SCPS225E August 2011 – October 2024 TCA9509
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
- 6 Parameter Measurement Information
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Revision History
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8.2.2.2 VILC and Pulldown Strength Requirements
For the TCA9509 to function correctly, all devices on the A-side must be able to pull the A-side below the voltage input low contention level (VILC). This means that the VOL of any device on the A-side must be below VILC min.
The VOL can be adjusted by changing the IOLthrough the device which is set by the pull-up resistance value. The pull-up resistance on the A-side must be carefully selected to ensure that the logic levels will be transferred correctly to the B-side.
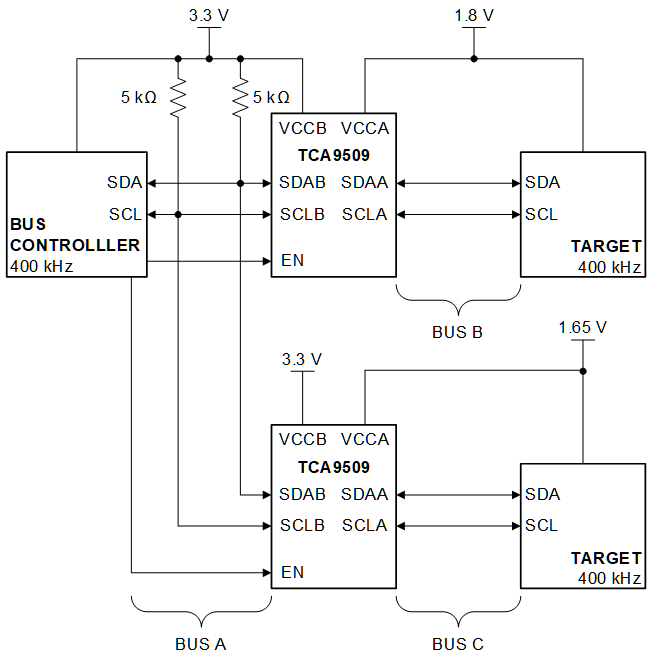 Figure 8-2 Typical Star Application
Figure 8-2 Typical Star ApplicationMultiple B-sides of TCA9509 can be connected in a star configuration, allowing all nodes to communicate with each other. The A-sides should not be connected together when used in a star/parallel configuration.
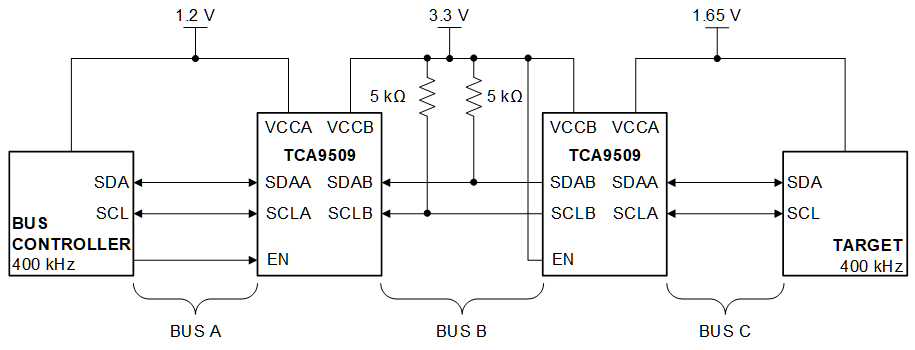 Figure 8-3 Typical Series Application, Two B-Sides Connected Together
Figure 8-3 Typical Series Application, Two B-Sides Connected Together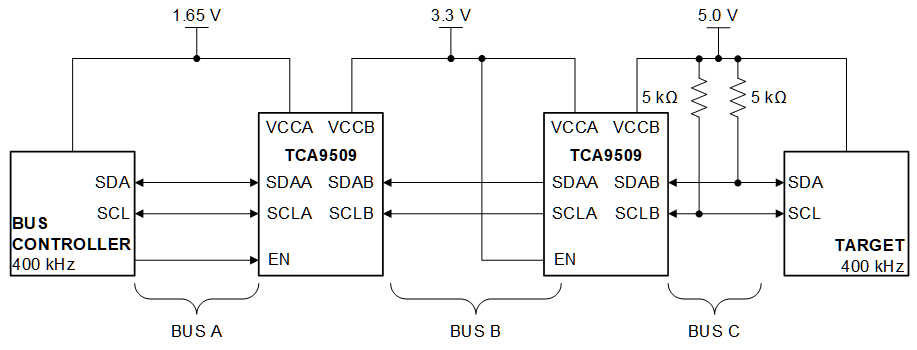 Figure 8-4 Typical Series Application, A-side Connected to B-Side
Figure 8-4 Typical Series Application, A-side Connected to B-SideTo further extend the I2C bus for long traces/cables, multiple TCA9509 devices can be connected in series as long as the A-side is connected to the B-side and VCCA ≤ (VCCB – 1 V) must also be met. Series connections can also be made by connecting both B-sides together while following power supply rule VCCA ≤ (VCCB – 1 V). I2C bus target devices can be connected to any of the bus segments. The number of devices that can be connected in series is limited by repeater delay/time-of-flight considerations on the maximum bus speed requirements.