at Vs+ = 3 V and 5 V, Vs– = GND, Vocm
is open, 50-Ω single-ended input to differential output, gain = 2 V/V, Rload =
500 Ω, and TA ≈ 25°C (unless otherwise noted)
 Figure 6-37 Main
Amplifier Differential Open-Loop Gain and Phase vs Frequency
Figure 6-37 Main
Amplifier Differential Open-Loop Gain and Phase vs Frequency Figure 6-39 Input
Spot Noise Over Frequency
Figure 6-39 Input
Spot Noise Over Frequency
| Common-mode in to differential out, gain of 2
simulation |
| |
Figure 6-41 CMRR
Over Frequency Figure 6-43 Common-Mode, Small- and Large-Signal Response (Vocm pin driven)
Figure 6-43 Common-Mode, Small- and Large-Signal Response (Vocm pin driven)
| Vocm
input either driven to mid-supply by low impedance
source, or allowed to float and default to
mid-supply |
Figure 6-45 Output Common-Mode Noise
| Single-ended to differential gain of 2 (see Figure 7-1), PSRR for negative supply to differential output
(1-kHz simulation) |
Figure 6-47 –PSRR
vs Vocm Approaching Vs–
| 3 lots, total of 2962 units trimmed at 5-V
supply |
Figure 6-49 Input
Offset Voltage
| 5-V
and 3-V delta from 25°C VIO, 25 units |
Figure 6-51 Input
Offset Voltage Over Temperature
| –40°C to +125°C endpoint drift, 3 lots, total of 68
units |
Figure 6-53 Input
Offset Voltage Drift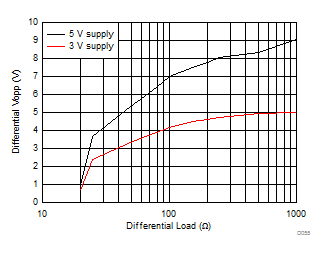
| Maximum differential output swing, Vocm at
midsupply |
Figure 6-55 Maximum Vopp vs Rload
| Vocm
input floating, 3 lots, total of 2962 units |
Figure 6-57 Common-Mode Output Offset From Vs+ / 2 Default Value
10
MHz, 1-Vpp input single to differential gain of 2,
see Figure 7-3 |
Figure 6-59 PD Turn On Waveform
| Single-ended input to differential output, simulated
differential output impedance, (closed-loop) gain of 2
and 5, see Figure 7-1 |
Figure 6-38 Closed-Loop Output Impedance
Single-ended input to differential output, gain of 2
(see Figure 7-1), simulated with 1% resistor, worst-case
mismatch |
Figure 6-40 Output Balance Error Over Frequency
Single-ended to differential, gain of 2
(see Figure 7-1)
PSRR
simulated to differential output |
Figure 6-42 PSRR
Over Frequency Figure 6-44 Common-Mode, Small- and Large-Step Response (Vocm pin driven)
Figure 6-44 Common-Mode, Small- and Large-Step Response (Vocm pin driven)
Average Vocm output offset of 37 units, Standard
deviation
< 2.5 mV,
see Figure 7-3 |
Figure 6-46 Vocm
Offset vs Vocm Setting
| Single-ended to differential gain of 2 (see Figure 7-1), PSRR for positive supply to differential output
(1-kHz simulation) |
Figure 6-48 +PSRR
vs Vocm Approaching Vs+
| 3 lots, total of 2962 units |
Figure 6-50 Input
Offset Current
| 5-V
and 3-V over temperature IOS, 25
units |
Figure 6-52 Input
Offset Current Over Temperature
| –40°C to +125°C endpoint drift, 3 lots, total of 68
units |
Figure 6-54 Input
Offset Current Drift Figure 6-56 Supply Current vs PD Voltage
Figure 6-56 Supply Current vs PD Voltage
| Input driven mid-supply, 3 lots, total of 2962
units |
|
Figure 6-58 Common-Mode Output Offset From Driven Vocm
10
MHz, 1-VPP input single to differential gain
of 2,
see Figure 7-3 |
Figure 6-60 PD Turn Off Waveform























