SPRSP96A March 2024 – September 2024 TDA4AEN-Q1 , TDA4VEN-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Device Comparison
-
5 Terminal Configuration and Functions
- 5.1 Pin Diagrams
- 5.2 Pin Attributes
- 5.3
Signal Descriptions
- 13
- 5.3.1 CPSW3G
- 5.3.2 CPTS
- 5.3.3 CSI-2
- 5.3.4 DDRSS
- 5.3.5 DSI
- 5.3.6 DSS
- 5.3.7 ECAP
- 5.3.8 Emulation and Debug
- 5.3.9 EPWM
- 5.3.10 EQEP
- 5.3.11 GPIO
- 5.3.12 GPMC
- 5.3.13 I2C
- 5.3.14 MCAN
- 5.3.15 MCASP
- 5.3.16 MCSPI
- 5.3.17 MDIO
- 5.3.18 MMC
- 5.3.19 OLDI
- 5.3.20 OSPI
- 5.3.21 Power Supply
- 5.3.22 Reserved
- 5.3.23 SERDES
- 5.3.24 System and Miscellaneous
- 5.3.25 TIMER
- 5.3.26 UART
- 5.3.27 USB
- 5.4 Pin Connectivity Requirements
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings for AEC - Q100 Qualified Devices in the AMW Package
- 6.3 Power-On Hours (POH)
- 6.4 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.5 Operating Performance Points
- 6.6
Electrical
Characteristics
- 6.6.1 I2C Open-Drain, and Fail-Safe (I2C OD FS) Electrical Characteristics
- 6.6.2 Fail-Safe Reset (FS RESET) Electrical Characteristics
- 6.6.3 High-Frequency Oscillator (HFOSC) Electrical Characteristics
- 6.6.4 Low-Frequency Oscillator (LFXOSC) Electrical Characteristics
- 6.6.5 SDIO Electrical Characteristics
- 6.6.6 LVCMOS Electrical Characteristics
- 6.6.7 CSI-2 (D-PHY) Electrical Characteristics
- 6.6.8 USB2PHY Electrical Characteristics
- 6.6.9 DDR Electrical Characteristics
- 6.7 VPP Specifications for One-Time Programmable (OTP) eFuses
- 6.8 Thermal Resistance Characteristics
- 6.9
Timing and Switching Characteristics
- 6.9.1 Timing Parameters and Information
- 6.9.2 Power Supply Requirements
- 6.9.3 System Timing
- 6.9.4 Clock Specifications
- 6.9.5
Peripherals
- 6.9.5.1 ATL
- 6.9.5.2 CPSW3G
- 6.9.5.3 CPTS
- 6.9.5.4 CSI-2
- 6.9.5.5 CSI-2 TX
- 6.9.5.6 DDRSS
- 6.9.5.7 DSS
- 6.9.5.8 ECAP
- 6.9.5.9 Emulation and Debug
- 6.9.5.10 EPWM
- 6.9.5.11 EQEP
- 6.9.5.12 GPIO
- 6.9.5.13 GPMC
- 6.9.5.14 I2C
- 6.9.5.15 MCAN
- 6.9.5.16 MCASP
- 6.9.5.17 MCSPI
- 6.9.5.18 MMCSD
- 6.9.5.19 OSPI
- 6.9.5.20 PCIe
- 6.9.5.21 Timers
- 6.9.5.22 UART
- 6.9.5.23 USB
- 7 Detailed Description
-
8 Applications,
Implementation, and Layout
- 8.1 Device Connection and Layout Fundamentals
- 8.2 Peripheral- and Interface-Specific Design Information
- 8.3 Clock Routing Guidelines
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Revision History
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- AMW|594
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
6.9.4.1.2 MCU_OSC0 LVCMOS Digital Clock Source
Figure 6-20 shows the recommended oscillator connections when MCU_OSC0_XI is connected to a 1.8V LVCMOS square-wave digital clock source.
Note:
- A DC steady-state condition is not allowed on MCU_OSC0_XI when the oscillator is
powered up. This is not allowed because MCU_OSC0_XI is internally AC coupled to a
comparator that can enter an unknown state when DC is applied to the input. Therefore,
application software must power down MCU_OSC0 any time MCU_OSC0_XI is not toggling
between logic states.
- The LVCMOS clock signal sourcing the MCU_OSC0_XI input must have monotonic
transitions. The clock source should be connected to MCU_OSC0_XI with a point-to-point
connection, via a series termination resistor placed near the clock source. The series
termination resistor value should match the clock source output impedance to the
transmission line impedance. For example, the series termination resistor value needs to
be 20 ohms if the clock source has an output impedance of 30 ohms and the PCB signal
trace has a characteristic impedance of 50 ohms. This allows the reflection that returns
from the far end of the un-terminated transmission line to be completely absorbed such
that is does not introduce any non-monotonic events on the signal.
- The PCB trace length connecting the LVCMOS clock source to MCU_OSC0_XI should be minimized. This reduces capacitive loading and decreases probability of external noise sources coupling into the clock signal. Reduced capacitive loading improves rise/fall times of the clock signal which reduces the probability of jitter being introduced in the system.
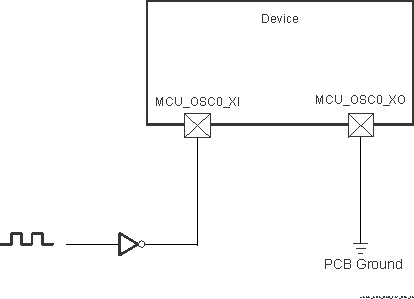 Figure 6-20 1.8V LVCMOS-Compatible
Clock Input
Figure 6-20 1.8V LVCMOS-Compatible
Clock InputTable 6-23 MCU_OSC0 LVCMOS Digital Clock Source Requirements
| PARAMETER | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fxtal | Frequency | 25 | MHz | ||||
| Frequency Stability and Tolerance | Ethernet RGMII and RMII not used | ±100 | ppm | ||||
| Ethernet RGMII and RMII using derived clock | ±50 | ||||||
| DC | Duty Cycle | 45 | 55 | % | |||
| tR/F | Rise/Fall Time (10%-90% rise, 90%-10% fall) | 4(1) | ns | ||||
| JPeriod(RMS) | Period Jitter, RMS (100k samples) | 20 | ps | ||||
| JPeriod(PK-PK) | Period Jitter, Peak to Peak (100k samples) | 300 | ps | ||||
| JPhase(RMS) | Phase Jitter, RMS (BW 100Hz to 1MHz) | 10(2) | ps | ||||
(1) Most LVCMOS oscillator datasheets define
their maximum Output Rise/Fall times with a capacitive load much larger than the actual
load that will be applied by the combined PCB trace capacitance and MCU_OSC0_XI input
capacitance. It should not be difficult to find a LVCMOS oscillator that meets this
requirement. However, the system designer must confirm the LVCMOS oscillator selected will
provide the appropriate rise/fall time to MCU_OSC0_XI input.
(2) Most LVCMOS oscillator datasheets define their max RMS Phase Jitter using a larger
bandwidth integration range than required by this device. To get a more appropriate value,
it may be necessary to contact the LVCMOS oscillator manufacture and ask them to provide a
maximum RMS Phase Jitter using the same bandwidth integration range that has been defined
for this parameter.