SLOS838C July 2013 – August 2015 TAS5731M
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.4 Thermal Information
- 7.5 PWM Operation at Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.6 DC Electrical Characteristics
- 7.7 AC Electrical Characteristics (BTL, PBTL)
- 7.8 Electrical Characteristics - PLL External Filter Components
- 7.9 Electrical Characteristic - I2C Serial Control Port Operation
- 7.10 Timing Requirements - PLL Input Parameters
- 7.11 Timing Requirements - Serial Audio Ports Slave Mode
- 7.12 Timing Requirements - I2C Serial Control Port Operation
- 7.13 Timing Requirements - Reset (RESET)
- 7.14 Typical Characteristics
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagrams
- 9.3
Feature Description
- 9.3.1 Power Supply
- 9.3.2 I2C Address Selection and Fault Output
- 9.3.3 Single-Filter PBTL Mode
- 9.3.4 Device Protection System
- 9.3.5 SSTIMER Functionality
- 9.3.6 Clock, Autodetection, and PLL
- 9.3.7 PWM Section
- 9.3.8 2.1-Mode Support
- 9.3.9 I2C Compatible Serial Control Interface
- 9.3.10 Audio Serial Interface
- 9.3.11 Dynamic Range Control (DRC)
- 9.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9.5 Programming
- 9.6
Register Maps
- 9.6.1 Clock Control Register (0x00)
- 9.6.2 Device ID Register (0x01)
- 9.6.3 Error Status Register (0x02)
- 9.6.4 System Control Register 1 (0x03)
- 9.6.5 Serial Data Interface Register (0x04)
- 9.6.6 System Control Register 2 (0x05)
- 9.6.7 Soft Mute Register (0x06)
- 9.6.8 Volume Registers (0x07, 0x08, 0x09, 0x0A)
- 9.6.9 Volume Configuration Register (0x0E)
- 9.6.10 Modulation Limit Register (0x10)
- 9.6.11 Interchannel Delay Registers (0x11, 0x12, 0x13, and 0x14)
- 9.6.12 PWM Shutdown Group Register (0x19)
- 9.6.13 Start/Stop Period Register (0x1A)
- 9.6.14 Oscillator Trim Register (0x1B)
- 9.6.15 BKND_ERR Register (0x1C)
- 9.6.16 Input Multiplexer Register (0x20)
- 9.6.17 Channel 4 Source Select Register (0x21)
- 9.6.18 PWM Output Mux Register (0x25)
- 9.6.19 DRC Control Register (0x46)
- 9.6.20 Bank Switch and EQ Control Register (0x50)
-
10Application and Implementation
- 10.1 Application Information
- 10.2
Typical Applications
- 10.2.1 Stereo Bridge Tied Load Application
- 10.2.2 Mono Parallel Bridge Tied Load Application
- 10.2.3 2.1 Application
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PHP|48
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- PHP|48
Orderable Information
6 Pin Configuration and Functions
PHP Package
48-Pin HTQFP
Top View
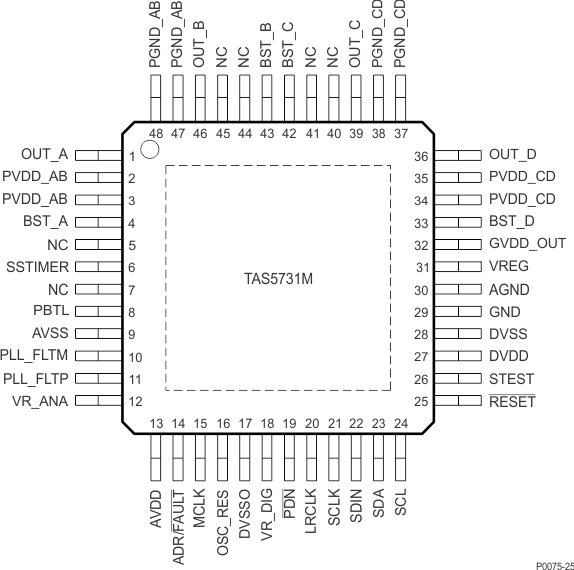
Pin Functions
| PIN | TYPE(1) | 5-V TOLERANT | TERMINATION(2) | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | ||||
| AGND | 30 | P | Local analog ground for power stage, which must be connected to the system ground. | ||
| ADR/FAULT | 14 | DIO | Dual function terminal which sets the LSB of the 7-bit I2C address to "0" if pulled to GND and to "1" if pulled to DVDD. If configured to be a fault output by the methods described in I²C Address Selection and Fault Output, this terminal is pulled low when an internal fault occurs. A pull-up or pull-down resistor is required, as is shown in the Typical Application Circuit Diagrams. If pulled high (to DVDD), a 15-kΩ resistor must be used to minimize in-rush current at power up and to isolate the net if the pin is used as a fault output, as described above. | ||
| AVDD | 13 | P | 3.3-V analog power supply | ||
| AVSS | 9 | P | Analog 3.3-V supply ground | ||
| BST_A | 4 | P | High-side bootstrap supply for half-bridge A | ||
| BST_B | 43 | P | High-side bootstrap supply for half-bridge B | ||
| BST_C | 42 | P | High-side bootstrap supply for half-bridge C | ||
| BST_D | 33 | P | High-side bootstrap supply for half-bridge D | ||
| DVDD | 27 | P | 3.3-V digital power supply | ||
| DVSS | 28 | P | Digital ground | ||
| DVSSO | 17 | P | Oscillator ground | ||
| GND | 29 | P | Analog ground for power stage | ||
| GVDD_OUT | 32 | P | Gate drive internal regulator output | ||
| LRCLK | 20 | DI | 5-V | Pulldown | Input serial audio data left/right clock (sample-rate clock) |
| MCLK | 15 | DI | 5-V | Pulldown | Master clock input |
| NC | 5, 7, 40, 41, 44, 45 | – | No connect | ||
| OSC_RES | 16 | AO | Oscillator trim resistor. Connect an 18.2-kΩ, 1% resistor to DVSSO. | ||
| OUT_A | 1 | O | Output, half-bridge A | ||
| OUT_B | 46 | O | Output, half-bridge B | ||
| OUT_C | 39 | O | Output, half-bridge C | ||
| OUT_D | 36 | O | Output, half-bridge D | ||
| PBTL | 8 | DI | Pulldown | Low means BTL mode; high means PBTL mode. Information goes directly to power stage. | |
| PDN | 19 | DI | 5-V | Pullup | Power down, active-low. PDN prepares the device for loss of power supplies by shutting down the noise shaper and initiating the PWM stop sequence. |
| PGND_AB | 47, 48 | P | Power ground for half-bridges A and B | ||
| PGND_CD | 37, 38 | P | Power ground for half-bridges C and D | ||
| PLL_FLTM | 10 | AO | PLL negative loop-filter terminal | ||
| PLL_FLTP | 11 | AO | PLL positive loop-filter terminal | ||
| PVDD_AB | 2, 3 | P | Power-supply input for half-bridge output A and B | ||
| PVDD_CD | 34, 35 | P | Power-supply input for half-bridge output C and D | ||
| RESET | 25 | DI | 5-V | Pullup | Reset, active-low. A system reset is generated by applying a logic low to this pin. RESET is an asynchronous control signal that restores the DAP to its default conditions and places the PWM in the hard-mute (high-impedance) state. |
| SCL | 24 | DI | 5-V | I2C serial control clock input | |
| SCLK | 21 | DI | 5-V | Pulldown | Serial audio-data clock (shift clock). SCLK is the serial-audio-port input-data bit clock. |
| SDA | 23 | DIO | 5-V | I2C serial control data interface input/output | |
| SDIN | 22 | DI | 5-V | Pulldown | Serial audio data input. SDIN supports three discrete (stereo) data formats. |
| SSTIMER | 6 | AI | Controls ramp time of OUT_x to minimize pop. Leave this pin floating for BD mode. Requires capacitor of 2.2 nF to GND in AD mode. The capacitor determines the ramp time. | ||
| STEST | 26 | DI | Factory test pin. Connect directly to DVSS. | ||
| VR_ANA | 12 | P | Internally regulated 1.8-V analog supply voltage. This pin must not be used to power external devices. | ||
| VR_DIG | 18 | P | Internally regulated 1.8-V digital supply voltage. This pin must not be used to power external devices. | ||
| VREG | 31 | P | Digital regulator output. Not to be used for powering external circuitry. | ||
| PowerPAD™ | P | Provides both electrical and thermal connection from the device to the board. A matching ground pad must be provided on the PCB and the device connected to it via solder. For proper electrical operation, this ground pad must be connected to the system ground | |||
(1) TYPE: A = analog; D = 3.3-V digital; P = power/ground/decoupling; I = input; O = output
(2) All pullups are 20-µA weak pullups and all pulldowns are 20-µA weak pulldowns. The pullups and pulldowns are included to assure proper input logic levels if the terminals are left unconnected (pull-ups → logic 1 input; pulldowns → logic 0 input). Devices that drive inputs with pullups must be able to sink 20 µA while maintaining a logic-0 drive level. Devices that drive inputs with pulldowns must be able to source 20 µA while maintaining a logic-1 drive level.