SLASET9A May 2019 – January 2023 TAS5825P
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3 Feature Description
- 9.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9.5 Programming and Control
- 9.6 Register Maps
-
10Application and Implementation
- 10.1 Application Information
- 10.2 Typical Applications
- 10.3 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10.4 Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RHB|32
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RHB|32
Orderable Information
9.5.3.1 Startup Procedures
- Configure ADR pin with proper setting for I2C device address.
- Bring up power supplies (it does not matter if PVDD or DVDD comes up first).
- Once power supplies are stable, bring up PDN to High, then start SCLK, LRCLK.
- Once I2S clock are stable, set the device into HiZ state and enable DSP via the I2C control port.
- Wait 5 ms at least. Then initialize the DSP Coefficient, and set the device to Play state
- The device is now in normal operation.
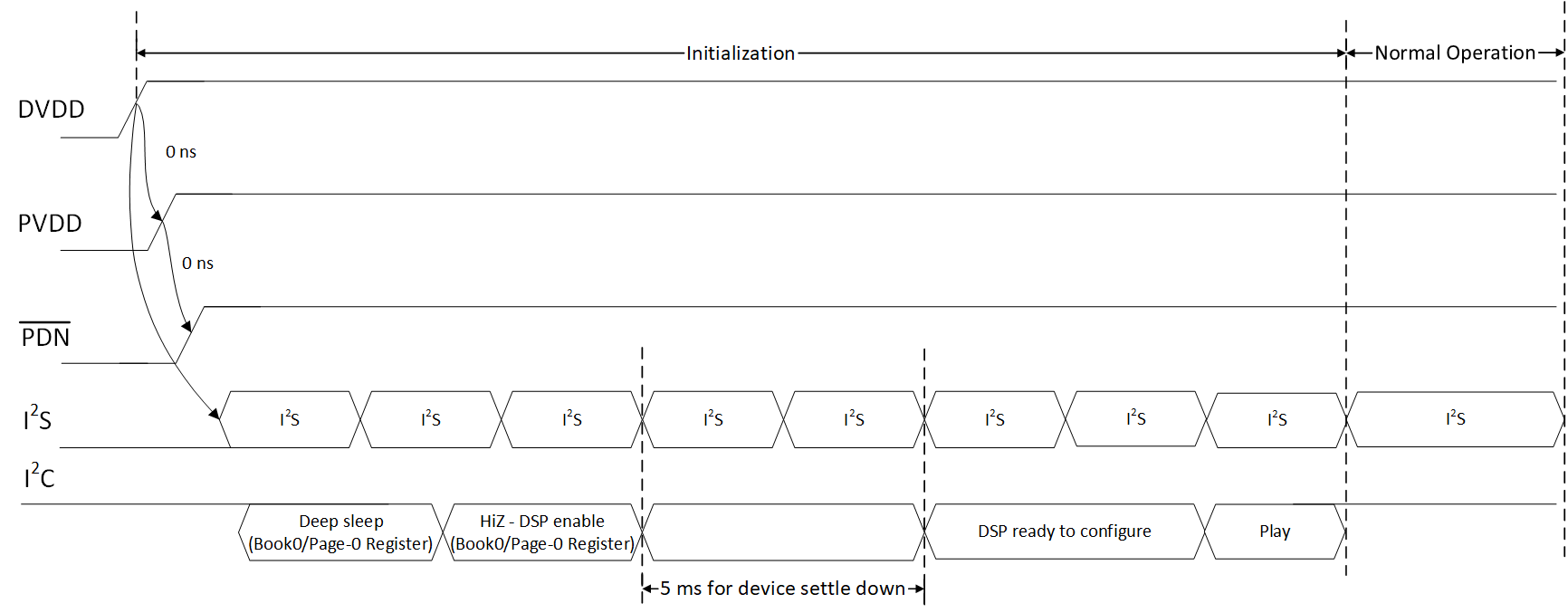
A. I2S only permits to start after DVDD fully powered up. But No sequence requirement with PDN.
B. I2C only response with PDN brought up to HIGH.
C. If I2C register is general register in Book
0, no sequence requirement, then write/read BEFORE or AFTER I2S clock ready. But if
I2C register is DSP register (Other BOOK/PAGE), TI suggests to follow the 5
ms requirements and make sure I2S clock is ready (Especially for the first time
initialization after power up).
D. No sequence requirement for PVDD and DVDD.
Figure 9-14 Start-up Sequence