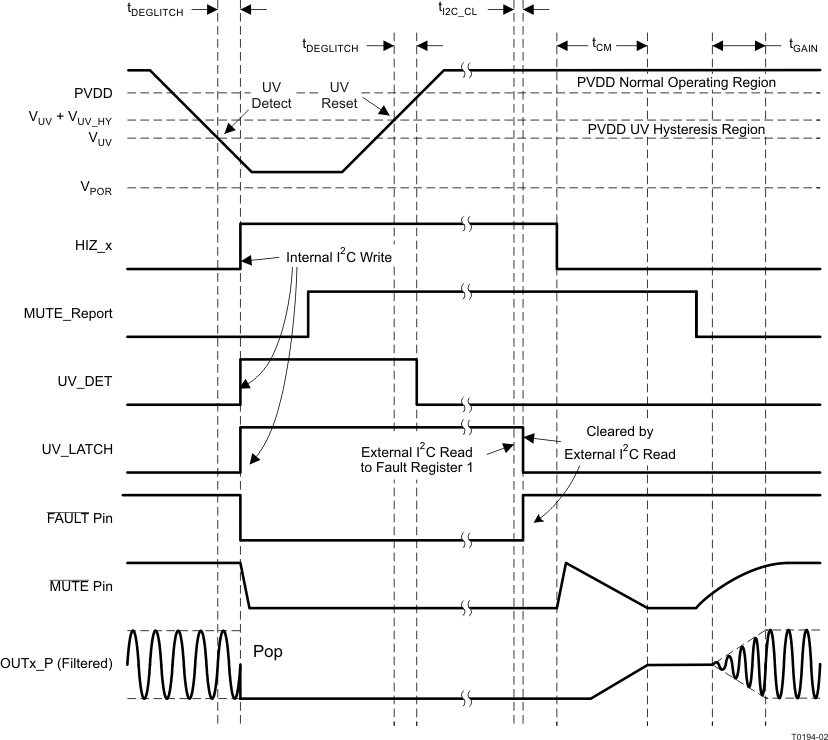 Figure 15. Timing Diagram for Latched-Global-Fault Shutdown and Restart
Figure 15. Timing Diagram for Latched-Global-Fault Shutdown and Restart (UV Shutdown and Recovery)
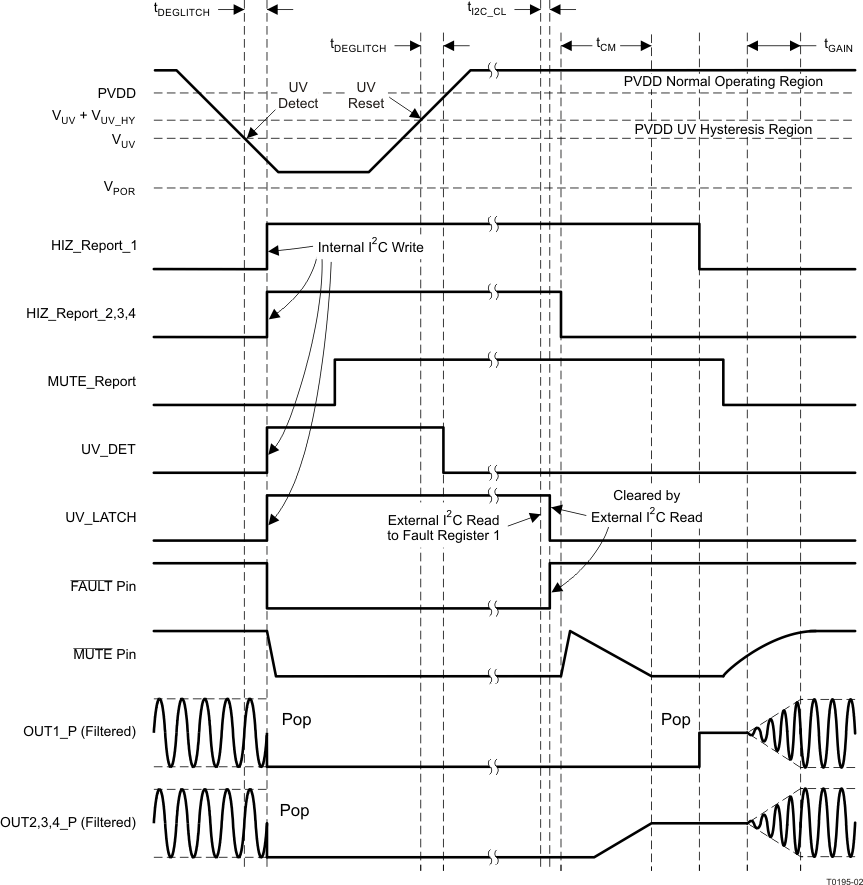 Figure 16. Timing Diagram for Latched-Global-Fault Shutdown and Individual-Channel Restart
Figure 16. Timing Diagram for Latched-Global-Fault Shutdown and Individual-Channel Restart (UV Shutdown and Recovery)
7.5 Programming
7.5.1 Random Write
As shown in Figure 17, a random write or single-byte write transfer begins with the master device transmitting a start condition followed by the I2C device address and the read/write bit. The read/write bit determines the direction of the data transfer. For a single-byte write data transfer, the read/write bit is a 0. After receiving the correct I2C device address and the read/write bit, the device responds with an acknowledge bit. Next, the master transmits the address byte or bytes corresponding to the internal memory address being accessed. After receiving the address byte, the device again responds with an acknowledge bit. Next, the master device transmits the data byte to be written to the memory address being accessed. After receiving the data byte, the TAS5414C-Q1 or TAS5424C-Q1 again responds with an acknowledge bit. Finally, the master device transmits a stop condition to complete the single-byte write transfer.
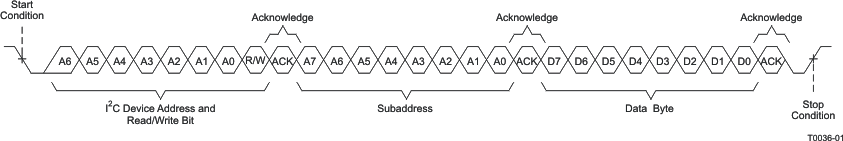 Figure 17. Random-Write Transfer
Figure 17. Random-Write Transfer
7.5.2 Sequential Write
A sequential write transfer is identical to a single-byte data-write transfer except for the transmisson of multiple data bytes by the master device to TAS5414C-Q1 or TAS5424C-Q1 as shown in Figure 18. After receiving each data byte, the device responds with an acknowledge bit and automatically increments the I2C subaddress by one.
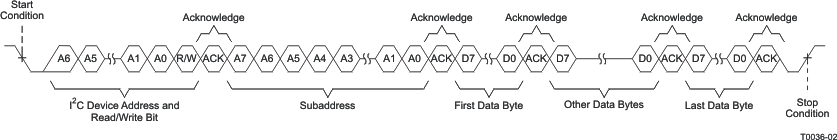 Figure 18. Sequential Write Transfer
Figure 18. Sequential Write Transfer
7.5.3 Random Read
As shown in Figure 19, a random read or single-byte read transfer begins with the master device transmitting a start condition followed by the I2C device address and the read/write bit. For the single-byte read transfer, the master device transmits both a write followed by a read. Initially, a write transfers the address byte or bytes of the internal memory address to be read. Thus, the read/write bit is a 0. After receiving the address and the read/write bit, the TAS5414C-Q1 or TAS5424C-Q1 responds with an acknowledge bit. In addition, after sending the internal memory address byte or bytes, the master device transmits another start condition followed by the device address and the read/write bit again. This time the read/write bit is a 1, indicating a read transfer. After receiving the address and the read/write bit, the device again responds with an acknowledge bit. Next, the TAS5414C-Q1 or TAS5424C-Q1 transmits the data byte from the memory address being read. After receiving the data byte, the master device transmits a not-acknowledge followed by a stop condition to complete the single-byte read transfer.
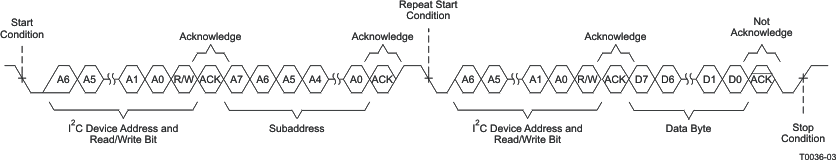 Figure 19. Random Read Transfer
Figure 19. Random Read Transfer
7.5.4 Sequential Read
A sequential read transfer is identical to a single-byte read transfer except for the transmission of multiple data bytes by the TAS5414C-Q1 or TAS5424C-Q1 to the master device as shown in Figure 20. Except for the last data byte, the master device responds with an acknowledge bit after receiving each data byte and automatically increments the I2C subaddress by one. After receiving the last data byte, the master device transmits a not-acknowledge followed by a stop condition to complete the transfer.
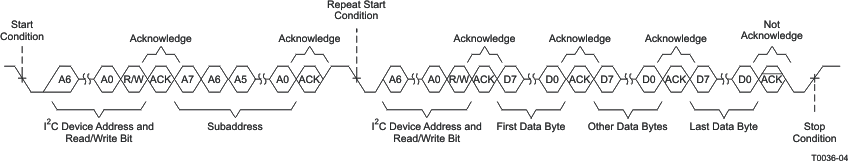 Figure 20. Sequential Read Transfer
Figure 20. Sequential Read Transfer
7.6 Register Maps
Table 6. TAS5414C-Q1 and TAS5424C-Q1 I2C Addresses
| I2C_ADDR VALUE | FIXED ADDRESS | SELECTABLE WITH ADDRESS PIN | READ/WRITE BIT | I2C ADDRESS |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSB | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | LSB | |||
| 0 (OSC MASTER) | I2C WRITE | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0xD8 |
| I2C READ | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0xD9 | |
| 1 (OSC SLAVE1) | I2C WRITE | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0xDA |
| I2C READ | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0xDB | |
| 2 (OSC SLAVE2) | I2C WRITE | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0xDC |
| I2C READ | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0xDD | |
| 3 (OSC SLAVE3) | I2C WRITE | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0xDE |
| I2C READ | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0xDF | |
Table 7. I2C Address Register Definitions
| ADDRESS | TYPE | REGISTER DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|
| 0x00 | Read | Latched fault register 1, global and channel fault |
| 0x01 | Read | Latched fault register 2, dc offset and overcurrent detect |
| 0x02 | Read | Latched diagnostic register 1, load diagnostics |
| 0x03 | Read | Latched diagnostic register 2, load diagnostics |
| 0x04 | Read | External status register 1, temperature and voltage detect |
| 0x05 | Read | External status register 2, Hi-Z and low-low state |
| 0x06 | Read | External status register 3, mute and play modes |
| 0x07 | Read | External status register 4, load diagnostics |
| 0x08 | Read, Write | External control register 1, channel gain select |
| 0x09 | Read, Write | External control register 2, overcurrent control |
| 0x0A | Read, Write | External control register 3, switching frequency and clip pin select |
| 0x0B | Read, Write | External control register 4, load diagnostic, master mode select |
| 0x0C | Read, Write | External control register 5, output state control |
| 0x0D | Read, Write | External control register 6, output state control |
| 0x0E, 0x0F | – | Not used |
| 0x10 | Read, Write | External control register 7, dc detect threshold selection |
| 0x13 | Read | External status register 5, overtemperature shutdown and thermal foldback |
Table 8. Fault Register 1 (0x00) Protection
| D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 | FUNCTION |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | No protection-created faults, default value |
| – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 1 | Overtemperature warning has occurred. |
| – | – | – | – | – | – | 1 | – | DC offset has occurred in any channel. |
| – | – | – | – | – | 1 | – | – | Overcurrent shutdown has occurred in any channel. |
| – | – | – | – | 1 | – | – | – | Overtemperature shutdown has occurred. |
| – | – | – | 1 | – | – | – | – | Charge-pump undervoltage has occurred. |
| – | – | 1 | – | – | – | – | – | AVDD, analog voltage, undervoltage has occurred. |
| – | 1 | – | – | – | – | – | – | PVDD undervoltage has occurred. |
| 1 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | PVDD overvoltage has occurred. |
Table 9. Fault Register 2 (0x01) Protection
| D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 | FUNCTION |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | No protection-created faults, default value |
| – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 1 | Overcurrent shutdown channel 1 has occurred. |
| – | – | – | – | – | – | 1 | – | Overcurrent shutdown channel 2 has occurred. |
| – | – | – | – | – | 1 | – | – | Overcurrent shutdown channel 3 has occurred. |
| – | – | – | – | 1 | – | – | – | Overcurrent shutdown channel 4 has occurred. |
| – | – | – | 1 | – | – | – | – | DC offset channel 1 has occurred. |
| – | – | 1 | – | – | – | – | – | DC offset channel 2 has occurred. |
| – | 1 | – | – | – | – | – | – | DC offset channel 3 has occurred. |
| 1 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | DC offset channel 4 has occurred. |
Table 10. Diagnostic Register 1 (0x02) Load Diagnostics
| D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 | FUNCTION |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | No load-diagnostic-created faults, default value |
| – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 1 | Output short to ground channel 1 has occurred. |
| – | – | – | – | – | – | 1 | – | Output short to PVDD channel 1 has occurred. |
| – | – | – | – | – | 1 | – | – | Shorted load channel 1 has occurred. |
| – | – | – | – | 1 | – | – | – | Open load channel 1 has occurred. |
| – | – | – | 1 | – | – | – | – | Output short to ground channel 2 has occurred. |
| – | – | 1 | – | – | – | – | – | Output short to PVDD channel 2 has occurred. |
| – | 1 | – | – | – | – | – | – | Shorted load channel 2 has occurred. |
| 1 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | Open load channel 2 has occurred. |
Table 11. Diagnostic Register 2 (0x03) Load Diagnostics
| D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 | FUNCTION |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | No load-diagnostic-created faults, default value |
| – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 1 | Output short to ground channel 3 has occurred. |
| – | – | – | – | – | – | 1 | – | Output short to PVDD channel 3 has occurred. |
| – | – | – | – | – | 1 | – | – | Shorted load channel 3 has occurred. |
| – | – | – | – | 1 | – | – | – | Open load channel 3 has occurred. |
| – | – | – | 1 | – | – | – | – | Output short to ground channel 4 has occurred. |
| – | – | 1 | – | – | – | – | – | Output short to PVDD channel 4 has occurred. |
| – | 1 | – | – | – | – | – | – | Shorted load channel 4 has occurred. |
| 1 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | Open load channel 4 has occurred. |
Table 12. External Status Register 1 (0x04) Fault Detection
| D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 | FUNCTION |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | No protection-created faults are present, default value. |
| – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 1 | PVDD overvoltage fault is present. |
| – | – | – | – | – | – | 1 | – | PVDD undervoltage fault is present. |
| – | – | – | – | – | 1 | – | – | AVDD, analog voltage fault is present. |
| – | – | – | – | 1 | – | – | – | Charge-pump voltage fault is present. |
| – | – | – | 1 | – | – | – | – | Overtemperature shutdown is present. |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | – | – | – | – | – | Overtemperature warning |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | – | – | – | – | – | Overtemperature warning level 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | – | – | – | – | – | Overtemperature warning level 2 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | – | – | – | – | – | Overtemperature warning level 3 |
Table 13. External Status Register 2 (0x05) Output State of Individual Channels
| D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 | FUNCTION |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | Output is in Hi-Z mode, not in low-low mode(1), default value. |
| – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 0 | Channel 1 Hi-Z mode (0 = not Hi-Z, 1 = Hi-Z) |
| – | – | – | – | – | – | 0 | – | Channel 2 Hi-Z mode (0 = not Hi-Z, 1 = Hi-Z) |
| – | – | – | – | – | 0 | – | – | Channel 3 Hi-Z mode (0 = not Hi-Z, 1 = Hi-Z) |
| – | – | – | – | 0 | – | – | – | Channel 4 Hi-Z mode (0 = not Hi-Z, 1 = Hi-Z) |
| – | – | – | 1 | – | – | – | – | Channel 1 low-low mode (0 = not low-low, 1 = low-low)(1) |
| – | – | 1 | – | – | – | – | – | Channel 2 low-low mode (0 = not low-low, 1 = low-low)(1) |
| – | 1 | – | – | – | – | – | – | Channel 3 low-low mode (0 = not low-low, 1 = low-low)(1) |
| 1 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | Channel 4 low-low mode (0 = not low-low, 1 = low-low)(1) |
Table 14. External Status Register 3 (0x06) Play and Mute Modes
| D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 | FUNCTION |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Mute mode is disabled, play mode disabled, default value, (Hi-Z mode). |
| – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 1 | Channel 1 play mode is enabled. |
| – | – | – | – | – | – | 1 | – | Channel 2 play mode is enabled. |
| – | – | – | – | – | 1 | – | – | Channel 3 play mode is enabled. |
| – | – | – | – | 1 | – | – | – | Channel 4 play mode is enabled. |
| – | – | – | 1 | – | – | – | – | Channel 1 mute mode is enabled. |
| – | – | 1 | – | – | – | – | – | Channel 2 mute mode is enabled. |
| – | 1 | – | – | – | – | – | – | Channel 3 mute mode is enabled. |
| 1 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | Channel 4 mute mode is enabled. |
Table 15. External Status Register 4 (0x07) Load Diagnostics
| D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 | FUNCTION |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | No channels are set in load diagnostics mode, default value. |
| – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 1 | Channel 1 is in load diagnostics mode. |
| – | – | – | – | – | – | 1 | – | Channel 2 is in load diagnostics mode. |
| – | – | – | – | – | 1 | – | – | Channel 3 is in load diagnostics mode. |
| – | – | – | – | 1 | – | – | – | Channel 4 is in load diagnostics mode. |
| – | – | – | 1 | – | – | – | – | Channel 1 is in overtemperature foldback. |
| – | – | 1 | – | – | – | – | – | Channel 2 is in overtemperature foldback. |
| – | 1 | – | – | – | – | – | – | Channel 3 is in overtemperature foldback. |
| 1 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | Channel 4 is in overtemperature foldback. |
Table 16. External Control Register 1 (0x08) Gain Select
| D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 | FUNCTION |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | Set gain for all channels to 26 dB, default value. |
| – | – | – | – | – | – | 0 | 0 | Set channel 1 gain to 12 dB. |
| – | – | – | – | – | – | 0 | 1 | Set channel 1 gain to 20 dB. |
| – | – | – | – | – | – | 1 | 1 | Set channel 1 gain to 32 dB. |
| – | – | – | – | 0 | 0 | – | – | Set channel 2 gain to 12 dB. |
| – | – | – | – | 0 | 1 | – | – | Set channel 2 gain to 20 dB. |
| – | – | – | – | 1 | 1 | – | – | Set channel 2 gain to 32 dB. |
| – | – | 0 | 0 | – | – | – | – | Set channel 3 gain to 12 dB. |
| – | – | 0 | 1 | – | – | – | – | Set channel 3 gain to 20 dB. |
| – | – | 1 | 1 | – | – | – | – | Set channel 3 gain to 32 dB. |
| 0 | 0 | – | – | – | – | – | – | Set channel 4 gain to 12 dB. |
| 0 | 1 | – | – | – | – | – | – | Set channel 4 gain to 20 dB. |
| 1 | 1 | – | – | – | – | – | – | Set channel 4 gain to 32 dB. |
Table 17. External Control Register 2 (0x09) Overcurrent Control
| D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 | FUNCTION |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Current limit level 2 for all channels, thermal foldback is active. |
| – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 1 | Disable thermal foldback |
| – | – | – | 0 | – | – | – | – | Set channel 1 overcurrent limit ( 0 - level 1, 1 - level 2) |
| – | – | 0 | – | – | – | – | – | Set channel 2 overcurrent limit ( 0 - level 1, 1 - level 2) |
| – | 0 | – | – | – | – | – | – | Set channel 3 overcurrent limit ( 0 - level 1, 1 - level 2) |
| 0 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | Set channel 4 overcurrent limit ( 0 - level 1, 1 - level 2) |
| – | – | – | – | 1 | 1 | 1 | – | Reserved |
Table 18. External Control Register 3 (0x0A) Switching Frequency Select and Clip_OTW Configuration
| D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 | FUNCTION |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | Set fS = 417 kHz, report clip and OTW, 45° phase, disable hard stop, CLIP_OTW pin does not report thermal foldback. |
| – | – | – | – | – | – | 0 | 0 | Set fS = 500 kHz |
| – | – | – | – | – | – | 1 | 0 | Set fS = 357 kHz |
| – | – | – | – | – | – | 1 | 1 | Invalid frequency selection (do not set) |
| – | – | – | – | 0 | 0 | – | – | Configure CLIP_OTW pin to report tweeter detect only. |
| – | – | – | – | 0 | 1 | – | – | Configure CLIP_OTW pin to report clip detect only. |
| – | – | – | – | 1 | 0 | – | – | Configure CLIP_OTW pin to report overtemperature warning only. |
| – | – | – | 1 | – | – | – | – | Enable hard-stop mode. |
| – | – | 1 | – | – | – | – | – | Set fS to a 180° phase difference between adjacent channels. |
| – | 1 | – | – | – | – | – | – | Send sync pulse from OSC_SYNC pin (device must be in master mode). |
| 1 | – | – | – | 1 | – | – | – | Configure CLIP_OTW pin to report thermal foldback |
Table 19. External Control Register 4 (0x0B) Load Diagnostics and Master/Slave Control
| D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 | FUNCTION |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Clock output disabled, master clock mode, dc detection enabled, load diagnostics disabled |
| – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 1 | Run channel 1 load diagnostics |
| – | – | – | – | – | – | 1 | – | Run channel 2 load diagnostics |
| – | – | – | – | – | 1 | – | – | Run channel 3 load diagnostics |
| – | – | – | – | 1 | – | – | – | Run channel 4 load diagnostics |
| – | – | – | 0 | – | – | – | – | Disable dc detection on all channels |
| – | – | 1 | – | – | – | – | – | Enable tweeter-detect mode |
| – | 0 | – | – | – | – | – | – | Enable slave mode (external oscillator is necessary) |
| 1 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | Enable clock output on OSC_SYNC pin (valid only in master mode) |
Table 20. External Control Register 5 (0x0C) Output Control
| D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 | FUNCTION |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | All channels, Hi-Z, mute, reset disabled, dc detect is enabled |
| – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 0 | Set channel 1 to mute mode, non-Hi-Z |
| – | – | – | – | – | – | 0 | – | Set channel 2 to mute mode, non-Hi-Z |
| – | – | – | – | – | 0 | – | – | Set channel 3 to mute mode, non-Hi-Z |
| – | – | – | – | 0 | – | – | – | Set channel 4 to mute mode, non-Hi-Z |
| – | – | – | 0 | – | – | – | – | Set non-Hi-Z channels to play mode, (unmute) |
| – | – | 1 | – | – | – | – | – | DC detect shutdown disabled, but still reports a fault |
| – | 1 | – | – | – | – | – | – | Reserved |
| 1 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | Reset device |
Table 21. External Control Register 6 (0x0D) Output Control
| D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 | FUNCTION |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Low-low state disabled, all channels |
| – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 1 | Set channel 1 to low-low state |
| – | – | – | – | – | – | 1 | – | Set channel 2 to low-low state |
| – | – | – | – | – | 1 | – | – | Set channel 3 to low-low state |
| – | – | – | – | 1 | – | – | – | Set channel 4 to low-low state |
| – | – | – | 1 | – | – | – | – | Connect channel 1 and channel 2 for parallel BTL mode |
| – | – | 1 | – | – | – | – | – | Connect channel 3 and channel 4 for parallel BTL mode |
| 1 | 1 | – | – | – | – | – | – | Reserved |
Table 22. External Control Register 7 (0x10) Miscellaneous Selection
| D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 | FUNCTION |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | Normal speed CM ramp, normal S2P & S2G timing, no delay between LDG phases, Crosstalk Enhancement Disabled, Default DC detect value (1.6V) |
| – | – | – | – | – | – | 0 | 0 | Minimum DC detect value (0.8 V) |
| – | – | – | – | – | – | 1 | 0 | Maximum DC detect value (2.4 V) |
| – | – | – | – | – | 1 | – | – | Enable crosstalk enhancement |
| – | – | – | – | 1 | – | – | – | Adds a 20-ms delay between load diagnostic phases |
| – | – | – | 1 | – | – | – | – | Short-to-power (S2P) and short-to-ground (S2G) load-diagnostic phases take 4x longer |
| – | – | 1 | – | – | – | – | – | Slow common-mode ramp, increase the default time by 3x |
| – | 1 | – | – | – | – | – | – | Reserved |
| 1 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | Slower common-mode (CM) ramp-down from mute mode |
Table 23. External Status Register 5 (0x13) Overtemperature and Thermal Foldback Status
| D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 | FUNCTION |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Default overtemperature foldback status, no channel is in foldback |
| – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 1 | Channel 1 in thermal foldback |
| – | – | – | – | – | – | 1 | – | Channel 2 in thermal foldback |
| – | – | – | – | – | 1 | – | – | Channel 3 in thermal foldback |
| – | – | – | – | 1 | – | – | – | Channel 4 in thermal foldback |
| – | – | – | 1 | – | – | – | – | Channel 1 in overtemperature shutdown |
| – | – | 1 | – | – | – | – | – | Channel 2 in overtemperature shutdown |
| – | 1 | – | – | – | – | – | – | Channel 3 in overtemperature shutdown |
| 1 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | Channel 4 in overtemperature shutdown |