SLOSE88 December 2024 TAS6754-Q1
ADVANCE INFORMATION
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
- 6 Parameter Measurement Information
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Power Supply
- 7.3.2 Serial Audio Port
- 7.3.3 Digital Audio Processing
- 7.3.4 Class-D operation and Spread Spectrum Control
- 7.3.5 Load Diagnostics
- 7.3.6 Protection and Monitoring
- 7.3.7 Hardware Control Pins
- 7.4
Device Functional Modes
- 7.4.1 Internal Reporting Signals
- 7.4.2 Device States and Flags
- 7.4.3 Fault Events
- 7.4.4 Warning Events
- 7.5 Programming
- 8 Application Information Disclaimer
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Revision History
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DKQ|56
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.3.6.7.3 Thermal Gain Foldback
Thermal Gain Foldback (TGFB) is a power limiting feature to protect the TAS6754-Q1 from excessive die temperature while maintaining audio output.
The main purpose of foldback power limiting is to keep the output stage within its safe power dissipation limit to avoid unexpected Overtemperature Shutdown. The feature provides a smooth audio response and allows for uninterrupted music playback when temperature limits are crossed. That means the TAS6754-Q1 does not simply shut down, but continues to operate with considerable music output power while avoiding the trigger of OTSD.
The DSP of TAS6754-Q1 monitors the die temperature continuously in real-time for safe operation. The device can warn the host if the die temperature is approaching the OTW limits. TAS6754-Q1 still functions until the temperature reaches the OTSD threshold, at which either individual channels or the amplifier is shut down.
If the channel die temperature rises above the configured foldback level, the thermal gain foldback circuit initially activates. The device starts to reduce the gain in steps of 0.25dB per sample and thereby output power. This attack rate can be configured. The configured max attenuations are individual to the level and do not stack between levels.
When the temperature decreases below the foldback level, the attenuation will be held for a configurable number of samples before the attenuation will begin releasing at the gain step rate of 0.1dB per sample. This release rate of the TGFB can be programmed.
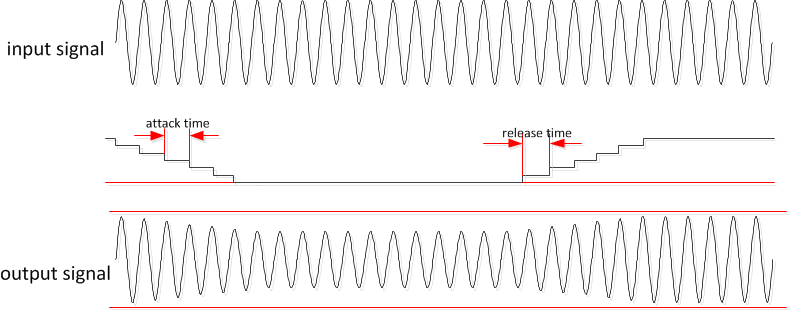 Figure 7-18 Thermal Foldback Attack and Release
Figure 7-18 Thermal Foldback Attack and Release