SLLSEL3C July 2015 – September 2017 TLK10031
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Device Overview
- 2 Revision History
- 3 Description
- 4 Terminal Configuration and Functions
-
5 Specifications
- 5.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 5.2 ESD Ratings
- 5.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 5.4 Thermal Information
- 5.5 Electrical Characteristics: High Speed Side Serial Transmitter
- 5.6 Electrical Characteristics: High Speed Side Serial Receiver
- 5.7 Electrical Characteristics: Low Speed Side Serial Transmitter
- 5.8 Electrical Characteristics: Low Speed Side Serial Receiver
- 5.9 Electrical Characteristics: LVCMOS (VDDO):
- 5.10 Electrical Characteristics: Clocks
- 5.11 Timing Requirements
- 5.12 Typical Characteristics
- 6 Parametric Measurement Information
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagrams
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 10GBASE-KR Transmit Data Path Overview
- 7.3.2 10GBASE-KR Receive Data Path Overview
- 7.3.3 Channel Synchronization Block
- 7.3.4 8B/10B Encoder
- 7.3.5 8B/10B Decoder
- 7.3.6 64B/66B Encoder/Scrambler
- 7.3.7 Forward Error Correction
- 7.3.8 64B/66B Decoder/Descrambler
- 7.3.9 Transmit Gearbox
- 7.3.10 Receive Gearbox
- 7.3.11 XAUI Lane Alignment / Code Gen (XAUI PCS)
- 7.3.12 Inter-Packet Gap (IPG) Characters
- 7.3.13 Clock Tolerance Compensation (CTC)
- 7.3.14 10GBASE-KR Auto-Negotiation
- 7.3.15 10GBASE-KR Link Training
- 7.3.16 10GBASE-KR Line Rate, PLL Settings, and Reference Clock Selection
- 7.3.17 10GBASE-KR Test Pattern Support
- 7.3.18 10GBASE-KR Latency
- 7.4
Device Functional Modes
- 7.4.1 10GBASE-KR Mode
- 7.4.2 1GBASE-KX Mode
- 7.4.3 General Purpose (10G) Serdes Mode Functional Description
- 7.4.4 General Purpose SERDES Receive Data Path
- 7.4.5 Channel Synchronization
- 7.4.6 8B/10B Encoder and Decoder
- 7.4.7 Lane Alignment Scheme for 8b/10b General Purpose Serdes Mode
- 7.4.8 Lane Alignment Components
- 7.4.9 Lane Alignment Operation
- 7.4.10 Line Rate, SERDES PLL Settings, and Reference Clock Selection for the General Purpose SERDES Mode
- 7.4.11 General Purpose SERDES Mode Test Pattern Support
- 7.4.12 General Purpose SERDES Mode Latency
- 7.4.13 Intelligent Switching Modes
- 7.4.14 Serial Loopback Modes
- 7.4.15 Latency Measurement Function (General Purpose SerDes Mode)
- 7.4.16 Power Down Mode
- 7.4.17 MDIO Management Interface
- 7.4.18 MDIO Protocol Timing
- 7.4.19 Clause 22 Indirect Addressing
- 7.4.20 Provisionable XAUI Clock Tolerance Compensation
- 7.5
Register Maps
- 7.5.1 Register Bit Definitions
- 7.5.2
Vendor Specific Device Registers
- 7.5.2.1 GLOBAL_CONTROL_1 (register: 0x0000) (default: 0x0610) (device address: 0x1E)
- 7.5.2.2 CHANNEL_CONTROL_1 (register: 0x0001) (default: 0x0B00) (device address: 0x1E)
- 7.5.2.3 HS_SERDES_CONTROL_1 (register: 0x0002 ) (default: 0x831D) (device address: 0x1E)
- 7.5.2.4 HS_SERDES_CONTROL_2 (register: 0x0003) (default: 0xA848) (device address: 0x1E)
- 7.5.2.5 HS_SERDES_CONTROL_3 (register: 0x0004) (default: 0x1500) (device address: 0x1E)
- 7.5.2.6 HS_SERDES_CONTROL_4 (register: 0x0005) (default: 0x2000) (device address: 0x1E)
- 7.5.2.7 LS_SERDES_CONTROL_1 (register: 0x0006) (default: 0xF115) (device address: 0x1E)
- 7.5.2.8 LS_SERDES_CONTROL_2 (register: 0x0007) (default: 0xDC04) (device address: 0x1E)
- 7.5.2.9 LS_SERDES_CONTROL_3 (register: 0x0008) (default: 0x000D) (device address: 0x1E)
- 7.5.2.10 HS_OVERLAY_CONTROL (register: 0x0009) (default: 0x0380) (device address: 0x1E)
- 7.5.2.11 LS_OVERLAY_CONTROL (register: 0x000A) (default: 0x4000) (device address: 0x1E)
- 7.5.2.12 LOOPBACK_TP_CONTROL (register: 0x000B) (default: 0x0D10) (device address: 0x1E)
- 7.5.2.13 LS_CONFIG_CONTROL (register: 0x000C) (default: 0x0330) (device address: 0x1E)
- 7.5.2.14 LS_CONFIG_CONTROL (register: 0x000C) (default: 0x0330) (device address: 0x1E)
- 7.5.2.15 CLK_CONTROL (register: 0x000D) (default: 0x2F80) (device address: 0x1E)
- 7.5.2.16 RESET_CONTROL (register: 0x000E) (default: 0x0000) (device address: 0x1E)
- 7.5.2.17 CHANNEL_STATUS_1 (register: 0x000F) (default: 0x0000) (device address: 0x1E)
- 7.5.2.18 HS_ERROR_COUNTER (register: 0x0010) (default: 0x0FFFD) (device address: 0x1E)
- 7.5.2.19 LS_LN0_ERROR_COUNTER (register: 0x0011) (default: 0xFFFD) (device address: 0x1E)
- 7.5.2.20 LS_LN1_ERROR_COUNTER (register: 0x0012 ) (default: 0xFFFD) (device address: 0x1E)
- 7.5.2.21 LS_LN2_ERROR_COUNTER (register: 0x0013) (default: 0xFFFD) (device address: 0x1E)
- 7.5.2.22 LS_LN3_ERROR_COUNTER (register: 0x0014) (default: 0xFFFD) (device address: 0x1E)
- 7.5.2.23 LS_STATUS_1 (register: 0x0015) (default: 0x0000) (device address: 0x1E)
- 7.5.2.24 HS_STATUS_1 (register: 0x0016) (default: 0x0000) (device address: 0x1E)
- 7.5.2.25 DST_CONTROL_1 (register = 0x0017) (default = 0x2000) (device address: 0x1E)
- 7.5.2.26 DST_CONTROL_2 (register = 0x0018 ) (default = 0x0C20) (device address: 0x1E)
- 7.5.2.27 DSR_CONTROL_1 (register = 0x0019) (default = 0x2500) (device address: 0x1E)
- 7.5.2.28 DSR_CONTROL_2 (register = 0x001A) (default = 0x4C20) (device address: 0x1E)
- 7.5.2.29 DATA_SWITCH_STATUS (register = 0x001B) (default = 0x1020) (device address: 0x1E)
- 7.5.2.30 LS_CH_CONTROL_1 (register =0x001C) (default =0x0000) (device address: 0x1E)
- 7.5.2.31 HS_CH_CONTROL_1 (register = 0x001D) (default = 0x0000) (device address: 0x1E)
- 7.5.2.32 EXT_ADDRESS_CONTROL (register = 0x001E) (default = 0x0000) (device address: 0x1E)
- 7.5.2.33 EXT_ADDRESS_DATA (register = 0x001F) (default = 0x0000) (device address: 0x1E)
- 7.5.2.34 VS_10G_LN_ALIGN_ACODE_P (register =0x8003) (default = 0x0283) (device address: 0x1E)
- 7.5.2.35 VS_10G_LN_ALIGN_ACODE_N (register =0x8004 ) (default = 0x017C) (device address: 0x1E)
- 7.5.2.36 MC_AUTO_CONTROL (register = 0x8021) (default = 0x000F) (device address: 0x1E)
- 7.5.2.37 DST_ON_CHAR_CONTROL (register = 0x802A) (default = 0x02FD) (device address: 0x1E)
- 7.5.2.38 DST_OFF_CHAR_CONTROL (register = 0x802B ) (default = 0x02FD) (device address: 0x1E)
- 7.5.2.39 DST_STUFF_CHAR_CONTROL (register = 0x802C) (default = 0x0207) (device address: 0x1E)
- 7.5.2.40 DSR_ON_CHAR_CONTROL (register = 0x802D) (default = 0x02FD) (device address: 0x1E)
- 7.5.2.41 DSR_OFF_CHAR_CONTROL (register = 0X802E) (default = 0x02FD) (device address: 0x1E)
- 7.5.2.42 DSR_STUFF_CHAR_CONTROL (register = 0x802F) (default = 0x0207) (device address: 0x1E)
- 7.5.2.43 LATENCY_MEASURE_CONTROL (register = 0x8040) (default = 0x0000) (device address: 0x1E)
- 7.5.2.44 LATENCY_COUNTER_2 (register = 0x8041) (default =0x0000) (device address: 0x1E)
- 7.5.2.45 LATENCY_COUNTER_1 (register = 0x8042) (default = 0x0000) (device address: 0x1E)
- 7.5.2.46 TRIGGER_LOAD_CONTROL (register =0x8100) (default = 0x0000) (device address: 0x1E)
- 7.5.2.47 TRIGGER_EN_CONTROL (register = 0x8101) (default = 0x0000) (device address: 0x1E)
- 7.5.3
PMA/PMD Registers
- 7.5.3.1 PMA_CONTROL_1 (register = 0x0000) (default = 0x0000) (device address: 0x01)
- 7.5.3.2 PMA_STATUS_1 (register = 0x0001) (default = 0x0002) (device address: 0x01)
- 7.5.3.3 PMA_DEV_IDENTIFIER_1 (register = 0x0002) (default = 0x4000) (device address: 0x01)
- 7.5.3.4 PMA_DEV_IDENTIFIER_2 (register = 0x0003) (default = 0x5100) (device address: 0x01)
- 7.5.3.5 PMA_SPEED_ABILITY (register = 0x0004) (default = 0x0011) (device address: 0x01)
- 7.5.3.6 PMA_DEV_PACKAGE_1 (register = 0x0005) (default = 0x000B) (device address: 0x01)
- 7.5.3.7 PMA_DEV_PACKAGE_2 (register = 0x0006) (default = 0x4000) (device address: 0x01)
- 7.5.3.8 PMA_DEV_PACKAGE_2 (register = 0x0006) (default = 0x4000) (device address: 0x01)
- 7.5.3.9 PMA_RX_SIGNAL_DET_STATUS (register = 0x000A) (default = 0x0000) (device address: 0x01)
- 7.5.3.10 PMA_EXTENDED_ABILITY (register = 0x000B) (default = 0x0050) (device address: 0x01)
- 7.5.3.11 LT_TRAIN_CONTROL (register =0x0096) (default = 0x0002) (device address: 0x01)
- 7.5.3.12 LT_TRAIN_STATUS (register = 0x0097) (default = 0x0000) (device address: 0x01)
- 7.5.3.13 LT_LINK_PARTNER_CONTROL (register = 0x0098) (default = 0x0000) (device address: 0x01)
- 7.5.3.14 LT_LINK_PARTNER_STATUS (register = 0x0099) (default = 0x0000) (device address: 0x01)
- 7.5.3.15 LT_LOCAL_DEVICE_CONTROL (register = 0x009A) (default = 0x0000) (device address: 0x01)
- 7.5.3.16 LT_LOCAL_DEVICE_STATUS (register = 0x009B) (default = 0x0000) (device address: 0x01)
- 7.5.3.17 KX_STATUS (register = 0x00A1) (default = 0x3000) (device address: 0x01)
- 7.5.3.18 KR_FEC_ABILITY (register = 0x00AA) (default = 0x0003) (device address: 0x01)
- 7.5.3.19 KR_FEC_CONTROL (register = 0x00AB) (default = 0x0000) (device address: 0x01)
- 7.5.3.20 KR_FEC_C_COUNT_1 (register = 0x00AC) (default = 0x0000) (device address: 0x01)
- 7.5.3.21 KR_FEC_C_COUNT_2 (register = 0x00AD) (default = 0x0000) (device address: 0x01)
- 7.5.3.22 KR_FEC_UC_COUNT_1 (register = 0x00AE) (default = 0x0000) (device address: 0x01)
- 7.5.3.23 KR_FEC_UC_COUNT_2 (register = 0x00AF) (default = 0x0000) (device address: 0x01)
- 7.5.3.24 KR_VS_FIFO_CONTROL_1 (register = 0x8001) (default = 0xCC4C) (device address: 0x01)
- 7.5.3.25 KR_VS_TP_GEN_CONTROL (register =0x8002) (default = 0x0000) (device address: 0x01)
- 7.5.3.26 KR_VS_TP_VER_CONTROL (register = 0x8003) (default = 0x0000) (device address: 0x01)
- 7.5.3.27 KR_VS_CTC_ERR_CODE_LN0 (register = 0x8005) (default = 0xCE00) (device address: 0x01)
- 7.5.3.28 KR_VS_CTC_ERR_CODE_LN1 (register = 0x8006) (default =0x0000) (device address: 0x01)
- 7.5.3.29 KR_VS_CTC_ERR_CODE_LN2 (register = 0x8007) (default = 0x0000) (device address: 0x01)
- 7.5.3.30 KR_VS_CTC_ERR_CODE_LN3 (register = 0x8008) (default = 0x0080) (device address: 0x01)
- 7.5.3.31 KR_VS_LN0_EOP_ERROR_COUNTER (register = 0x8010) (default = 0xFFFD) (device address: 0x01)
- 7.5.3.32 KR_VS_LN1_EOP_ERROR_COUNTER (register = 0x8011) (default = 0xFFFD) (device address: 0x01)
- 7.5.3.33 KR_VS_LN2_EOP_ERROR_COUNTER (register = 0x8012) (default = 0xFFFD) (device address: 0x01)
- 7.5.3.34 KR_VS_LN3_EOP_ERROR_COUNTER (register =0x8013 ) (default = 0xFFFD) (device address: 0x01)
- 7.5.3.35 KR_VS_TX_CTC_DROP_COUNT (register = 0x8014) (default = 0xFFFD) (device address: 0x01)
- 7.5.3.36 KR_VS_TX_CTC_INSERT_COUNT (register = 0x8015) (default = 0xFFFD) (device address: 0x01)
- 7.5.3.37 KR_VS_RX_CTC_DROP_COUNT (register = 0x8016) (default = 0xFFFD) (device address: 0x01)
- 7.5.3.38 KR_VS_RX_CTC_INSERT_COUNT (register = 0x8017) (default = 0xFFFD) (device address: 0x01)
- 7.5.3.39 KR_VS_STATUS_1 (register = 0x8018) (default = 0x0000) (device address: 0x01)
- 7.5.3.40 KR_VS_TX_CRCJ_ERR_COUNT_1 (register = 0x8019) (default = 0xFFFF) (device address: 0x01)
- 7.5.3.41 KR_VS_TX_CRCJ_ERR_COUNT_2 (register = 0x801A) (default = 0xFFFD) (device address: 0x01)
- 7.5.3.42 KR_VS_TX_LN0_HLM_ERR_COUNT (register = 0x801B) (default = 0xFFFD) (device address: 0x01)
- 7.5.3.43 KR_VS_TX_LN1_HLM_ERR_COUNT (register = 0x801C) (default = 0xFFFD) (device address: 0x01)
- 7.5.3.44 KR_VS_TX_LN2_HLM_ERR_COUNT (register = 0x801D) (default = 0xFFFD) (device address: 0x01)
- 7.5.3.45 KR_VS_TX_LN3_HLM_ERR_COUNT (register = 0x801E) (default = 0xFFFD) (device address: 0x01)
- 7.5.3.46 LT_VS_CONTROL_2 (register = 0x9001) (default = 0x0000) (device address: 0x01)
- 7.5.4
PCS Registers
- 7.5.4.1 PCS_CONTROL (register = 0x0000) (default = 0x0000) (device address: 0x03)
- 7.5.4.2 PCS_STATUS_1 (register = 0x0001) (default = 0x0002) (device address: 0x03)
- 7.5.4.3 PCS_STATUS_2 (register = 0x0008) (default = 0x8001) (device address: 0x03)
- 7.5.4.4 KR_PCS_STATUS_1 (register = 0x0020) (default = 0x0004) (device address: 0x03)
- 7.5.4.5 KR_PCS_STATUS_2 (register = 0x0021) (default = 0x0000) (device address: 0x03)
- 7.5.4.6 PCS_TP_SEED_A0 (register = 0x0022) (default = 0x0000) (device address: 0x03)
- 7.5.4.7 PCS_TP_SEED_A1 (register = 0x0023) (default = 0x0000) (device address: 0x03)
- 7.5.4.8 PCS_TP_SEED_A2 (register = 0x0024) (default = 0x0000) (device address: 0x03)
- 7.5.4.9 PCS_TP_SEED_A3 (register = 0x0025) (default = 0x0000) (device address: 0x03)
- 7.5.4.10 PCS_TP_SEED_B0 (register = 0x0026) (default = 0x0000) (device address: 0x03)
- 7.5.4.11 PCS_TP_SEED_B1 (register = 0x0027) (default = 0x0000) (device address: 0x03)
- 7.5.4.12 PCS_TP_SEED_B2 (register = 0x0028) (default = 0x0000) (device address: 0x03)
- 7.5.4.13 PCS_TP_SEED_B3 (register = 0x0029) (default = 0x0000) (device address: 0x03)
- 7.5.4.14 PCS_TP_CONTROL (register = 0x002A) (default = 0x0000) (device address: 0x03)
- 7.5.4.15 PCS_TP_ERR_COUNT (register = 0x002B) (default = 0x0000) (device address: 0x03)
- 7.5.4.16 PCS_VS_CONTROL (register = 0x8000) (default = 0x00B0) (device address: 0x03)
- 7.5.4.17 PCS_VS_STATUS (register = 0x8010) (default = 0x00FD) (device address: 0x03)
- 7.5.5
Auto-Negotiation Registers
- 7.5.5.1 AN_CONTROL (register = 0x0000) (default = 0x3000) (device address: 0x07)
- 7.5.5.2 AN_STATUS (register = 0x0001) (default = 0x0088) (device address: 0x07)
- 7.5.5.3 AN_DEV_PACKAGE (register = 0x0005) (default = 0x0080) (device address: 0x07)
- 7.5.5.4 AN_ADVERTISEMENT_1 (register = 0x0010) (default = 0x1001) (device address: 0x07)
- 7.5.5.5 AN_ADVERTISEMENT_2 (register = 0x0011) (default = 0x0080) (device address: 0x07)
- 7.5.5.6 AN_ADVERTISEMENT_3 (register = 0x0012) (default = 0x4000) (device address: 0x07)
- 7.5.5.7 AN_LP_ADVERTISEMENT_1 (register = 0x0013) (default = 0x0001) (device address: 0x07)
- 7.5.5.8 AN_LP_ADVERTISEMENT_2 (register = 0x0014) (default = 0x0000) (device address: 0x07)
- 7.5.5.9 AN_LP_ADVERTISEMENT_3 (register = 0x0015) (default = 0x0000) (device address: 0x07)
- 7.5.5.10 AN_XNP_TRANSMIT_1 (register = 0x0016) (default = 0x2000) (device address: 0x07)
- 7.5.5.11 AN_XNP_TRANSMIT_2 (register = 0x0017) (default = 0x0000) (device address: 0x07)
- 7.5.5.12 AN_XNP_TRANSMIT_3 (register = 0x0018) (default = 0x0000) (device address: 0x07)
- 7.5.5.13 AN_LP_XNP_ABILITY_1 (register = 0x0019) (default = 0x0000) (device address: 0x07)
- 7.5.5.14 AN_LP_XNP_ABILITY_2 (register = 0x001A) (default = 0x0000) (device address: 0x07)
- 7.5.5.15 AN_LP_XNP_ABILITY_3 (register = 0x001B) (default = 0x0000) (device address: 0x07)
- 7.5.5.16 AN_BP_STATUS (register = 0x0030) (default = 0x0001) (device address: 0x07)
- 8 Applications and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical Packaging and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- CTR|144
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7 Detailed Description
7.1 Overview
Various interfaces of the TLK10031 device are shown in Figure 7-1. A simplified block diagram of both the transmit and receive data path is shown in Figure 7-2. This low-power transceiver consists of two serializer/deserializer (SERDES) blocks, one on the low speed side and the other on the high speed side. The core logic block that lies between the two SERDES blocks carries out all the logic functions including channel synchronization, lane alignment, 8B/10B and 64B/66B encoding/decoding, as well as test pattern generation and verification.
The TLK10031 provides a management data input/output (MDIO Clause 22/45) interface as well as a JTAG interface for device configuration, control, and monitoring. Detailed description of the TLK10031 pin functions is provided in Section 4.
7.2 Functional Block Diagrams
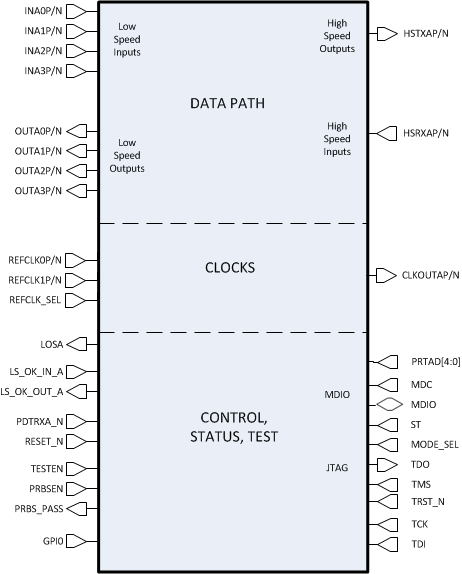 Figure 7-1 TLK10031 Interfaces
Figure 7-1 TLK10031 Interfaces
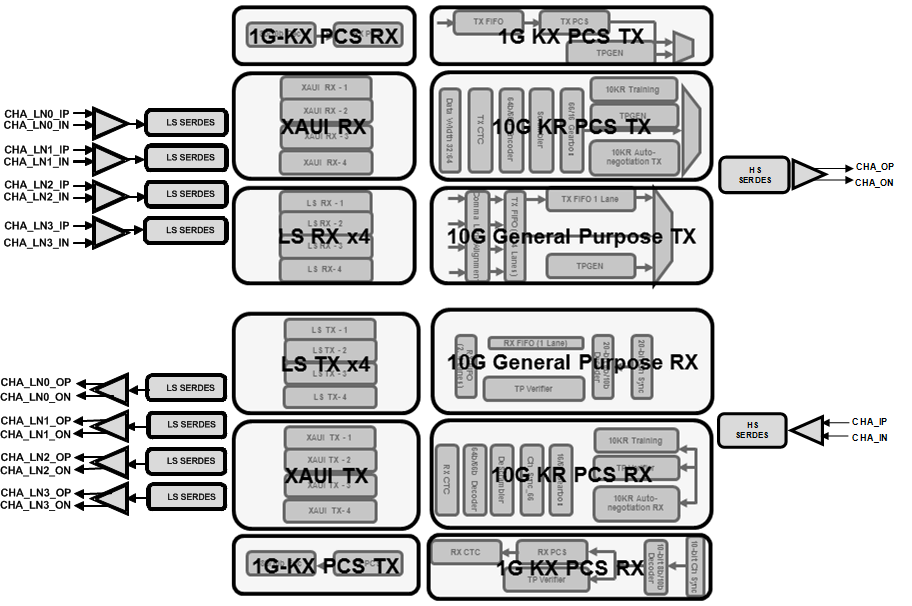 Figure 7-2 A Simplified Block Diagram of the TLK10031 Data Paths
Figure 7-2 A Simplified Block Diagram of the TLK10031 Data Paths
7.3 Feature Description
7.3.1 10GBASE-KR Transmit Data Path Overview
In 10GBASE-KR Mode, the TLK10031 takes in XAUI data on the four low speed input lanes. The serial data in each lane is deserialized into 10-bit parallel data, then byte aligned (channel synchronized) based on comma detection. The four XAUI lanes are then aligned with one another, and the aligned data is input to four 8B/10B decoders. The decoded data is then input to the transmit clock tolerance compensation (CTC) block which compensates for any frequency offsets between the incoming XAUI data and the local reference clock. The CTC block then delivers the data to a 64B/66B encoder and a scrambler. The resulting scrambled 10GBASE-KR data is then input to a transmit gearbox which in turn delivers it to the high speed side SERDES for serialization and output through the HSTXAP/N*P/N pins.
7.3.2 10GBASE-KR Receive Data Path Overview
In the receive direction, the TLK10031 takes in 64B/66B-encoded serial 10GBASE-KR data on the HSTXAP/N*P/N pins. This data is deserialized by a high speed SERDES, then input to a receive gearbox. After the gearbox, the data is aligned to 66-bit frames, descrambled, 64B/66B decoded, and then input to the receive CTC block. After CTC, the data is encoded by four 8B/10B encoders, and the resulting four 10-bit parallel words are serialized by the low speed SERDES blocks. The four serial XAUI output lanes are transmitted out the OUTAP/N*P/N pins.
7.3.3 Channel Synchronization Block
When parallel data is clocked into a parallel-to-serial converter, the byte boundary that was associated with the parallel data is lost in the serialization of the data. When the serial data is received and converted to parallel format again, a method is needed to be able to recognize the byte boundary again. Generally, this is accomplished through the use of a synchronization pattern. This is a unique pattern of 1’s and 0’s that either cannot occur as part of valid data or is a pattern that repeats at defined intervals. 8B/10B encoding contains a character called the comma (b’0011111’ or b’1100000’) which is used by the comma detect circuit to align the received serial data back to its original byte boundary. The TLK10031 channel synchronization block detects the comma pattern found in the K28.5 character, generating a synchronization signal aligning the data to their 10-bit boundaries for decoding. It is important to note that the comma can be either a (b’0011111’) or the inverse (b’1100000’) depending on the running disparity. The TLK10031 decoder will detect both patterns.
The TLK10031 performs channel synchronization per lane as shown in the flowchart of Figure 7-3.
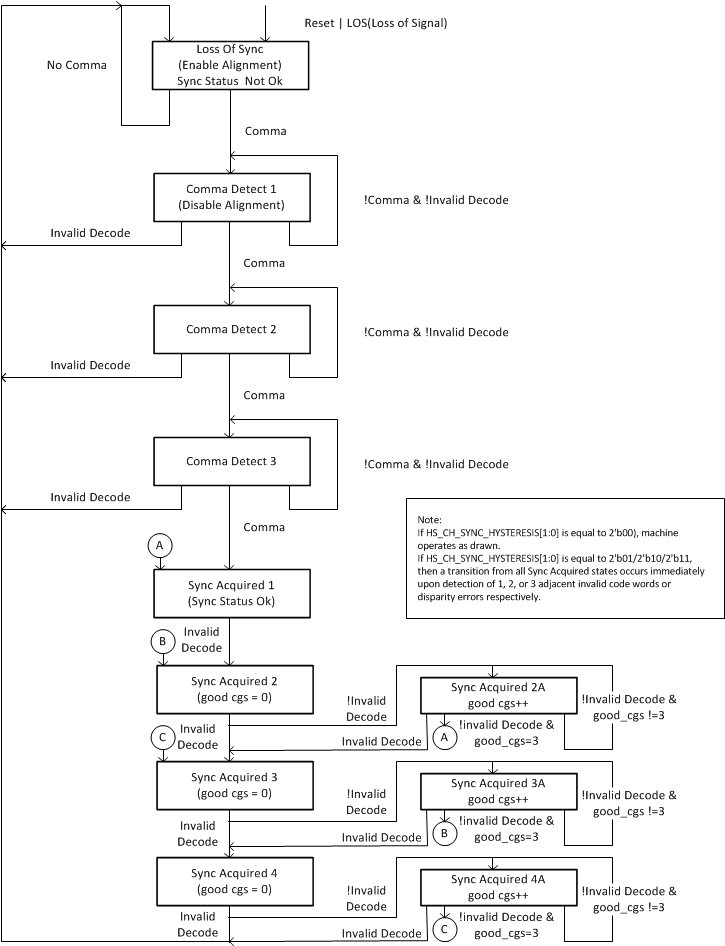 Figure 7-3 Channel Synchronization Flowchart
Figure 7-3 Channel Synchronization Flowchart
7.3.4 8B/10B Encoder
Embedded-clock serial interfaces require a method of encoding to ensure sufficient transition density for the receiving CDR to acquire and maintain lock. The encoding scheme also maintains the signal DC balance by keeping the number of ones and zeros balanced which allows for AC coupled data transmission. The TLK10031 uses the 8B/10B encoding algorithm that is used by the 10 Gbps and 1 Gbps Ethernet and Fibre Channel standards. This provides good transition density for clock recovery and improves error checking.
The 8B/10B encoder converts each 8-bit wide data to a 10-bit wide encoded data character to improve its transition density. This transmission code includes /D/ characters, used for transmitting data, and /K/ characters, used for transmitting protocol information. Each /K/ or /D/ character code word can also have both a positive and a negative disparity version. The disparity of a code word is selected by the encoder to balance the running disparity of the serialized data stream.
7.3.5 8B/10B Decoder
Once the Channel Synchronization block has identified the byte boundaries from the received serial data stream, the 8B/10B decoder converts 10-bit 8B/10B-encoded characters into their respective 8-bit formats. When a code word error or running disparity error is detected in the decoded data, the error is reported in the status register (1E.000F) and the LOS pin is asserted (depending on the LOS overlay selection).
7.3.6 64B/66B Encoder/Scrambler
To facilitate the transmission of data received from the media access control (MAC) layer, the TLK10031 encodes data received from the MAC using the 64B/66B encoding algorithm defined in the IEEE802.3-2008 standard. The TLK10031 takes two consecutive transfers from the XAUI interface and encodes them into a 66-bit code word. The information from the two XAUI transfers includes 64 bits of data and 8 bits of control information after 8B/10B decoding.
If the 64B/66B encoder detects an invalid packet format from the XAUI interface, it replaces erroneous information with appropriately-encoded error information. The resulting 66-bit code word is then sent on to the transmit gearbox.
The encoding process implemented in the TLK10031 includes two steps:
- an encoding step, which converts the 72 bits of data (8 data bytes plus 8 control-code indicators) received from the transmit CTC FIFO into a 66-bit code word
- a scrambling step, which scrambles 64 bits of encoded data using the scrambler polynomial x58+x39+1. The 66 bits created by the encoder consists of 64 bits of data and a 2-bit synchronization field consisting of either 01 or 10. Only the 64 bits of data are scrambled, leaving the two synchronization bits unmodified. The two synchronization bits allow the receive gearbox to obtain frame alignment and, in addition, ensure an edge transition of at least once in 66 bits of data. The encoding process allows a limited amount of control information to be sent in-line with the data.
7.3.7 Forward Error Correction
Optionally enabled, Forward Error Correction (FEC) follows the IEEE 802.3-2008 standard, and is able to correct a burst errors up to 11 bits. In the TX data path, the FEC logic resides between the scrambler and gearbox. In the RX datapath, FEC resides between the gearbox and descrambler. Frame alignment is handled inside the RX FEC block during FEC operation, and the RX gearbox sync header alignment is bypassed. Because latency is increased in both the TX and RX data paths with FEC enabled, it is disabled by default and must be enabled through MDIO programming. Note that FEC by nature will add latency due to frame storage.
7.3.8 64B/66B Decoder/Descrambler
The data received from the serial 10GBASE-KR is 64B/66B-encoded data. The TLK10031 decodes the data received using the 64B/66B decoding algorithm defined in the IEEE 802.3-2008 standard. The TLK10031 creates consecutive 72-bit data words from the encoded 66-bit code words for transfer over the XAUI interface to the MAC. The information for the two XAUI transfers includes 64 bits of data and 8 bits of control information before 8B/10B encoding.
Not all 64B/66B block payloads are valid. Invalid block payloads are handled by the 64B/66B decoder block and appropriate error handling is provided, as defined in the IEEE 802.3-2008 standard. The decoding algorithm includes two steps: a descrambling step which descrambles 64 bits of the 66-bit code word with the scrambling polynomial x58+x39+1, and a decoding step which converts the 66 bits of data received into 64 bits of data and 8 bits of control information. These words are sent to the receive CTC FIFO.
7.3.9 Transmit Gearbox
The function of the transmit gearbox is to convert the 66-bit encoded, scrambled data stream into a 16-bit-wide data stream to be sent out to the serializer and ultimately to the physical medium attachment (PMA) device. The gearbox is needed because while the effective bit rate of the 66-bit data stream is equal to the effective bit rate of the 16-bit data, the clock rates of the two buses are of different frequencies.
7.3.10 Receive Gearbox
While the transmit gearbox only performs the task of converting 66-bit data to be transported on to the 16-bit serializer, the receive gearbox has more to do than just the reverse of this function. The receive gearbox must also determine where within the incoming data stream the boundaries of the 66-bit code words are.
The receive gearbox has the responsibility of initially synchronizing the header field of the code words and continuously monitoring the ongoing synchronization. After obtaining synchronization to the incoming data stream, the gearbox assembles 66-bit code words and presents these to the 64B/66B decoder.
Note that in FEC mode, the Receive Gearbox blindly converts 16-bit data to 66-bit data and depends on the RX FEC logic to frame align the data.
7.3.11 XAUI Lane Alignment / Code Gen (XAUI PCS)
The XAUI interface standard is defined to allow for 21 UI of skew between lanes. This block is implemented to handle up to 30 UI (XAUI UI) of skew between lanes using /A/ characters. The state machine follows the standard 802.3-2008 defined state machine.
7.3.12 Inter-Packet Gap (IPG) Characters
The XAUI interface transports information that consists of packets and inter-packet gap (IPG) characters. The IEEE 802.3-2008 standard defines that the IPG, when transferred over the XAUI interface, consists of alignment characters (/A/), control characters (/K/) and replacement characters (/R/).
TLK10031 converts all AKR characters to IDLE characters, performs insertions or deletions on the IDLE characters, and transmits only encoded IDLE characters out to the 10GBASE-KR interface. The receive channel expects encoded IDLE characters to enter the 10GBASE-KR interface, and performs insertions and deletions on IDLE characters and then converts IDLE characters back to AKR characters. Any AKR characters received on the high speed interface are by default converted to IDLE characters for reconversion to AKR columns.
Both the transmit and receive FIFOs rely upon a valid IDLE stream to perform clock tolerance compensation (CTC).
7.3.13 Clock Tolerance Compensation (CTC)
The XAUI interface is defined to allow for separate clock domains on each side of the link. Though the reference clocks for two devices on a XAUI link have the same specified frequencies, there can be slight differences that, if not compensated for, will lead to over or under run of the FIFO’s on the receive/transmit data path. The TLK10031 provides compensation for these differences in clock frequencies via the insertion or the removal of idle (/I/) characters on all lanes, as shown in Figure 7-4 and
Figure 7-5.
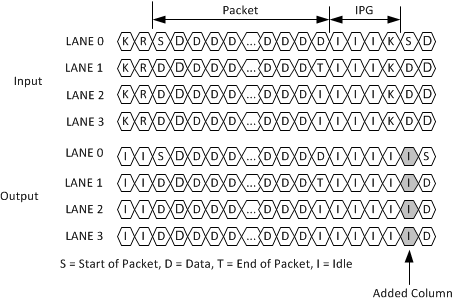 Figure 7-4 Clock Tolerance Compensation: Add
Figure 7-4 Clock Tolerance Compensation: Add
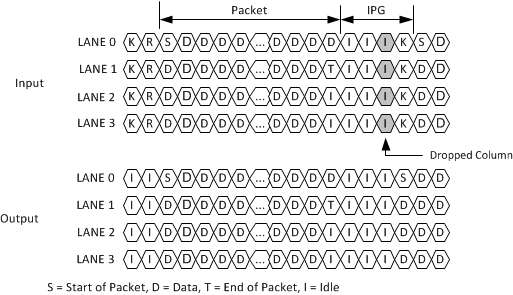 Figure 7-5 Clock Tolerance Compensation: Drop
Figure 7-5 Clock Tolerance Compensation: Drop
The TLK10031 allows for provisioning of both the CTC FIFO depth and the low/high watermark thresholds that trigger idle insertion/deletion beyond the standard requirements. This allows for optimization between maximum clock tolerance and packet length. For more information on the TLK10031 CTC provisioning, see Section 7.4.20.
7.3.14 10GBASE-KR Auto-Negotiation
When TLK10031 is selected to operate in 10GKR/1G-KX mode (MODE_SEL pin held low), Clause 73 Auto-Negotiation will commence after power up or hardware or software reset. The data path chosen from the result of Auto-Negotiation will be the highest speed of 10G-KR or 1G-KX as advertised in the MDIO ability fields (set to 10G-KR by default). If 10G-KR is chosen, link training will commence immediately following the completion of Auto-Negotiation. Legacy devices that operate in 1G-KX mode and do not support Clause 73 Auto Negotiation will be recognized through the Clause 73 parallel detection mechanism.
7.3.15 10GBASE-KR Link Training
Link training for 10G-KR mode is performed after auto-negotiation, and follows the procedure described in IEEE 802.3-2008. The high speed TX SERDES side will update pre-emphasis tap coefficients as requested through the Coefficient update field. Received training patterns are monitored for bit errors (MDIO configurable), and requests are made to update partner channel TX coefficients until optimal settings are achieved.
The RX link training algorithm consists of sending a series of requests to move the link partner’s transmitter tap coefficients to the center point of an error free region. Once link training has completed, the 10G-KR data path is enabled. If link is lost, the entire process repeats with auto-negotiation, link training, and 10G-KR mode.
TLK10031 also offers a manual mode whereby coefficient update requests are handled through external software management.
7.3.16 10GBASE-KR Line Rate, PLL Settings, and Reference Clock Selection
The TLK10031 includes internal low-jitter high quality oscillators that are used as frequency multipliers for the low speed and high speed SERDES and other internal circuits of the device. Specific MDIO registers are available for SERDES rate and PLL multiplier selection to match line rates and reference clock (REFCLK0/1) frequencies for various applications.
The external differential reference clock has a large operating frequency range allowing support for many different applications. A low-jitter reference clock should be used, and its frequency accuracy should be within ±200 PPM of the incoming serial data rate (±100 PPM of nominal data rate).
When the TLK10031 device is set to operate in the 10GBASE-KR mode with a low speed side line rate of 3.125 Gbps and a high speed side line rate of 10.3125 Gbps, the reference clock choices are as shown in Table 7-1. In general, using a higher reference clock frequency results in improved jitter performance.
Table 7-1 Specific Line Rate and Reference Clock Selection for the 10GBASE-KR Mode:
| LOW SPEED SIDE | HIGH SPEED SIDE | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Line Rate (Mbps) | SERDES PLL Multiplier | Rate | REFCLKP/N (MHz) | Line Rate (Mbps) | SERDES PLL Multiplier | Rate | REFCLKP/N (MHz) | |
| 3125 | 10 | Full | 156.25 | 10312.5 | 16.5 | Full | 156.25 | |
| 3125 | 5 | Full | 312.5 | 10312.5 | 8.25 | Full | 312.5 | |
7.3.17 10GBASE-KR Test Pattern Support
The TLK10031 has the capability to generate and verify various test patterns for self-test and system diagnostic measurements. The following test patterns are supported:
- High Speed (HS) Side: PRBS 27 – 1, PRBS 223 – 1, PRBS 231 – 1, Square Wave with Provisionable Length, and KR Pseudo-Random Pattern
- Low Speed (LS) Side: PRBS 27 – 1, PRBS 223 – 1, PRBS 231 – 1, High Frequency, Low Frequency, Mixed Frequency, CRPAT, CJPAT.
The TLK10031 provides two pins: PRBSEN and PRBS_PASS, for additional control and monitoring of PRBS pattern generation and verification. When PRBSEN is asserted high, the internal PRBS generator and verifier circuits are enabled on both transmit and receive data paths on high speed and low speed sides. PRBS 27-1 is selected by default, and can be changed through MDIO.
When PRBS test is enabled (PRBSEN=1):
- PRBS_PASS = 1 indicates that PRBS pattern reception is error free.
- PRBS_PASS = 0 indicates that a PRBS error is detected. The side (high speed or low speed), and the lane (for low speed side) that this signal refers to is chosen through MDIO.
7.3.18 10GBASE-KR Latency
The latency through the TLK10031 in 10GBASE-KR mode is as shown in Figure 7-6. Note that the latency ranges shown indicate static rather than dynamic latency variance, i.e., the range of possible latencies when the serial link is initially established. During normal operation, the latency through the device is fixed.
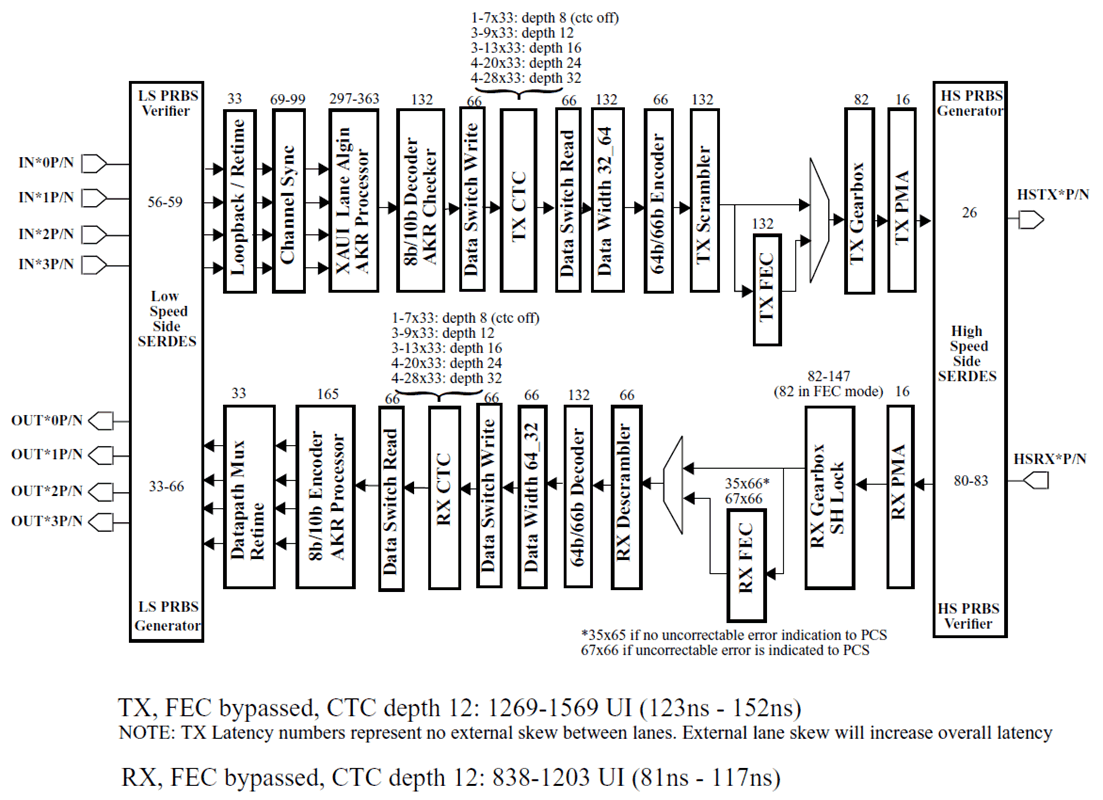 Figure 7-6 10GBASE-KR Mode Latency Per Block
Figure 7-6 10GBASE-KR Mode Latency Per Block
7.4 Device Functional Modes
The TLK10031 is a versatile high-speed transceiver device that is designed to perform various physical layer functions in three operating modes: 10GBASE-KR Mode, 1G-KX Mode, and General Purpose (10G) SERDES Mode. The three modes are described in three separate sections. The device operating mode is determined by the MODE_SEL and ST pin settings, as well as MDIO register 1E.0001 bit 10.
7.4.1 10GBASE-KR Mode
A simplified block diagram of the transmit and receive data paths in 10GBASE-KR mode is shown in Figure 7-7. This section gives a high-level overview of how data moves through these paths, then gives a more detailed description of each block’s functionality.
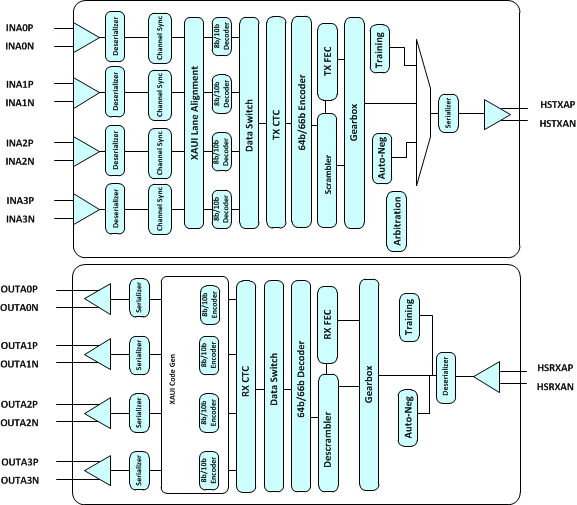 Figure 7-7 A Simplified KR Data Path Block Diagram
Figure 7-7 A Simplified KR Data Path Block Diagram
Table 7-2 TLK10031 Operating Mode Selection
| ST = 0 (Clause 45) | ST = 1 (Clause 22) | |
|---|---|---|
| {MODE_SEL pin, Register 1E.0001 bit 10} | ||
| 1x | 10G | 10G |
| 01 | 10G | 10G |
| 00 | 10G-KR/1G-KX (Determined by Auto Neg) |
1G-KX (No Auto Neg) |
7.4.2 1GBASE-KX Mode
A simplified block diagram of the 1GBASE-KX data path is shown in Figure 7-8.
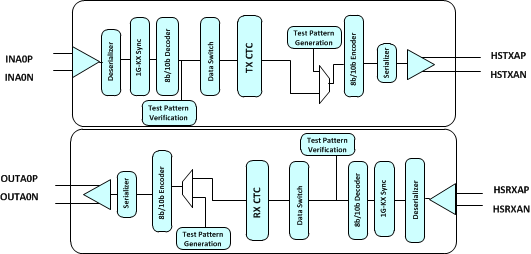 Figure 7-8 A Simplified Block Diagram of the 1GKX Data Path
Figure 7-8 A Simplified Block Diagram of the 1GKX Data Path
7.4.2.1 Channel Sync Block
This block is used to align the deserialized signals to the proper 10-bit word boundaries. The Channel Sync block generates a synchronization flag indicating incoming data is synchronized to the correct word boundary. This module implements the synchronization state machine found in Figure 36-9 of the IEEE 802.3-2008 Standard. A synchronization status signal, latched low, is available to indicate synchronization errors.
7.4.2.2 8b/10b Encoder and Decoder Blocks
As in the 10GBASE-KR operating mode, these blocks are used to convert between 10-bit (encoded) data and 8-bit data words. They can be optionally bypassed. A code invalid signal, latched low, is available to indicate 8b/10b encode and decode errors.
7.4.2.3 TX CTC
The transmit clock tolerance compensation (CTC) block acts as a FIFO with add and delete capabilities, adding and deleting 2 cycles each time to support ±200ppm during IFG (no errors) between the read and write clocks. This block implements a 12 deep asynchronous FIFO with a usable space 8 deep. It has two separate pointer tracking systems. One determines when to delete or insert and another determines when to reset. Inserts and deletes are only allowed during non-errored inter-frame gaps and occurs 2 cycles at a time. It has an auto reset feature once collision occurs. If a collision occurs, the indication is latched high until read by MDIO.
7.4.2.4 1GBASE-KX Line Rate, PLL Settings, and Reference Clock Selection
When the TLK10031 is configured to operate in the 1GBASE-KX mode, the available line rates, reference clock frequencies, and corresponding PLL multipliers are summarized in Table 7-3.
Table 7-3 Specific Line Rate and Reference Clock Selection for the 1GBASE-KX Mode
| LOW SPEED SIDE | HIGH SPEED SIDE | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Line Rate (Mbps) |
SERDES PLL Multiplier |
Rate | REFCLKP/N (MHz) |
Line Rate (Mbps(1)) |
SERDES PLL Multiplier |
Rate | REFCLKP/N (MHz) |
|
| 3125(2) | 10 | Full | 156.25 | 3125(2) | 10 | Full | 156.25 | |
| 3125(2) | 5 | Full | 312.5 | 3125(2) | 5 | Full | 312.5 | |
| 1250 | 10 | Half | 125(2) | 1250 | 20 | Quarter | 125(2) | |
| 1250 | 8 | Half | 156.25 | 1250 | 16 | Quarter | 156.25 | |
| 1250 | 8 | Quarter | 312.5 | 1250 | 8 | Quarter | 312.5 | |
7.4.2.5 1GBASE-KX Mode Latency
The latency through the TLK10031 in 1G-KX mode is as shown in Figure 7-9. Note that the latency ranges shown indicate static rather than dynamic latency variance, i.e., the range of possible latencies when the serial link is initially established. During normal operation, the latency through the device is fixed.
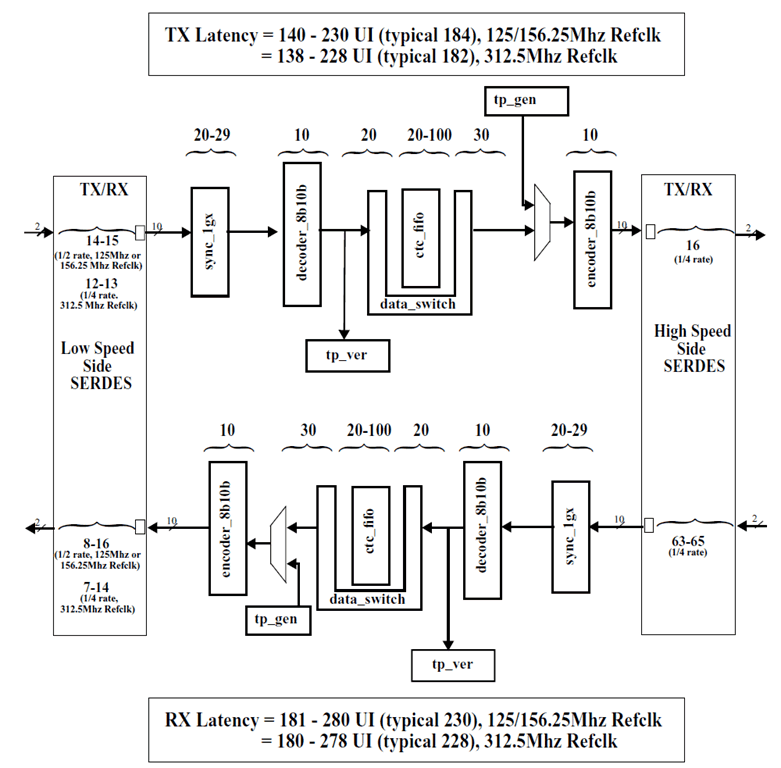 Figure 7-9 1G-KX Mode Latency
Figure 7-9 1G-KX Mode Latency
7.4.2.5.1 Test Pattern Generator
In 1G-KX mode, this block can be used to generate test patterns allowing the 1G-KX channel to be tested for compliance while in a system environment or for diagnostic purposes. Test patterns generated are high/low/mixed frequency and CRPAT long or short.
7.4.2.5.2 Test Pattern Verifier
The 1G-KX test pattern verifier performs the verification and error reporting for the CRPAT Long and Short test patterns specified in Annex 36A of the IEEE 802.3-2008 standard. Errors are reported to MDIO registers.
7.4.3 General Purpose (10G) Serdes Mode Functional Description
A block diagram showing the transmit and receive data paths of the TLK10031 operating in General Purpose (10G) SerDes mode is shown in Figure 7-10.
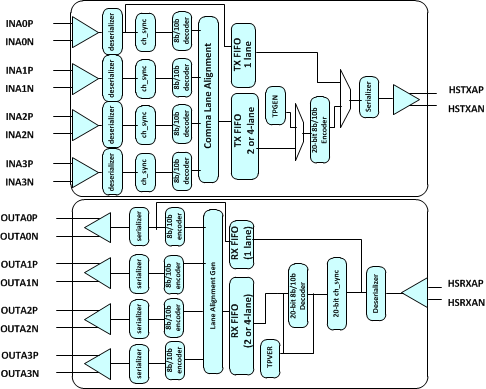 Figure 7-10 Block Diagram Showing General Purpose SerDes Mode
Figure 7-10 Block Diagram Showing General Purpose SerDes Mode
7.4.3.1 General Purpose SERDES Transmit Data Path
The TLK10031 General Purpose SERDES low speed to high speed (transmit) data path with the device configured to operate in the normal transceiver (mission) mode is shown in the upper half of Figure 7-10. In this mode, 8B/10B encoded serial data (INA*P/N) in 2 or 4 lanes is received by the low speed side SERDES and deserialized into 10-bit parallel data for each lane. The data in each individual lane is then byte aligned (channel synchronized) and then 8B/10B decoded into 8-bit parallel data for each lane. The lane data is then lane aligned by the Lane Alignment Slave. 32 bits of lane aligned parallel data is input to a transmit FIFO which delivers it to an 8B/10B encoder, 16 data bits at a time. The resulting 20-bit 8B/10B encoded parallel data is sent to the high speed side SERDES for serialization and output through the HSTXAP*P/N pins.
7.4.4 General Purpose SERDES Receive Data Path
With the device configured to operate in the normal transceiver (mission) mode, the high speed to low speed (receive) data path is shown in the lower half of Figure 7-10. 8B/10B encoded serial data (HSRXAP*P/N) is received by the high speed side SERDES and deserialized into 20-bit parallel data. The data is then byte aligned, 8B/10B decoded into 16-bit parallel data, and then delivered to a receive FIFO. The receive FIFO in turn delivers 32-bit parallel data to the Lane Alignment Master which splits the data into the same number of lanes as configured on the transmit data path. The lane data is then 8B/10B encoded and the resulting 10-bit parallel data for each lane is input to the low speed side SERDES for serialization and output through the OUTAP*P/N pins.
7.4.5 Channel Synchronization
As in the 10GBASE-KR mode, the channel synchronization block is used in the 10G General Purpose SERDES mode to align received serial data to a defined byte boundary. The channel synchronization block detects the comma pattern found in the K28.5 character, and follows the synchronization flowchart shown in Figure 7-3.
7.4.6 8B/10B Encoder and Decoder
As in the 10GBASE-KR and 1GBASE-KX modes, the 8B/10B encoder and decoder blocks are used to convert between 10-bit (encoded) and 8-bit (unencoded) data words.
7.4.7 Lane Alignment Scheme for 8b/10b General Purpose Serdes Mode
Lower rate multi-lane serial signals must be byte aligned and lane aligned such that high speed multiplexing (proper reconstruction of higher rate signal) is possible. For that reason, the TLK10031 implements a special lane alignment scheme on the low speed (LS) side for 8b/10b data that does not contain XAUI alignment characters.
During lane alignment, a proprietary pattern (or a custom comma compliant data stream) is sent by the LS transmitter to the LS receiver on each active lane. This pattern allows the LS receiver to both delineate byte boundaries within a lower speed lane and align bytes across the lanes (2 or 4) such that the original higher rate data ordering is restored.
Lane alignment completes successfully when the LS receiver asserts a “Link Status OK” signal monitored by the LS transmitter on the link partner device such as an FPGA. The TLK10031 sends out the “Link Status OK” signals through the LS_OK_OUT_A output pins, and monitors the “Link Status OK” signals from the link partner device through the LS_OK_IN_A input pins. If the link partner device does not need the TLK10031 Lane Alignment Master (LAM) to send proprietary lane alignment pattern, LS_OK_IN_A can be tied high on the application board or set through MDIO register bits.
The lane alignment scheme is activated under any of the following conditions:
- Device/System power up (after configuration/provisioning)
- Loss of channel synchronization assertion on any enabled LS lane
- Loss of signal assertion on any enabled LS lane
- LS SERDES PLL Lock indication deassertion
- After device configuration change
- After software determined LS 8B/10B decoder error rate threshold exceeded
- After device reset is deasserted
- Any time the LS receiver deasserts “Link Status OK”.
- Presence of reoccurring higher level / protocol framing errors
All the above conditions are selectable through MDIO register provisioning.
The block diagram of the lane alignment scheme is shown in Figure 7-11.
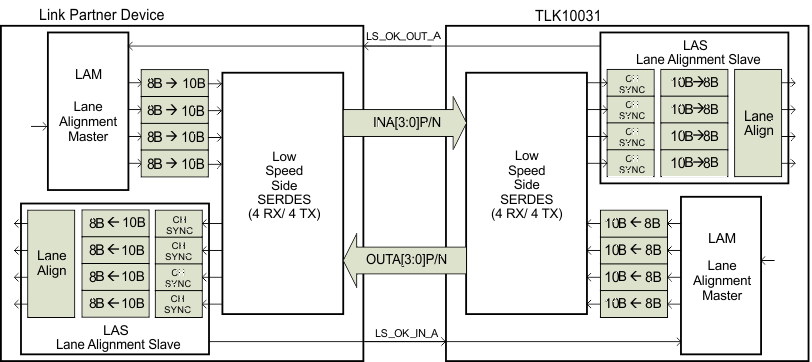 Figure 7-11 Block Diagram of the Lane Alignment Scheme
Figure 7-11 Block Diagram of the Lane Alignment Scheme
7.4.8 Lane Alignment Components
- Lane Alignment Master (LAM)
- Responsible for generating proprietary LS lane alignment initialization pattern
- Resides in the TLK10031 receive path
- Responsible for bringing up LS receive link for the data sent from the TLK10031 to a link partner device
- Monitors the LS_OK_IN_A pins for “Link Status OK” signals sent from the Lane Alignment Slave (LAS) of the link partner device
- Resides in the link partner device
- Responsible for bringing up LS transmit link for the data sent from the link partner device to the TLK10031
- Monitors the “Link Status OK” signals sent from the LS_OK_OUT_A pins of the Lane Alignment Slave (LAS) of the TLK10031
- Lane Alignment Slave (LAS)
- Responsible for monitoring the LS lane alignment initialization pattern
- Performs channel synchronization per lane (2 or 4 lanes) through byte rotation
- Performs lane alignment and realignment of bytes across lanes
- Resides in the TLK10031 transmit path
- Generates the “Link Status OK” signal for the LAM on the link partner device
- Resides in the link partner device
- Generates the “Link Status OK” signal for the LAM on the TLK10031 device.
Reference code from Texas Instruments is available for the LAM and LAS modules for easy integration into FPGAs.
7.4.9 Lane Alignment Operation
During lane alignment, the LAM sends a repeating pattern of 49 characters (control + data) simultaneously across all enabled LS lanes. These simultaneous streams are then encoded by 8B/10B encoders in parallel. The proprietary lane alignment pattern consists of the following characters:
/K28.5/ (CTL=1, Data=0xBC)
Repeat the following sequence of 12 characters four times:
/D30.5/ (CTL=0, Data=0xBE)
/D23.6/ (CTL=0, Data=0xD7)
/D3.1/ (CTL=0, Data=0x23)
/D7.2/ (CTL=0, Data=0x47)
/D11.3/ (CTL=0, Data=0x6B)
/D15.4/ (CTL=0, Data=0x8F)
/D19.5/ (CTL=0, Data=0xB3)
/D20.0/ (CTL=0, Data=0x14)
/D30.2/ (CTL=0, Data=0x5E)
/D27.7/ (CTL=0, Data=0xFB)
/D21.1/ (CTL=0, Data=0x35)
/D25.2/ (CTL=0, Data=0x59)
The above 49-character sequence is repeated until LS_OK_IN_A is asserted. Once LS_OK_IN_A is asserted, the LAM resumes transmitting traffic received from the high speed side SERDES immediately.
The TLK10031 performs lane alignment across the lanes similar in fashion to the IEEE 802.3-2008 (XAUI) specification. XAUI only operates across 4 lanes while LAS operates with 2 or 4 lanes. The lane alignment state machine is shown in Figure 7-12. The TLK10031 uses the comma (K28.5) character for lane to lane alignment by default, but can be provisioned to use XAUI's /A/ character as well.
Lane alignment checking is not performed by the LAS after lane alignment is achieved. After LAM detects that the LS_OK_IN_A signal is asserted, normal system traffic is carried instead of the proprietary lane alignment pattern.
Channel synchronization is performed during lane alignment and normal system operation.
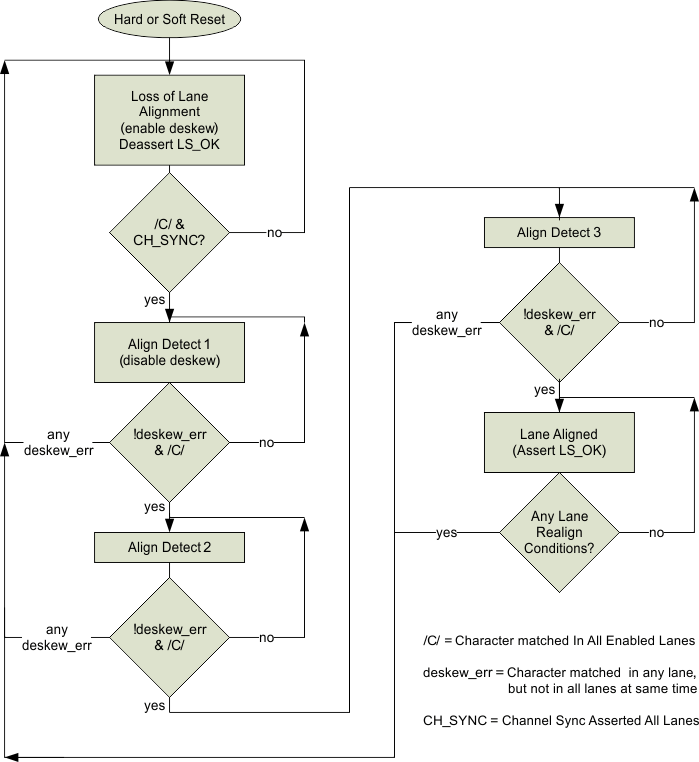 Figure 7-12 Lane Alignment State Machine
Figure 7-12 Lane Alignment State Machine
7.4.10 Line Rate, SERDES PLL Settings, and Reference Clock Selection for the General Purpose SERDES Mode
When the TLK10031 is set to operate in the General Purpose SERDES mode, the following tables show a summary of line rates and reference clock frequencies used for CPRI/OBSAI for 1:1, 2:1 and 4:1 operation modes.
Table 7-4 Specific Line Rate Selection for the 1:1 General Purpose Operation Mode
| LOW SPEED SIDE | HIGH SPEED SIDE | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Line Rate (Mbps) |
SERDES PLL Multiplier |
Rate | REFCLKP/N (MHz) |
Line Rate (Mbps) |
SERDES PLL Multiplier |
Rate | REFCLKP/N (MHz) |
|
| 4915.2 | 20 | Full | 122.88 | 4915.2 | 20 | Half | 122.88 | |
| 3840 | 12.5 | Full | 153.6 | 3840 | 12.5 | Half | 153.6 | |
| 3125 | 10 | Full | 156.25 | 3125 | 10 | Half | 156.25 | |
| 3125 | 5 | Full | 312.5 | 3125 | 5 | Half | 312.5 | |
| 3072 | 10 | Full | 153.6 | 3072 | 10 | Half | 153.6 | |
| 2457.6 | 8/10 | Full | 153.6/122.88 | 2457.6 | 16/20 | Quarter | 153.6/122.88 | |
| 1920 | 12.5 | Half | 153.6 | 1920 | 12.5 | Quarter | 153.6 | |
| 1536 | 10 | Half | 153.6 | 1536 | 10 | Quarter | 153.6 | |
| 1228.8 | 8/10 | Half | 153.6/122.88 | 1228.8 | 16/20 | Eighth | 153.6/122.88 | |
Table 7-5 Specific Line Rate and Reference Clock Selection for the 2:1 General Purpose Operation Mode
| LOW SPEED SIDE | HIGH SPEED SIDE | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Line Rate (Mbps) |
SERDES PLL Multiplier |
Rate | REFCLKP/N (MHz) |
Line Rate (Mbps) |
SERDES PLL Multiplier |
Rate | REFCLKP/N (MHz) |
|
| 4915.2 | 20 | Full | 122.88 | 9830.4 | 20 | Full | 122.88 | |
| 3840 | 12.5 | Full | 153.6 | 7680 | 12.5 | Full | 153.6 | |
| 3072 | 10 | Full | 153.6 | 6144 | 10 | Full | 153.6 | |
| 2457.6 | 8/10 | Full | 153.6/122.88 | 4915.2 | 16/20 | Half | 153.6/122.88 | |
| 1920 | 12.5 | Half | 153.6 | 3840 | 12.5 | Half | 153.6 | |
| 1536 | 10 | Half | 153.6 | 3072 | 10 | Half | 153.6 | |
| 1228.8 | 8/10 | Half | 153.6/122.88 | 2457.6 | 16/20 | Quarter | 153.6/122.88 | |
| 768 | 10 | Quarter | 153.6 | 1536 | 10 | Quarter | 153.6 | |
| 614.4 | 8/10 | Quarter | 153.6/122.88 | 1228.8 | 16/20 | Eighth | 153.6/122.88 | |
Table 7-6 Specific Line Rate and Reference Clock Selection for the 4:1 General Purpose Operation Mode
| LOW SPEED SIDE | HIGH SPEED SIDE | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Line Rate (Mbps) |
SERDES PLL Multiplier |
Rate | REFCLKP/N (MHz) |
Line Rate (Mbps) |
SERDES PLL Multiplier |
Rate | REFCLKP/N (MHz) |
|
| 2457.6 | 8/10 | Full | 153.6/122.88 | 9830.4 | 16/20 | Full | 153.6/122.88 | |
| 1536 | 10 | Half | 153.6 | 6144 | 10 | Full | 153.6 | |
| 1228.8 | 8/10 | Half | 153.6/122.88 | 4915.2 | 16/20 | Half | 153.6/122.88 | |
| 768 | 10 | Quarter | 153.6 | 3072 | 10 | Half | 153.6 | |
| 614.4 | 8/10 | Quarter | 153.6/122.88 | 2457.6 | 16/20 | Quarter | 153.6/122.88 | |
Table 7-4, Table 7-5, and Table 7-6 indicate two possible reference clock frequencies for CPRI/OBSAI applications: 153.6MHz and 122.88MHz, which can be used based on the application preference. The SERDES PLL Multiplier (MPY) has been given for each reference clock frequency respectively. The low speed side and the high speed side SERDES use the same reference clock frequency.
For other line rates not shown in Table 7-4, Table 7-5, or Table 7-6, valid reference clock frequencies can be selected with the help of the information provided in Table 7-7 and Table 7-8 for the low speed and high speed side SERDES. The reference clock frequency has to be the same for the two SERDES and must be within the specified valid ranges for different PLL multipliers.
Table 7-7 Line Rate and Reference Clock Frequency Ranges for the Low Speed Side SERDES (General Purpose Mode)
| SERDES PLL Multiplier (MPY) |
Reference Clock (MHz) | Full Rate (Gbps) | Half Rate (Gbps) | Quarter Rate (Gbps) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | Max | Min | Max | Min | Max | Min | Max | |
| 4 | 250 | 425 | 2 | 3.4 | 1 | 1.7 | 0.5 | 0.85 |
| 5 | 200 | 425 | 2 | 4.25 | 1 | 2.125 | 0.5 | 1.0625 |
| 6 | 166.667 | 416.667 | 2 | 5 | 1 | 2.5 | 0.5 | 1.25 |
| 8 | 125 | 312.5 | 2 | 5 | 1 | 2.5 | 0.5 | 1.25 |
| 10 | 122.88 | 250 | 2.4576 | 5 | 1.2288 | 2.5 | 0.6144 | 1.25 |
| 12 | 122.88 | 208.333 | 2.94912 | 5 | 1.47456 | 2.5 | 0.73728 | 1.25 |
| 12.5 | 122.88 | 200 | 3.072 | 5 | 1.536 | 2.5 | 0.768 | 1.25 |
| 15 | 122.88 | 166.667 | 3.6864 | 5 | 1.8432 | 2.5 | 0.9216 | 1.25 |
| 20 | 122.88 | 125 | 4.9152 | 5 | 2.4576 | 2.5 | 1.2288 | 1.25 |
| RateScale: Full Rate = 0.5, Half Rate = 1, Quarter Rate = 2 | ||||||||
Table 7-8 Line Rate and Reference Clock Frequency Ranges for the High Speed Side SERDES (General Purpose Mode)
| SERDES PLL Multiplier (MPY) |
Reference Clock (MHz) | Full Rate (Gbps) | Half Rate (Gbps) | Quarter Rate (Gbps) | Eighth Rate (Gbps) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | Max | Min | Max | Min | Max | Min | Max | Min | Max | |
| 4 | 375 | 425 | 6 | 6.8 | 3 | 3.4 | 1.5 | 1.7 | ||
| 5 | 300 | 425 | 6 | 8.5 | 3 | 4.25 | 1.5 | 2.125 | 1.0 | 1.0625 |
| 6 | 250 | 416.667 | 6 | 10 | 3 | 5 | 1.5 | 2.5 | 1.0 | 1.25 |
| 8 | 187.5 | 312.5 | 6 | 10 | 3 | 5 | 1.5 | 2.5 | 1.0 | 1.25 |
| 10 | 150 | 250 | 6 | 10 | 3 | 5 | 1.5 | 2.5 | 1.0 | 1.25 |
| 12 | 125 | 208.333 | 6 | 10 | 3 | 5 | 1.5 | 2.5 | 1.0 | 1.25 |
| 12.5 | 153.6 | 200 | 7.68 | 10 | 3.84 | 5 | 1.92 | 2.5 | 1.0 | 1.25 |
| 15 | 122.88 | 166.667 | 7.3728 | 10 | 3.6864 | 5 | 1.8432 | 2.5 | 1.0 | 1.25 |
| 16 | 122.88 | 156.25 | 7.86432 | 10 | 3.932 | 5 | 1.966 | 2.5 | 1.0 | 1.25 |
| 20 | 122.88 | 125 | 9.8304 | 10 | 4.9152 | 5 | 2.4576 | 2.5 | 1.2288 | 1.25 |
| RateScale: Full Rate = 0.25, Half Rate = 0.5, Quarter Rate = 1, Eighth Rate = 2 | ||||||||||
For example, in the 2:1 operation mode, if the low speed side line rate is 1.987Gbps, the high-speed side line rate will be 3.974Gbps. The following steps can be taken to make a reference clock frequency selection:
- Determine the appropriate SERDES rate modes that support the required line rates. Table 7-7 shows that the 1.987Gbps line rate on the low speed side is only supported in the half rate mode (RateScale = 1). Table 7-8 shows that the 3.974Gbps line rate on the high speed side is only supported in the half rate mode (RateScale = 1).
- For each SERDES side, and for all available PLL multipliers (MPY), compute the corresponding reference clock frequencies using the formula:
- Mark all the common frequencies that appear on both SERDES sides. Note and discard all those that fall outside the allowed range. In this example, the common frequencies are highlighted in Table 7-9. The highest and lowest computed reference clock frequencies must be discarded because they exceed the recommended range.
- Select any of the remaining marked common reference clock frequencies. Higher reference clock frequencies are generally preferred. In this example, any of the following reference clock frequencies can be selected: 397.4MHz, 331.167MHz, 248.375MHz, 198.7MHz, 165.583MHz, 158.96MHz, and 132.467MHz
Reference Clock Frequency = (LineRate x RateScale)/MPY
The computed reference clock frequencies are shown in Table 7-9 along with the valid minimum and maximum frequency values.
Table 7-9 Reference Clock Frequency Selection Example
| LOW SPEED SIDE SERDES | HIGH SPEED SIDE SERDES | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SERDES PLL MULTIPLIER |
REFERENCE CLOCK FREQUENCY (MHz) | SERDES PLL MULTIPLIER |
REFERENCE CLOCK FREQUENCY (MHz) | |||||
| COMPUTED | MIN | MAX | COMPUTED | MIN | MAX | |||
| 4 | 496.750 | 250 | 425 | 4 | 496.750 | 375 | 425 | |
| 5 | 397.400 | 200 | 425 | 5 | 397.400 | 300 | 425 | |
| 6 | 331.167 | 166.667 | 416.667 | 6 | 331.167 | 250 | 416.667 | |
| 8 | 248.375 | 125 | 312.5 | 8 | 248.375 | 187.5 | 312.5 | |
| 10 | 198.700 | 122.88 | 250 | 10 | 198.700 | 150 | 250 | |
| 12 | 165.583 | 122.88 | 208.333 | 12 | 165.583 | 125 | 208.333 | |
| 12.5 | 158.960 | 122.88 | 200 | 12.5 | 158.960 | 153.6 | 200 | |
| 15 | 132.467 | 122.88 | 166.667 | 15 | 132.467 | 122.88 | 166.667 | |
| 20 | 99.350 | 122.88 | 125 | 20 | 99.350 | 122.88 | 125 | |
7.4.11 General Purpose SERDES Mode Test Pattern Support
The TLK10031 has the capability to generate and verify various test patterns for self-test and system diagnostic measurements. Most of the same test pattern support is available for 10G General Purpose Mode as for 10G-KR. (See Register 1E.000B for details).
7.4.12 General Purpose SERDES Mode Latency
The latency through the TLK10031 in General Purpose SERDES mode is as shown in Figure 7-13. Note that the latency ranges shown indicate static rather than dynamic latency variance, i.e., the range of possible latencies when the serial link is initially established. During normal operation, the latency through the device is fixed.
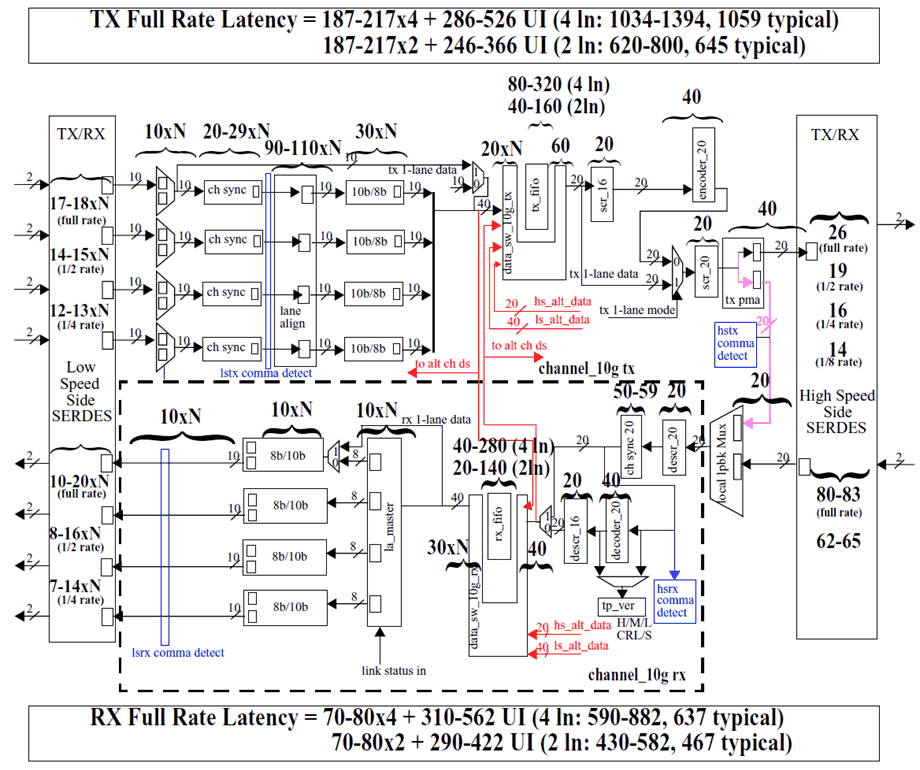 Figure 7-13 General Purpose SERDES Mode Latency
Figure 7-13 General Purpose SERDES Mode Latency
7.4.12.1 Clocking Architecture (All Modes)
A simplified clocking architecture for the TLK10031 is captured in Figure 7-14. The device has an option of operating with a differential reference clock provided either on pins REFCLK0P/N or REFCLK1P/N. The choice is made either through MDIO or through REFCLK_SEL pins. The low speed side SERDES, high speed side SERDES and the associated part of the digital core can operate from the same or different reference clock.
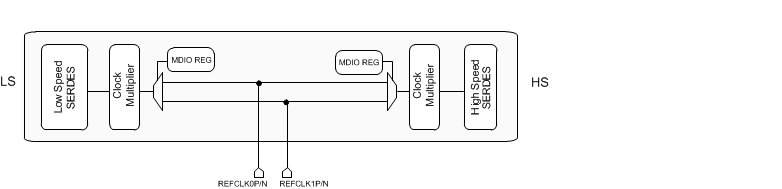 Figure 7-14 Reference Clock Architecture
Figure 7-14 Reference Clock Architecture
The TLK10031 has one output port - CLKOUTAP/N. This output port can be configured to output the byte clock from either the low speed or high speed serdes. The output clock can also be chosen to be synchronous with the transmit clock rate. Various divider values can be chosen using the MDIO interface. The maximum CLKOUT frequency is 500 MHz.
7.4.12.2 Integrated Smart Switch
The TLK10031 allows for adjustable routing of data within the device. Each output port may be configured to output data corresponding to any input port.
Figure 7-15 illustrates the different possible data path routings.
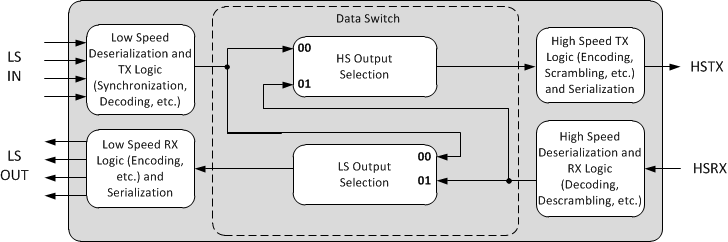 Figure 7-15 Signal Routings for Integrated Smart Switch
Figure 7-15 Signal Routings for Integrated Smart Switch
7.4.13 Intelligent Switching Modes
The TLK10031 supports various switching modes that allow for the user to choose when changes in data routing take effect. There are three options:
- Wait for the end of the current packet, insert IDLEs, then switch to the new input source at the start of its next packet. This option allows the current packet to complete so that data is not lost.
- Drop current packet and insert a programmable character (such as Local Fault), then switch to the new input source at the start of its next packet. This can provide a more immediate switch-over at the expense of the current packet’s data.
- Immediately switch lanes without packet monitoring.
7.4.14 Serial Loopback Modes
The TLK10031 supports internal loopback of the serial output signals for self-test and system diagnostic purposes. Loopback mode can be enabled independently for each SERDES via MDIO register bits. When loopback mode is enabled for a particular SERDES, the serial output data will be internally routed to the SERDES’s serial input port. The output data will remain available for monitoring on the output pins.
7.4.15 Latency Measurement Function (General Purpose SerDes Mode)
The TLK10031 includes a latency measurement function to support CPRI and OBSAI type applications. There are two start and two stop locations for the latency counter as shown in Figure 7-16. The start and stop locations are selectable through MDIO register bits. The elapsed time from a comma detected at an assigned counter start location to a comma detected at an assigned counter stop location is measured and reported through the MDIO interface. The following three control characters (containing commas) are monitored:
- K28.1 (control = 1, data = 0x3C)
- K28.5 (control = 1, data = 0xBC)
- K28.7 (control = 1, data = 0xFC).
The first comma found at the assigned counter start location will start up the latency counter. The first comma detected at the assigned counter stop location will stop the latency counter. The 20-bit latency counter result of this measurement is readable through the MDIO interface. The accuracy of the measurement is a function of the serial bit rate. The register will return a value of 0xFFFFF if the duration between transmit and receive comma detection exceeds the depth of the counter. Only one measurement value is stored internally until the 20-bit results counter is read. The counter will return zero in cases where a transmit comma was never detected (indicating the results counter never began counting). In addition, the stopwatch counter can be configured to be started or stopped manually based on the state of the PRTAD0 pin (see MDIO register map for details).
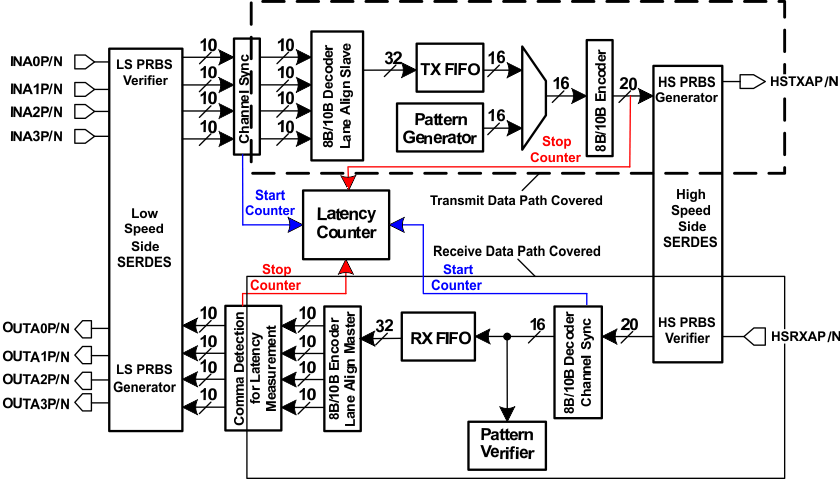 Figure 7-16 Location of TX and RX Comma Character Detection
Figure 7-16 Location of TX and RX Comma Character Detection
In high speed side SERDES full rate mode, the latency measurement function runs off of an internal clock which is equal to the frequency of the transmit serial bit rate divided by 8. In half rate mode, the latency measurement function runs off of an internal clock which is equal to the serial bit rate divided by 4. In quarter rate mode, the latency measurement function runs off of an internal clock which is equal to the serial bit rate divided by 2. In eighth rate mode, the latency measurement function runs off of a clock which is equal to the serial bit rate.
The latency measurement does not include the low speed side transmit SERDES contribution as well as part of the channel synchronization block. The latency introduced by those two is up to (18 + 10) x N high speed side unit intervals (UIs), where N = 2, 4 is the multiplex factor. The latency measurement also doesn’t account for the low speed side receive SERDES contribution which is estimated to be up to 20 x N high speed side UIs.
The latency measurement accuracy in all cases is equal to plus or minus one latency measurement clock period. The measurement clock can be divided down if a longer duration measurement is required, in which case the accuracy of the measurement is accordingly reduced. The high speed latency measurement clock is divided by either 1, 2, 4, or 8 via register settings. The high speed latency measurement clock may only be used when operating at one of the serial rates specified in the CPRI/OBSAI specifications. It is also possible to run the latency measurement function off of the recovered byte clock (giving a latency measurement clock frequency equal to the serial bit rate divided by 20).
The accuracy for the standard based CPRI/OBSAI application rates is shown in Table 7-10, and assumes the latency measurement clock is not divided down per user selection (division is required to measure a duration greater than 682 µs). For each division of 2 in the measurement clock, the accuracy is also reduced by a factor of two.
Table 7-10 CPRI/OBSAI Latency Measurement Function Accuracy (Undivided Measurement Clock)
| LINE RATE (Gbps) |
RATE | LATENCY CLOCK FREQUENCY (GHz) |
ACCURACY (± ns) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.2288 | Eighth | 1.2288 | 0.8138 |
| 1.536 | Quarter | 0.768 | 1.302 |
| 2.4576 | Quarter | 1.2288 | 0.8138 |
| 3.072 | Half | 0.768 | 1.302 |
| 3.84 | Half | 0.96 | 1.0417 |
| 4.9152 | Half | 1.2288 | 0.8138 |
| 6.144 | Full | 0.768 | 1.302 |
| 7.68 | Full | 0.96 | 1.0417 |
| 9.8304 | Full | 1.2288 | 0.8138 |
7.4.16 Power Down Mode
The TLK10031 can be put in power down either through device input pins or through MDIO control register 1E.0001.
- PDTRXA_N: Active low, power down
7.4.16.1 High Speed CML Output
The high speed data output driver is implemented using Current Mode Logic (CML) with integrated pull up resistors. The transmit outputs must be AC coupled.
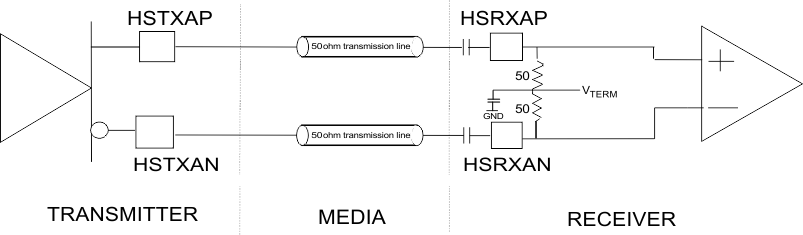 Figure 7-17 Example of High Speed I/O AC Coupled Mode
Figure 7-17 Example of High Speed I/O AC Coupled Mode
Current Mode Logic (CML) drivers often require external components. The disadvantage of the external component is a limited edge rate due to package and line parasitic. The CML driver on TLK10031 has on-chip 50 Ω termination resistors terminated to VDDT, providing optimum performance for increased speed requirements. The transmitter output driver is highly configurable allowing output amplitude and de-emphasis to be tuned to the channel's individual requirements. Software programmability allows for very flexible output amplitude control. Only AC coupled output mode is supported.
When transmitting data across long lengths of PCB trace or cable, the high frequency content of the signal is attenuated due to dielectric losses and the skin effect of the media. This causes a “smearing” of the data eye when viewed on an oscilloscope. The net result is reduced timing margins for the receiver and clock recovery circuits. In order to provide equalization for the high frequency loss, 4-tap finite impulse response (FIR) transmit de-emphasis is implemented Output swing control is via MDIO.
7.4.16.2 High Speed Receiver
The high speed receiver is differential CML with internal termination resistors. The receiver requires AC coupling. The termination impedances of the receivers are configured as 100 Ω with the center tap weakly tied to 0.7×VDDT, and a capacitor is used to create an AC ground (see Figure 7-17).
TLK10031 serial receivers incorporate adaptive equalizers. This circuit compensates for channel insertion loss by amplifying the high frequency components of the signal, reducing inter-symbol interference. Equalization can be enabled or disabled per register settings. Both feed-forward equalization (FFE) and decision feedback equalization (DFE) are used to minimize the pre-cursor and post-cursor components (respectively) of intersymbol interference.
7.4.16.3 Loss of Signal Output Generation (LOS)
Loss of input signal detection is based on the voltage level of each serial input signal INA*P/N, HSRXAP/N. When LOS indication is enabled and the channel's differential serial receive input level is < 75 mVpp, the channel's respective LOS indicator (LOSA) are asserted (high true). If the input signal is >150 mVpp, the LOS indicator will be deasserted (low false). Outside of these ranges, the LOS indicator is undefined. The LOS indicators can also directly be read through the MDIO interface.
The following additional critical status conditions can be combined with the loss of signal condition enabling additional real-time status signal visibility on the LOSA output:
- Loss of Channel Synchronization Status – Logically OR’d with LOS condition(s) when enabled. Loss of channel synchronization can be optionally logically OR’d (disabled by default) with the internally generated LOS condition.
- Loss of PLL Lock Status on LS and HS sides – Logically OR’d with LOS condition(s) when enabled. The internal PLL loss of lock status bit is optionally OR’d (disabled by default) with the other internally generated loss of signal conditions.
- Receive 8B/10B Decode Error (Invalid Code Word or Running Disparity Error) – Logically OR’d with LOS condition(s) when enabled. The occurrence of an 8B/10B decode error (invalid code word or disparity error) is optionally OR’d (disabled by default) with the other internally generated loss of signal conditions.
- AGCLOCK (Active Gain Control Currently Locked) – Inverted and Logically OR’d with LOS condition(s) when enabled. HS RX SERDES adaptive gain control unlocked indication is optionally OR’d (disabled by default) with the other internally generated loss of signal conditions.
- AZDONE (Auto Zero Calibration Done) - Inverted and Logically OR’d with LOS conditions(s) when enabled. HS RX SERDES auto-zero not done indication is optionally OR’d (disabled by default) with the other internally generated loss of signal conditions.
Refer to Figure 7-18, which shows the detailed implementation of the LOSA signal along with the associated MDIO control registers for the General Purpose SERDES mode. More details about LOS settings including configurations related to the 10GBASE-KR mode can be found in the Programmers Reference section.
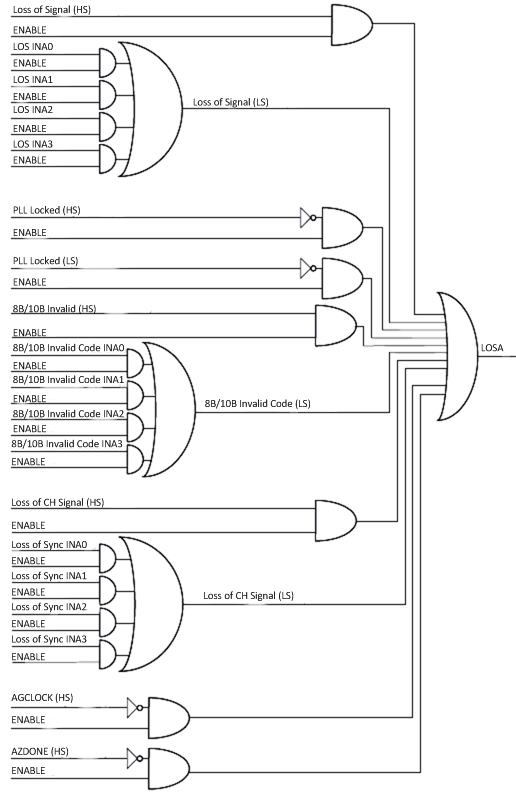 Figure 7-18 LOSA – Logic Circuit Implementation
Figure 7-18 LOSA – Logic Circuit Implementation
7.4.17 MDIO Management Interface
The TLK10031 supports the Management Data Input/Output (MDIO) Interface as defined in Clauses 22 and 45 of the IEEE 802.3-2008 Ethernet specification. The MDIO allows register-based management and control of the serial links.
The MDIO Management Interface consists of a bi-directional data path (MDIO) and a clock reference (MDC). The device identification and port address are determined by control pins (see Section 4). Also, whether the device responds as a Clause 22 or Clause 45 device is also determined by control pin ST (see Section 4).
In Clause 45 (ST = 0) and Clause 22 (ST = 1), the top 4 control pins PRTAD[4:1] determine the device port address. In this mode, TLK10031 responds if the PHY address field on the MDIO protocol (PA[4:1]) matches PRTAD[4:1] pin value, and the PHY address field PA[0] = 0.
In Clause 22 (ST = 1) mode, only 32 (5’b00000 to 5’b11111) register addresses can be accessed through standard protocol. Due to this limitation, an indirect addressing method (More description in Clause 22 Indirect Addressing section) is implemented to provide access to all device specific control/status registers that cannot be accessed through the standard Clause 22 register address space.
Write transactions which address an invalid register or device or a read only register will be ignored. Read transactions which address an invalid register or device will return a 0.
7.4.18 MDIO Protocol Timing
Timing for a Clause 45 address transaction is shown in Figure 7-19. The Clause 45 timing required to write to the internal registers is shown in Figure 7-20. The Clause 45 timing required to read from the internal registers is shown in Figure 7-21. The Clause 45 timing required to read from the internal registers and then increment the active address for the next transaction is shown in Figure 7-22. The Clause 22 timing required to read from the internal registers is shown in Figure 7-23. The Clause 22 timing required to write to the internal registers is shown in Figure 7-24.
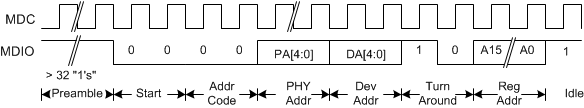 Figure 7-19 CL45 - Management Interface Extended Space Address Timing
Figure 7-19 CL45 - Management Interface Extended Space Address Timing
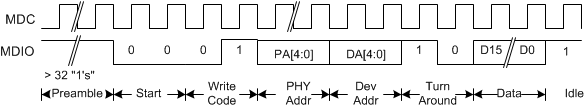 Figure 7-20 CL45 - Management Interface Extended Space Write Timing
Figure 7-20 CL45 - Management Interface Extended Space Write Timing
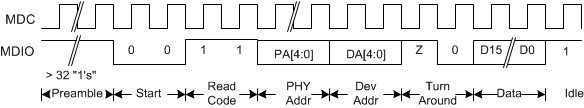 Figure 7-21 CL45 - Management Interface Extended Space Read Timing
Figure 7-21 CL45 - Management Interface Extended Space Read Timing
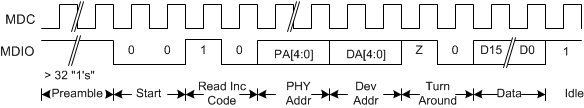 Figure 7-22 CL45 - Management Interface Extended Space Read And Increment Timing
Figure 7-22 CL45 - Management Interface Extended Space Read And Increment Timing
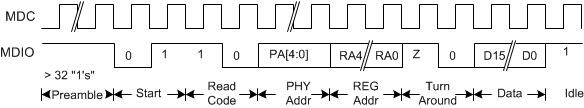 Figure 7-23 CL22 - Management Interface Read Timing
Figure 7-23 CL22 - Management Interface Read Timing
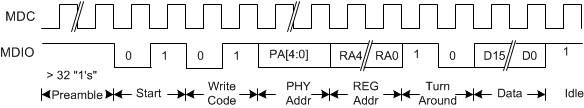 Figure 7-24 CL22 - Management Interface Write Timing
Figure 7-24 CL22 - Management Interface Write Timing
The IEEE 802.3 Clause 22/45 specification defines many of the registers, and additional registers have been implemented for expanded functionality.
7.4.19 Clause 22 Indirect Addressing
Due to Clause 22 register space limitations, an indirect addressing method is implemented so that the extended register space can be accessed through Clause 22. All the device specific control and status registers that cannot be accessed through Clause 22 direct addressing can be accessed through this indirect addressing method. To access this register space, an address control register (Reg 30, 5’h1E) should be written with the register address followed by a read/write transaction to address content register (Reg 31, 5’h1F) to access the contents of the address specified in address control register. Following timing diagrams illustrate an example write transaction to Register 16’h9000 using indirect addressing in Clause 22.
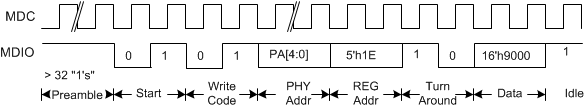 Figure 7-25 CL22 – Indirect Address Method – Address Write
Figure 7-25 CL22 – Indirect Address Method – Address Write
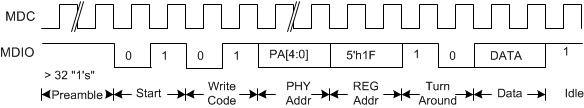 Figure 7-26 CL22 - Indirect Address Method – Data Write
Figure 7-26 CL22 - Indirect Address Method – Data Write
Following timing diagrams illustrate an example read transaction to read contents of Register 16’h9000 using indirect addressing in Clause 22.
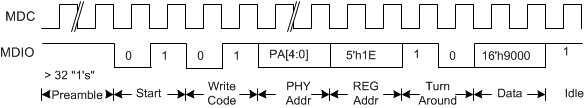 Figure 7-27 CL22 - Indirect Address Method – Address Write
Figure 7-27 CL22 - Indirect Address Method – Address Write
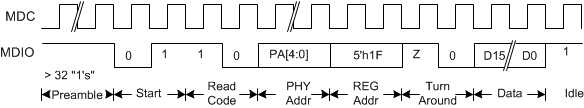 Figure 7-28 CL22 - Indirect Address Method – Data Read
Figure 7-28 CL22 - Indirect Address Method – Data Read
7.4.20 Provisionable XAUI Clock Tolerance Compensation
The XAUI interface is defined to allow for separate clock domains on each side of the link. Though the reference clocks for two devices on a XAUI/KR link have the same specified frequencies, there are slight differences that, if not compensated for, will lead to over or under run of the FIFOs on the receive/transmit data paths.
The XAUI CTC block performs the clock domain transition and rate compensation by utilizing a FIFO that is 32 deep and 40-bits wide. The usable FIFO size in the RX and TX directions is dependent upon the RX_FIFO_DEPTH and TX_FIFO_DEPTH MDIO fields, respectively. The word format is illustrated in Figure 7-29.
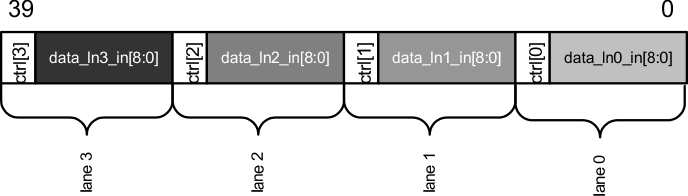 Figure 7-29 XAUI CTC FIFO Word Format
Figure 7-29 XAUI CTC FIFO Word Format
The XAUI CTC performs one of the following operations to compensate the clock rate difference:
- Delete Idle column from the data stream
- Delete Sequence column from the data stream (enabled via MDIO)
- Insert Idle column to the data stream.
The following rules apply for insertion/removal:
- Idle insertion/deletion occurs in groups of 4 idle characters (i.e., in columns)
- Idle characters are added following Idle or Sequence ordered_set
- Idle characters are not added while data is being received
- When deleting Idle characters, minimum IPG of 5 characters is maintained. /T/ characters are counted towards IPG.
- The first Idle column after /T/ is never deleted
- Sequence ordered_sets are deleted only when two consecutive Sequence columns are received. In this case, only one of the two Sequence columns will be deleted.
7.4.20.1 Insertion:
When the FIFO fill level is at or below LOW watermark (insertion is triggered), the XAUI CTC needs to insert an IDLE column. It does so by skipping a read from the FIFO and inserting IDLE column to the data stream. It continues the insertion until the FIFO fill level is above the mid point. This occurs on the read side of the FIFO.
7.4.20.2 Removal:
When the FIFO fill level is at or above HIGH watermark (deletion is triggered), the XAUI CTC needs to remove an IDLE column. It does so by skipping a write to the FIFO and discarding the IDLE column or Sequence ordered_set. It continues the deletion until the FIFO fill level is below the mid point. This occurs on the write side of the FIFO.
On the write side of the XAUI CTC FIFO a 40-bit write is performed at every cycle of the 312.5 MHz clock except during removal when it discards the IDLE or sequence ordered_set. On the read side of the XAUI CTC FIFO a 40-bit read is performed at every cycle of the 312.5 MHz clock except during insertion when it generates IDLE columns to the output while not reading the FIFO at all.
In IEEE 802.3-2008 the XAUI clock rate tolerance is given as 3.125 GHz ± 100 ppm, the XGMII clock rate tolerance is given as 156.25 MHz ± 0.02% (which is equivalent to 200ppm), and the Jumbo packet size is 9600 bytes which is equivalent to 2400 cycles of 312.5 MHz clock. The average inter-frame gap is 12 bytes (3 columns), which implies that there is one opportunity to insert/delete a column in between every packet on average. This gives one column deletion/insertion in every 2400 columns which results in a 400 ppm tolerance capability. If the IPG increases, then more clock rate variance or larger packet size can be supported. Note that the maximum frequency tolerance is limited by the frequency accuracy requirement of the reference clock.
The number of words in the FIFO (fifo_depth[2:0]) and the HIGH/LOW watermark levels (wmk_sel[1:0]) are set through MDIO register 01.8001, and determine the allowable difference between the write clock and the read clock as well as the maximum packet size that can be processed without FIFO collision. At these watermarks the drop and insert start respectively and must happen before it hits overflow/underflow condition. Although the FIFO is supposed to never overflow/underflow given the average IPG, if it ever happens the overflow/underflow indications signal the error to the MDIO interface and the FIFO is reset. Note that the overflow/underflow status indications are latched high and cleared when read.
Table 7-11 shows XAUI CTC FIFO configuration and capabilities:
Table 7-11 XAUI CTC FIFO Configurations
| fifo_depth[2:0] | FIFO Depth | wmk_sel[1:0] | LOW Watermark | HIGH Watermark | Max Latency (Cycles) | Nom Latency (Cycles) | Min Latency (Cycles) | Max pkt size (400ppm) | Max pkt size (200ppm) | Max pkt size (100ppm) | Max pkt size (50ppm) | Min #of removable columns in | IPG to support the max pkt size | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1xx | 32 | 11 | 15 | 18 | 28 | 16 | 4 | 100KB | 200KB | 400KB | 800KB | 10 | default | |
| 10 | 13 | 20 | 28 | 16 | 4 | 80KB | 160KB | 320KB | 640KB | 8 | ||||
| 01 | 10 | 23 | 28 | 16 | 4 | 50KB | 100KB | 200KB | 400KB | 5 | ||||
| 00 | 6 | 27 | 28 | 16 | 4 | 10KB | 20KB | 40KB | 80KB | 1 | ||||
| 011 | 24 | 11 | 11 | 14 | 20 | 12 | 4 | 60KB | 120KB | 240KB | 480KB | 6 | ||
| 10 | 9 | 16 | 20 | 12 | 4 | 40KB | 80KB | 160KB | 320KB | 4 | ||||
| 0x | 6 | 19 | 20 | 12 | 4 | 10KB | 20KB | 40KB | 80KB | 1 | ||||
| 010 | 16 | 1x | 7 | 10 | 13 | 8 | 3 | 30KB | 60KB | 120KB | 240KB | 3 | ||
| 0x | 5 | 12 | 13 | 8 | 3 | 10KB | 20KB | 40KB | 80KB | 1 | ||||
| 001 | 12 | xx | 5 | 8 | 9 | 6 | 3 | 10KB | 20KB | 40KB | 80KB | 1 | ||
| 000 | 8 | Plain FIFO, No CTC | 7 | 4 | 1 | No limit on pkt size (needs 0 ppm to work) | ||||||||
NOTE
To support the max packet sizes as shown in Table 7-11, it is assumed that there are enough IDLE columns in IPG for deletion. Below is one example:
Configure the FIFO to be 32-deep (fifo_depth[2:0] = 3’b1xx) and set the LOW/HIGH Watermarks to 10/23 (wmk_sel[1:0] = 2’b01). If the write clock is faster than the read clock by 200ppm, to support the max packet size of 100KB, a minimum of 5 removable columns in IPG is required (either IDLE columns or Sequence ordered_sets). If there are only 4 removable columns in IPG, the max packet size supported is dropped to 80KB. If there are only 3 removable columns in IPG, the max packet size supported is dropped to 60KB, and so on. As a rule of thumb, one removable column in IPG corresponds to 10KB at 400ppm, 20KB at 200ppm, 40KB at 100ppm, and 80KB at 50ppm
Figure 7-30 through Figure 7-40 illustrate XAUI CTC FIFO configuration and capabilities. The green region (the middle of the FIFO fill level) indicates that the FIFO is operating stability without insertion or deletion. The more green bars in the figure, the more clock wander it can tolerate. The more yellow bars in the figure, the bigger packet size it can support.
 Figure 7-30 Organization of the XAUI CTC FIFO (32-Deep, Low Watermark)
Figure 7-30 Organization of the XAUI CTC FIFO (32-Deep, Low Watermark)
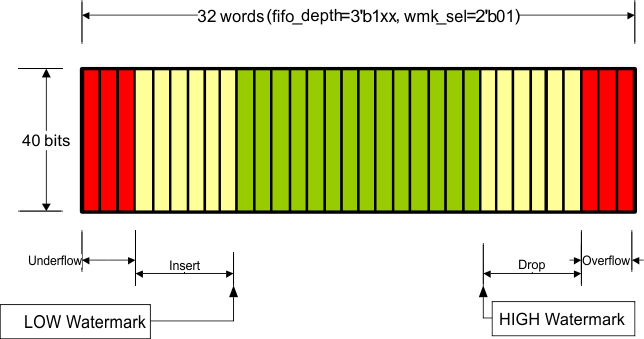 Figure 7-31 Organization of the XAUI CTC FIFO (32-Deep, Mid Watermark)
Figure 7-31 Organization of the XAUI CTC FIFO (32-Deep, Mid Watermark)
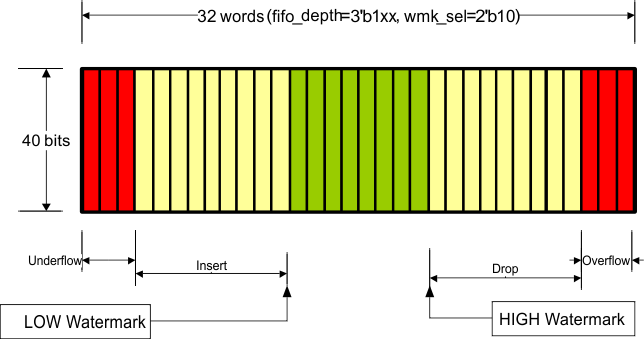 Figure 7-32 Organization of the XAUI CTC FIFO (32-Deep, Mid-High Watermark)
Figure 7-32 Organization of the XAUI CTC FIFO (32-Deep, Mid-High Watermark)
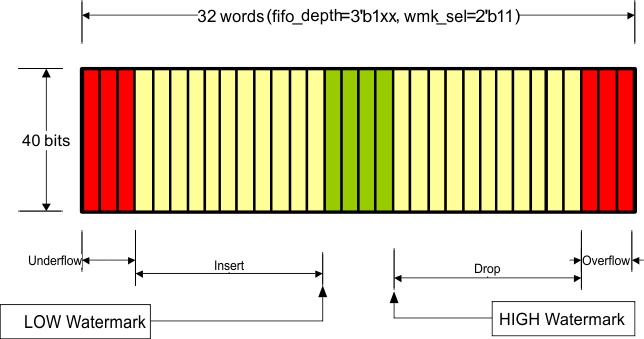 Figure 7-33 Organization of the XAUI CTC FIFO (32-Deep, High Watermark)
Figure 7-33 Organization of the XAUI CTC FIFO (32-Deep, High Watermark)
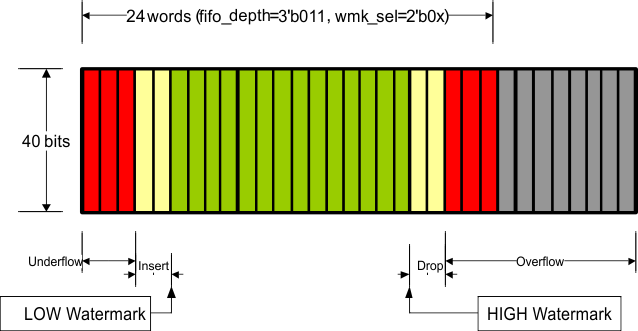 Figure 7-34 Organization of the XAUI CTC FIFO (24-Deep, Low Watermark)
Figure 7-34 Organization of the XAUI CTC FIFO (24-Deep, Low Watermark)
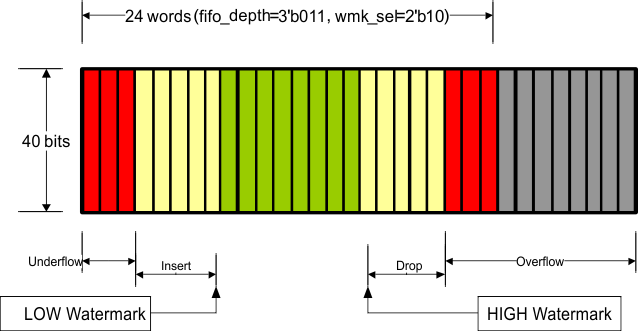 Figure 7-35 Organization of the XAUI CTC FIFO (24-Deep, Mid Watermark)
Figure 7-35 Organization of the XAUI CTC FIFO (24-Deep, Mid Watermark)
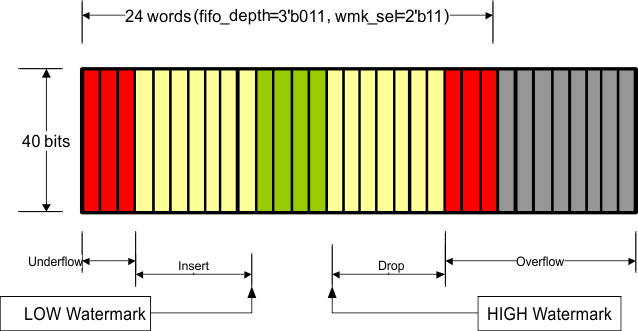 Figure 7-36 Organization of the XAUI CTC FIFO (24-Deep, High Watermark)
Figure 7-36 Organization of the XAUI CTC FIFO (24-Deep, High Watermark)
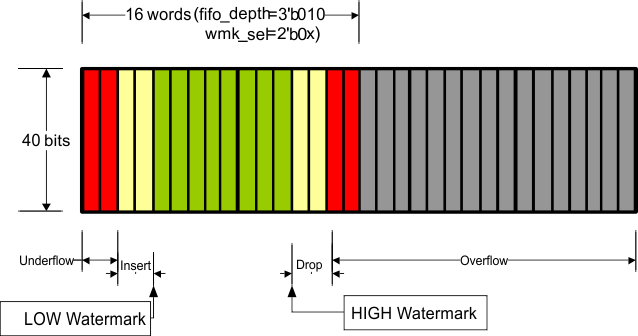 Figure 7-37 Organization of the XAUI CTC FIFO (16-Deep, Low Watermark)
Figure 7-37 Organization of the XAUI CTC FIFO (16-Deep, Low Watermark)
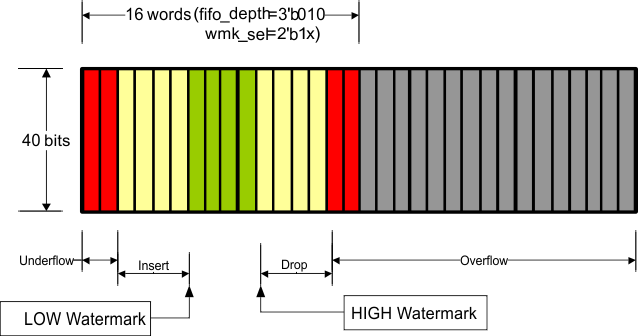 Figure 7-38 Organization of the XAUI CTC FIFO (16-Deep, High Watermark)
Figure 7-38 Organization of the XAUI CTC FIFO (16-Deep, High Watermark)
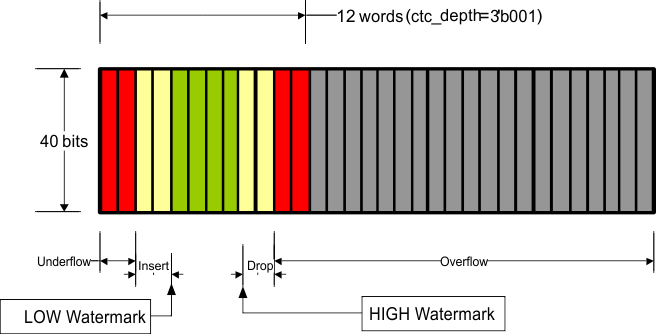 Figure 7-39 Organization of the XAUI CTC FIFO (12-Deep)
Figure 7-39 Organization of the XAUI CTC FIFO (12-Deep)
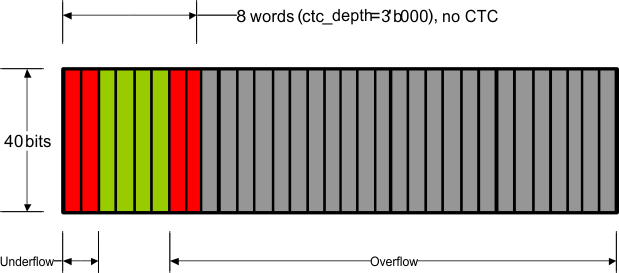 Figure 7-40 Organization of the XAUI CTC FIFO (8-Deep)
Figure 7-40 Organization of the XAUI CTC FIFO (8-Deep)
7.5 Register Maps
7.5.1 Register Bit Definitions
7.5.1.1 RW: Read-Write
User can write 0 or 1 to this register bit. Reading this register bit returns the same value that has been written.
7.5.1.2 RW/SC: Read-Write Self-Clearing
User can write 0 or 1 to this register bit. Writing a "1" to this register creates a high pulse. Reading this register bit always returns 0.
7.5.1.3 RO: Read-Only
This register can only be read. Writing to this register bit has no effect. Reading from this register bit returns its current value.
7.5.1.4 RO/LH: Read-Only Latched High
This register can only be read. Writing to this register bit has no effect. Reading a "1" from this register bit indicates that either the condition is occurring or it has occurred since the last time it was read. Reading a "0" from this register bit indicates that the condition is not occurring presently, and it has not occurred since the last time the register was read. A latched high register, when read high, should be read again to distinguish if a condition occurred previously or is still occurring. If it occurred previously, the second read will read low. If it is still occurring, the second read will read high. Reading this register bit automatically resets its value to 0.
7.5.1.5 RO/LL: Read-Only Latched Low
This register can only be read. Writing to this register bit has no effect. Reading a "0" from this register bit indicates that either the condition is occurring or it has occurred since the last time it was read. Reading a "1" from this register bit indicates that the condition is not occurring presently, and it has not occurred since the last time the register was read. A latched low register, when read low, should be read again to distinguish if a condition occurred previously or is still occurring. If it occurred previously, the second read will read high. If it is still occurring, the second read will read low. Reading this register bit automatically sets its value to 1.
7.5.1.6 COR: Clear-On-Read
This register can only be read. Writing to this register bit has no effect. Reading from this register bit returns its current value, then resets its value to 0. Counter value freezes at Max.
Following code letters in Name field of each control/status register bit(s) indicate the mode that they are applicable/valid.
R = Indicates control/status bit(s) valid in 10GKR mode
X = Indicates control/status bit(s) valid in 1GKX mode
G = Indicates control/status bit(s) valid in 10G general purpose serdes mode
7.5.2 Vendor Specific Device Registers
Below registers can be accessed directly through Clause 22 and Clause 45. In Clause 45 mode, these registers can be accessed by setting device address field to 0x1E (DA[4:0] = 5’b11110). In Clause 22 mode, these registers can be accessed by setting 5 bit register address field to same value as 5 LSB bits of Register Address field specified for each register. For example, 16 bit register address 0x001C in clause 45 mode can be accessed by setting register address field to 5’h1C in clause 22 mode.
7.5.2.1 GLOBAL_CONTROL_1 (register: 0x0000) (default: 0x0610) (device address: 0x1E)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| GLOBAL_RESET (RXG) |
PRTAD0_PIN_EN_SEL[2:0] (RXG) |
RESERVED | RESERVED | ||||
| R/W | R/W | R/W | R/W | ||||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| RESERVED | PRTAD0_ PIN_EN (RXG) |
PRBS_PASS_OVERLAY[4:0] (RXG) |
|||||
| R/W | R/W | R/W | |||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-12 GLOBAL_CONTROL_1 Field Description
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | GLOBAL_RESET (RXG) |
R/W (2) |
Global reset. 0 = Normal operation (Default 1’b0) 1 = Resets TX and RX data path including MDIO registers. Equivalent to asserting RESET_N. |
|
| 14:12 | PRTAD0_PIN_EN_SEL[2:0] (RXG) |
R/W | PRTAD0 pin selection control. Valid only when 1E.0000 bit 5 is 1. PRTAD0 is used for the assignment specified below 000 = Stopwatch (Default 3’b000) 001 = Reserved 010 = Tx data switch 011 = Rx data switch 100 = Reserved 101 = Reserved 11x = Reserved |
|
| 11 | Reserved (RXG) |
Reserved For TI use only. Always reads 0. |
||
| 10:7 | RESERVED | R/W | For TI use only (Default 5’b1100) | |
| 6 | RESERVED | R/W | For TI use only. Always reads 0. | |
| 5 | PRTAD0_PIN_EN (RXG) |
R/W | PRTAD0 pin enable control. 0 = Input pin (PRTAD0) is used for the assignment specified in 1E.0000 bits 14:12 (Default 1’b0) 1 = Input pin (PRTAD0) is not used for the assignment specified in 1E.0000 bits 14:12 |
|
| 4:0 | PRBS_PASS_OVERLAY[4:0] (RXG) |
R/W | PRBS_PASS pin status selection. Applicable only when PRBS test pattern verification is enabled on HS side or LS side. PRBS_PASS pin reflects PRBS verification status on HS/LS side. LS Serdes lanes 1/2/3 are not applicable in 1GKX modes. 1xx00 = PRBS_PASS reflects HS serdes PRBS verification. If PRBS verification fails on HS serdes, PRBS_PASS will be asserted low. (Default 5’b10000) 00000 = Status from HS Serdes side 00001 = Reserved 000x1 = Reserved 00100 = Status from LS Serdes side Lane 0 00101 = Status from LS Serdes side Lane 1 00110 = Status from LS Serdes side Lane 2 00111 = Status from LS Serdes side Lane 3 01000 = Reserved 01001 = Reserved 0101x = Reserved 01100 = Reserved 01101 = Reserved 01110 = Reserved 01111 = Reserved |
7.5.2.2 CHANNEL_CONTROL_1 (register: 0x0001) (default: 0x0B00) (device address: 0x1E)(1)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| POWERDOWN (RXG) |
LT_TRAINING_CONTROL (XG) |
10G_RX_MODE_SEL (G) |
10G_TX_MODE_SEL (G) |
SW_PCS_SEL (RX) |
SW_DEV_MODE_SEL (RXG) |
10G_RX_DEMUX_SEL (G) |
10G_TX_MUX_SEL (G) |
| R/W | R/W | R/W | R/W | R/W | R/W | R/W | R/W |
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| RESERVED | REFCLK_SW_SEL (RXG) |
LS_REFCLK_SEL (RXG) |
|||||
| R | R/W | R/W | |||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-13 CHANNEL_CONTROL_1 Field Description
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | POWERDOWN (RXG) |
R/W | Setting this bit high powers down entire data path with exception that MDIO interface stays active. 0 = Normal operation (Default 1’b0) 1 = Power Down mode is enabled. |
|
| 14 | LT_TRAINING_CONTROL (XG) |
R/W | Link training control. Valid in 10G and 1GKX modes only. 0 = Link training disabled(Default 1’b0) 1 = Link training enable control dependent on LT_TRAINING_ENABLE (1E.0036 bit 1). |
|
| 13 | 10G_RX_MODE_SEL (G) |
R/W | RX mode selection. Valid in 10G only. 0 = RX mode dependent upon RX_DEMUX_SEL(Default 1’b0) 1 = Enables 1 to 1 mode on receive channel. |
|
| 12 | 10G_TX_MODE_SEL (G) |
R/W | TX mode selection Valid in 10G only. 0 = TX mode dependent upon TX_MUX_SEL (Default 1’b0) 1 = Enables 1 to 1 mode on transmit channel. |
|
| 11 | SW_PCS_SEL (RX) |
R/W | Applicable in Clause 45 mode only. Valid only when MODE_SEL pin is 0, AN_ENABLE (07.0000 bit 12) is 0 and SW_DEV_MODE_SEL (1E.0001 bit 10) is 0. 0 = Set device to 10G-KR mode(Default 1’b1) 1 = Set device to 1G-KX mode |
|
| 10 | SW_DEV_MODE_SEL (RXG) |
R/W | Valid only when MODE_SEL pin is 0 0 = Device set to 10G mode 1 = In clause 45 mode, device mode is set using Auto negotiation. In clause 22 mode, device set to 1G-KX mode(Default 1’b0) |
|
| 9 | 10G_RX_DEMUX_SEL (G) |
R/W | RX De-Mux selection control for lane de-serialization on receive channel. Valid in 10G and when 10G_RX_MODE_SEL (1E.0001 bit 13) is LOW 0 = 1 to 2 1 = 1 to 4 (Default 1’b1) |
|
| 8 | 10G_TX_MUX_SEL (G) |
R/W | TX Mux selection control for lane serialization on transmit channel. Valid in 10G and when 10G_TX_MODE_SEL (1E.0001 bit 12) is LOW 0 = 2 to 1 1 = 4 to 1 (Default 1’b1) |
|
| 7:2 | RESERVED | R/O | For TI use only | |
| 1 | REFCLK_SW_SEL (RXG) |
R/W | HS Reference clock selection. 0 = Selects REFCLK_0_P/N as clock reference to HS side serdes macro(Default 1’b0) 1 = Selects REFCLK_1_P/N as clock reference to HS side serdes macro |
|
| 0 | LS_REFCLK_SEL (RXG) |
R/W | LS Reference clock selection. 0 = LS side serdes macro reference clock is same as HS side serdes reference clock (E.g. If REFCLK_0_P/N is selected as HS side serdes macro reference clock, REFCLK_0_P/N is selected as LS side serdes macro reference clock and vice versa) (Default 1’b0) 1 = Alternate reference clock is selected as clock reference to LS side serdes macro (E.g. If REFCLK_0_P/N is selected as HS side serdes macro reference clock, REFCLK_1_P/N is selected as LS side serdes macro reference clock and vice versa) |
7.5.2.3 HS_SERDES_CONTROL_1 (register: 0x0002 ) (default: 0x831D) (device address: 0x1E)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| RESERVED | HS_LOOP_BANDWIDTH[1:0] (RXG) |
||||||
| R/W | R/W | ||||||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| RESERVED | HS_VRANGE (RXG |
RESERVED | HS_ENPLL (RXG) |
HS_PLL_MULT[3:0] (RXG) |
|||
| R/W | R/W | R/W | R/W | R/W | |||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-14 HS_SERDES_CONTROL_1 Field Description
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:10 | For TI use only (Default 6’b100000) | |||
| 9:8 | HS_LOOP_BANDWIDTH[1:0] (RXG) |
R/W | HS Serdes PLL Loop Bandwidth settings 00 = Medium Bandwidth 01 = Low Bandwidth 10 = High Bandwidth 11 = Ultra High Bandwidth. (Default 2'b11) |
|
| 7 | RESERVED | R/W | For TI use only (Default 1’b0) | |
| 6 | HS_VRANGE (RXG) |
R/W | HS Serdes PLL VCO range selection. 0 = VCO runs at higher end of frequency range (Default 1’b0) 1 = VCO runs at lower end of frequency range This bit needs to be set HIGH if VCO frequency (REFCLK *HS_PLL_MULT) is below 2.5 GHz. |
|
| 5 | RESERVED | R/W | For TI use only (Default 1’b0) | |
| 4 | HS_ENPLL (RXG) |
R/W | HS Serdes PLL enable control. HS Serdes PLL is automatically disabled when PD_TRXx_N is asserted LOW or when register bit 1E.0001 bit 15 is set HIGH. 0 = Disables PLL in HS serdes 1 = Enables PLL in HS serdes (Default 1’b1) |
|
| 3:0 | HS_PLL_MULT[3:0] (RXG) |
R/W | HS Serdes PLL multiplier setting (Default 4’b1101). Refer : Table 7-15 HS PLL multiplier control |
Table 7-15 HS PLL Multiplier Control
| HS_PLL_MULT[3:0] | HS_PLL_MULT[3:0] | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Value | PLL Multiplier factor | Value | PLL Multiplier factor |
| 0000 | Reserved | 1000 | 12x |
| 0001 | Reserved | 1001 | 12.5x |
| 0010 | 4x | 1010 | 15x |
| 0011 | 5x | 1011 | 16x |
| 0100 | 6x | 1100 | 16.5x |
| 0101 | 8x | 1101 | 20x |
| 0110 | 8.25x | 1110 | 25x |
| 0111 | 10x | 1111 | Reserved |
7.5.2.4 HS_SERDES_CONTROL_2 (register: 0x0003) (default: 0xA848) (device address: 0x1E)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| HS_SWING[3:0] (RXG) |
HS_ENTX (RXG) |
HS_EQHLD (RXG) |
HS_RATE_TX [1:0] (RXG) |
||||
| R/W | R/W | R/W | R/W | ||||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| HS_AGCCTRL[1:0] (RXG |
HS_AZCAL[1:0] (RXG) |
HS_ENRX (RXG) |
HS_RATE_RX [2:0] (RXG) |
||||
| R/W | R/W | R/W | R/W | ||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-16 HS_SERDES_CONTROL_2 Field Description
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:12 | HS_SWING[3:0] (RXG) |
R/W | Transmitter Output swing control for HS Serdes. (Default 4’b1010) Refer Table 7-17. |
|
| 11 | HS_ENTX (RXG) |
R/W | HS Serdes transmitter enable control. HS Serdes transmitter is automatically disabled when PD_TRXx_N is asserted LOW or when register bit 1E.0001 bit 15 is set HIGH. 0 = Disables HS serdes transmitter 1 = Enables HS serdes transmitter (Default 1’b1) |
|
| 10 | HS_EQHLD (RXG) |
R/W | HSRX Equalizer hold control. 0 = Normal operation (Default 1’b0) 1 = Holds equalizer and long tail correction in its current state |
|
| 9:8 | HS_RATE_TX [1:0] (RXG) |
R/W | HS Serdes TX rate settings. 00 = Full rate (Default 2’b00) 01 = Half rate 10 = Quarter rate 11 = Eighth rate |
|
| 7:6 | HS_AGCCTRL[1:0] (RXG) |
R/W | Adaptive gain control loop. 00 = Attenuator will not change after lock has been achieved, even if AGC becomes unlocked 01 = Attenuator will not change when in lock state, but could change when AGC becomes unlocked (Default 2’b01) 10 = Force the attenuator off 11 = Force the attenuator on |
|
| 5:4 | HS_AZCAL[1:0] (RXG) |
R/W | Auto zero calibration. 00 = Auto zero calibration initiated when receiver is enabled (Default 2’b00) 01 = Auto zero calibration disabled 10 = Forced with automatic update. 11 = Forced without automatic update |
|
| 3 | HS_ENRX (RXG) |
R/W | HS Serdes receiver enable control. HS Serdes receiver is automatically disabled when PD_TRXx_N is asserted LOW or when register bit 1E.0001 bit 15 is set HIGH. 0 = Disables HS serdes receiver 1 = Enables HS serdes receiver (Default 1’b1) |
|
| 2:0 | HS_RATE_RX [2:0] (RXG) |
R/W | HS Serdes RX rate settings. This setting is automatically controlled and value set through these register bits is ignored unless REFCLK_FREQ_SEL_1 or related OVERRIDE bit is set. 000 = Full rate (Default 3’b000) 001 = Half rate 110 = Quarter rate 111 = Eighth rate 001 = Reserved 01x = Reserved 100 = Reserved |
Table 7-17 HSTX AC Mode Output Swing Control
| HS_SWING[3:0] | AC MODE |
|---|---|
| TYPICAL AMPLITUDE (mVdfpp) | |
| 0000 | 130 |
| 0001 | 220 |
| 0010 | 300 |
| 0011 | 390 |
| 0100 | 480 |
| 0101 | 570 |
| 0110 | 660 |
| 0111 | 750 |
| 1000 | 830 |
| 1001 | 930 |
| 1010 | 1020 |
| 1011 | 1110 |
| 1100 | 1180 |
| 1101 | 1270 |
| 1110 | 1340 |
| 1111 | 1400 |
7.5.2.5 HS_SERDES_CONTROL_3 (register: 0x0004) (default: 0x1500) (device address: 0x1E)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| HS_ENTRACK (RXG) |
HS_EQPRE[2:0] (RXG) |
HS_CDRFMULT[1:0] (RXG) |
HS_CDRTHR[1:0] (RXG) |
||||
| R/W | R/W | R/W | R/W | ||||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| RESERVED | HS_PEAK_DISABLE (RXG) |
HS_H1CDRMODE (RXG) |
HS_TWCRF[4:0] (RXG) |
||||
| R/W | R/W | R/W | R/W | ||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-18 HS_SERDES_CONTROL_3 Field Description
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | HS_ENTRACK (RXG) |
R/W | HSRX ADC Track mode. 0 = Normal operation (Default 1’b0) 1 = Forces ADC into track mode |
|
| 14:12 | HS_EQPRE[2:0] (RXG) |
R/W | Serdes Rx precursor equalizer selection 000 = 1/9 cursor amplitude 001 = 3/9 cursor amplitude (Default 3’b001) 010 = 5/9 cursor amplitude 011 = 7/9 cursor amplitude 100 = 9/9 cursor amplitude 101 = 11/9 cursor amplitude 110 = 13/9 cursor amplitude 111 = Disable |
|
| 11:10 | HS_CDRFMULT[1:0] (RXG) |
R/W | Clock data recovery algorithm frequency multiplication selection (Default 2'b01) 00 =First order. Frequency offset tracking disabled 01 = Second order. 1x mode 10 = Second order. 2x mode 11 = Reserved |
|
| 9:8 | HS_CDRTHR[1:0] (RXG) |
R/W | Clock data recovery algorithm threshold selection (Default 2'b01) 00 = Four vote threshold 01 = Eight vote threshold 10 = Sixteen vote threshold 11 = Thirty two vote threshold |
|
| 7 | RESERVED | R/W | For TI use only (Default 1’b0) | |
| 6 | HS_PEAK_DISABLE (RXG) |
R/W | HS Serdes PEAK_DISABLE control 0 = Normal operation (Default 1’b0) 1 = Disables high frequency peaking. Suitable for <6 Gbps operation |
|
| 5 | HS_H1CDRMODE (RXG) |
R/W | HS_Serdes H1CDRMODE control 0 = Normal operation (Default 1’b0) 1 = Enables CDR mode suitable for short channel operation. |
|
| 4:0 | HS_TWCRF[4:0] (RXG) |
R/W | Cursor Reduction Factor (Default 5’b00000). Refer to Table 7-19 |
Table 7-19 HSTX Cursor Reduction Factor Weights
| HS_TWCRF[4:0] | HS_TWCRF[4:0] | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Value | Cursor reduction (%) | Value | Cursor reduction (%) |
| 00000 | 0 | 10000 | 17 |
| 00001 | 2.5 | 10001 | 20 |
| 00010 | 5.0 | 10010 | 22 |
| 00011 | 7.5 | 10011 | 25 |
| 00100 | 10.0 | 10100 | 27 |
| 00101 | 12 | 10101 | 30 |
| 00110 | 15 | 10110 | 32 |
| 00111 | Reserved | 10111 | 35 |
| 01000 | 11000 | 37 | |
| 01001 | 11001 | 40 | |
| 01010 | 11010 | 42 | |
| 01011 | 11011 | 45 | |
| 01100 | 11100 | 47 | |
| 01101 | 11101 | 50 | |
| 01110 | 11110 | 52 | |
| 01111 | 11111 | 55 |
7.5.2.6 HS_SERDES_CONTROL_4 (register: 0x0005) (default: 0x2000) (device address: 0x1E)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| HS_RX_ INVPAIR (RXG) |
HS_TX_ INVPAIR (RXG) |
RESERVED | HS_TWPOST1[4:0] (RXG) |
||||
| R/W | R/W | R/W | R/W | ||||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| HS_TWPRE[3:0] (RXG) |
HS_TWPOST2[3:0] (RXG) |
||||||
| R/W | R/W | ||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-20 HS_SERDES_CONTROL_4 Field Description
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | HS_RX_INVPAIR (RXG) |
R/W | Receiver polarity. 0 = Normal polarity. HSRXxP considered positive data. HSRXxN considered negative data (Default 1’b0) 1 = Inverted polarity. HSRXxP considered negative data. HSRXxN considered positive data |
|
| 14 | HS_TX_INVPAIR (RXG) |
R/W | Transmitter polarity. 0 = Normal polarity. HSTXxP considered positive data and HSTXxN considered negative data (Default 1’b0) 1 = Inverted polarity. HSTXxP considered negative data and HSTXxN considered positive data |
|
| 13 | RESERVED | R/W | For TI use only (Default 1’b1) | |
| 12:8 | HS_TWPOST1[4:0] (RXG) |
R/W | Adjacent post cursor1 Tap weight. Selects TAP settings for TX waveform. (Default 5’b00000 ) Refer Table 7-21. |
|
| 7:4 | HS_TWPRE[3:0] (RXG) |
R/W | Precursor Tap weight. Selects TAP settings for TX waveform. (Default 4’b0000) Refer Table 7-23. |
|
| 3:0 | HS_TWPOST2[3:0] (RXG) |
R/W | Adjacent post cursor2 Tap weight. Selects TAP settings for TX waveform. (Default 4’b0000) Refer Table 7-22. |
Table 7-21 HSTX Post-Cursor1 Transmit Tap Weights
| HS_TWPOST1[4:0] | HS_TWPOST1[4:0] | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Value | Tap weight (%) | Value | Tap weight (%) |
| 00000 | 0 | 10000 | 0 |
| 00001 | +2.5 | 10001 | –2.5 |
| 00010 | +5.0 | 10010 | –5.0 |
| 00011 | +7.5 | 10011 | –7.5 |
| 00100 | +10.0 | 10100 | –10.0 |
| 00101 | +12.5 | 10101 | –12.5 |
| 00110 | +15.0 | 10110 | –15.0 |
| 00111 | +17.5 | 10111 | –17.5 |
| 01000 | +20.0 | 11000 | –20.0 |
| 01001 | +22.5 | 11001 | –22.5 |
| 01010 | +25.0 | 11010 | –25.0 |
| 01011 | +27.5 | 11011 | –27.5 |
| 01100 | +30.0 | 11100 | –30.0 |
| 01101 | +32.5 | 11101 | –32.5 |
| 01110 | +35.0 | 11110 | –35.0 |
| 01111 | +37.5 | 11111 | -37.5 |
Table 7-22 HSTX Post-Cursor2 Transmit Tap Weights
| HS_TWPOST2[3:0] | HS_TWPOST2[3:0] | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Value | Tap weight (%) | Value | Tap weight (%) |
| 0000 | 0 | 1000 | 0 |
| 0001 | +2.5 | 1001 | –2.5 |
| 0010 | +5.0 | 1010 | –5.0 |
| 0011 | +7.5 | 1011 | –7.5 |
| 0100 | +10.0 | 1100 | –10.0 |
| 0101 | +12.5 | 1101 | –12.5 |
| 0110 | +15.0 | 1110 | –15.0 |
| 0111 | +17.5 | 1111 | –17.5 |
Table 7-23 HSTX Pre-Cursor Transmit Tap Weights
| HS_TWPRE[3:0] | HS_TWPRE[3:0] | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Value | Tap weight (%) | Value | Tap weight (%) |
| 0000 | 0 | 1000 | 0 |
| 0001 | +2.5 | 1001 | –2.5 |
| 0010 | +5.0 | 1010 | –5.0 |
| 0011 | +7.5 | 1011 | –7.5 |
| 0100 | +10.0 | 1100 | –10.0 |
| 0101 | +12.5 | 1101 | –12.5 |
| 0110 | +15.0 | 1110 | –15.0 |
| 0111 | +17.5 | 1111 | –17.5 |
7.5.2.7 LS_SERDES_CONTROL_1 (register: 0x0006) (default: 0xF115) (device address: 0x1E)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| LS_LN_CFG_EN[3:0] (RXG) |
RESERVED | LS_LOOP_BANDWIDTH[1:0] (RXG) |
|||||
| R/W | R/W | R/W | |||||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| RESERVED | LS_ENPLL (RXG) |
LS_MPY[3:0] (RXG) |
|||||
| R/W | R/W | R/W | |||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-24 LS_SERDES_CONTROL_1 Field Description
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:12 | LS_LN_CFG_EN[3:0] (RXG) |
R/W | Configuration control for LS Serdes Lane settings (Default 4’b1111) [3] corresponds to LN3, [2] corresponds to LN2 [1] corresponds to LN1, [0] corresponds to LN0 0 = Writes to LS_SERDES_CONTROL_2 and LS_SERDES_CONTROL_3 and LS_CH_CONTROL_1 control registers do not affect respective LS Serdes lane 1 = Writes to LS_SERDES_CONTROL_2 and LS_SERDES_CONTROL_3 and LS_CH_CONTROL_1 control registers affect respective LS Serdes lane For example, if subsequent writes to LS_SERDES_CONTROL_2 and LS_SERDES_CONTROL_3 and LS_CH_CONTROL_1 registers need to affect the settings in Lanes 0 and 1, LS_LN_CFG_EN[3:0] should be set to 4’b0011 Read values in LS_SERDES_CONTROL_2 and LS_SERDES_CONTROL_3 and LS_CH_CONTROL_1 reflect the settings value for Lane selected through LS_LN_CFG_EN[3:0]. To read Lane 0 settings, LS_LN_CFG_EN[3:0] should be set to 4’b0001 To read Lane 1 settings, LS_LN_CFG_EN[3:0] should be set to 4’b0010 To read Lane 2 settings, LS_LN_CFG_EN[3:0] should be set to 4’b0100 To read Lane 3 settings, LS_LN_CFG_EN[3:0] should be set to 4’b1000 Read values of LS_SERDES_CONTROL_2 and LS_SERDES_CONTROL_3 and LS_CH_CONTROL_1 registers are not valid for any other LS_LN_CFG_EN[3:0] combination |
|
| 11:10 | RESERVED | R/W | For TI use only (Default 2’b00) | |
| 9:8 | LS_LOOP_BANDWIDTH[1:0] (RXG) |
R/W | LS Serdes PLL Loop Bandwidth settings 00 = Reserved 01 = Applicable when external JC_PLL is NOT used (Default 2’b01) 10 = Applicable when external JC_PLL is used 11 = Reserved |
|
| 7:5 | RESERVED | R/W | For TI use only (Default 3’b000) | |
| 4 | LS_ENPLL (RXG) |
R/W | LS Serdes PLL enable control. LS Serdes PLL is automatically disabled when PD_TRXx_N is asserted LOW or when register bit 1E.0001 bit 15 is set HIGH. 0 = Disables PLL in LS serdes 1 = Enables PLL in LS serdes (Default 1’b1) |
|
| 3:0 | LS_MPY[3:0] (RXG) |
R/W | LS Serdes PLL multiplier setting (Default 4’b0101). Refer 10GKR supported rates for valid PLL Multiplier values. Refer to Table 7-25. |
Table 7-25 LS PLL Multiplier Control
| LS_MPY[3:0] | LS_MPY[3:0] | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Value | PLL Multiplier factor | Value | PLL Multiplier factor |
| 0000 | 4x | 1000 | 15x |
| 0001 | 5x | 1001 | 20x |
| 0010 | 6x | 1010 | 25x |
| 0011 | Reserved | 1011 | Reserved |
| 0100 | 8x | 1100 | Reserved |
| 0101 | 10x | 1101 | 50x |
| 0110 | 12x | 1110 | 65x |
| 0111 | 12.5x | 1111 | Reserved |
7.5.2.8 LS_SERDES_CONTROL_2 (register: 0x0007) (default: 0xDC04) (device address: 0x1E)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| RESERVED | LS_SWING[2:0] (RXG) |
LS_LOS (RXG) |
LS_TX_ENRX (RXG) |
LS_TX_RATE [1:0] (RXG) |
|||
| R/W | R/W | R/W | R/W | R/W | |||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| LS_DE[3:0] (RXG) |
RESERVED | LS_RX_ENTX (RXG) |
LS_RX_RATE [1:0] (RXG) |
||||
| R/W | R/W | R/W | R/W | ||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-26 LS_SERDES_CONTROL_2 Field Description
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | RESERVED | R/W | For TI use only. | |
| 14:12 | LS_SWING[2:0] (RXG) |
R/W | Output swing control on LS Serdes side. (Default 3’b101) Refer to Table 7-27. |
|
| 11 | LS_LOS (RXG) |
R/W | LS Serdes LOS detector control 0 = Disable Loss of signal detection on LS serdes lane inputs 1 = Enable Loss of signal detection on LS serdes lane inputs (Default 1’b1) |
|
| 10 | LS_TX_ENRX (RXG) |
R/W | LS Serdes enable control on the transmit channel. LS Serdes per lane on transmitter channel is automatically disabled when PD_TRXx_N is asserted LOW or when register bit 1E.0001 bit 15 is set HIGH. Lanes 3 and 2 are automatically disabled when in 2ln 10G mode on transmit channel. Lanes 3, 2 and 1 are automatically disabled when in 1ln 10G mode or 1G-KX mode on transmit channel. 0 = Disables LS serdes lane 1 = Enables LS serdes lane (Default 1’b1) |
|
| 9:8 | LS_TX_RATE [1:0] (RXG) |
R/W | LS Serdes lane rate settings on transmit channel. 00 = Full rate (Default 2’b00) 01 = Half rate 10 = Quarter rate 11 = Reserved |
|
| 7:4 | LS_DE[3:0] (RXG) |
R/W | LS Serdes De-emphasis settings. (Default 4’b0000) Refer to Table 7-28. |
|
| 3 | RESERVED | R/W | For TI use only. | |
| 2 | LS_RX_ENTX (RXG) |
R/W | LS Serdes lane enable control on receive channel. LS Serdes per lane on receiver channel is automatically disabled when PD_TRXx_N is asserted LOW or when register bit 1E.0001 bit 15 is set HIGH. Lanes 3 and 2 are automatically disabled when in 2ln 10G mode on receive channel. Lanes 3, 2 and 1 are automatically disabled when in 1ln 10G or 1G-KX mode on receive channel. 0 = Disables LS serdes lane 1 = Enables LS serdes lane (Default 1’b1) |
|
| 1:0 | LS_RX_RATE [1:0] (RXG) |
R/W | LS Serdes lane rate settings on receive channel. 00 = Full rate (Default 2’b00) 01 = Half rate 10 = Quarter rate 11 = Reserved |
Table 7-27 LSRX Output AC Mode Output Swing Control
| LS_SWING[2:0] | AC MODE |
|---|---|
| TYPICAL AMPLITUDE (mVdfpp) | |
| 000 | 190 |
| 001 | 380 |
| 010 | 560 |
| 011 | 710 |
| 100 | 850 |
| 101 | 950 |
| 110 | 1010 |
| 111 | 1050 |
Table 7-28 LSRX Output De-emphasis
| LS_DE[3:0] | LS_DE[3:0] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | Amplitude reduction | Value | Amplitude reduction | ||
| (%) | dB | (%) | dB | ||
| 0000 | 0 | 0 | 1000 | 38.08 | –4.16 |
| 0001 | 4.76 | –0.42 | 1001 | 42.85 | –4.86 |
| 0010 | 9.52 | –0.87 | 1010 | 47.61 | –5.61 |
| 0011 | 14.28 | –1.34 | 1011 | 52.38 | –6.44 |
| 0100 | 19.04 | –1.83 | 1100 | 57.14 | –7.35 |
| 0101 | 23.8 | –2.36 | 1101 | 61.9 | –8.38 |
| 0110 | 28.56 | –2.92 | 1110 | 66.66 | –9.54 |
| 0111 | 33.32 | –3.52 | 1111 | 71.42 | –10.87 |
7.5.2.9 LS_SERDES_CONTROL_3 (register: 0x0008) (default: 0x000D) (device address: 0x1E)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| LS_RX_ INVPAIR (RXG) |
LS_TX_ INVPAIR (RXG) |
RESERVED | LS_EQ[3:0] (RXG) |
||||
| R/W | R/W | R/W | R/W | ||||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| RESERVED | |||||||
| R/W | |||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-29 LS_SERDES_CONTROL_3 Field Description
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | LS_RX_INVPAIR (RXG) |
R/W | LS Serdes lane outputs polarity on the receive channel. (y = Lane 0 or 1 or 2 or 3) 0 = Normal polarity. OUTAyP considered positive data. OUTxyN considered negative data (Default 1’b0) 1 = Inverted polarity. OUTAyP considered negative data. OUTxyN considered positive data |
|
| 14 | LS_TX_INVPAIR (RXG) |
R/W | LS Serdes lane inputs polarity on the transmit channel. (y = Lane 0 or 1 or 2 or 3) 0 = Normal polarity. INAyP considered positive data and INAyN considered negative data (Default 1’b0) 1 = Inverted polarity. INAyP considered negative data and INAyP considered positive data |
|
| 13:12 | RESERVED | R/W | For TI use only (Default 2’b00) | |
| 11:8 | LS_EQ[3:0] (RXG) |
R/W | LS Serdes Equalization control (Default 4’b0000). Table 7-30 | |
| 7:0 | RESERVED | R/W | For TI use only (Default 8'b00001101) |
Table 7-30 LS_EQ Serdes Equalization
| LS_EQ[3:0] | LS_EQ[3:0] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | Low Freq Gain | Zero Freq | Value | Low Freq Gain | Zero Freq |
| 0000 | Maximum | 1000 | Adaptive | 365 MHz | |
| 0001 | Adaptive | 1001 | 275 MHz | ||
| 0010 | Reserved | 1010 | 195 MHz | ||
| 0011 | 1011 | 140 MHz | |||
| 0100 | 1100 | 105 MHz | |||
| 0101 | 1101 | 75 MHz | |||
| 0110 | 1110 | 55 MHz | |||
| 0111 | 1111 | 50 MHz | |||
7.5.2.10 HS_OVERLAY_CONTROL (register: 0x0009) (default: 0x0380) (device address: 0x1E)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| LS_OK_OUT_GATE[1:0] (G) |
LS_OK_IN_GATE[1:0] (G) |
RESERVED | |||||
| R/W | R/W | R/W | |||||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| HS_LOS_ MASK (G) |
RESERVED | HS_CH_SYNC_OVERLAY (RXG) |
HS_INVALID_ CODE_ OVERLAY (RXG) |
HS_AGCLOCK_ OVERLAY (RXG) |
HS_AZDONE_OVERLAY (RXG) |
HS_PLL_LOCK_OVERLAY (RXG) |
HS_LOS_ OVERLAY (RXG) |
| R/W | R/W | R/W | R/W | R/W | R/W | R/W | R/W |
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-31 HS_OVERLAY_CONTROL Field Description
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:14 | LS_OK_OUT_GATE[1:0] (G) |
R/W | LS_OK_OUT_A gating control | |
| X0 | Gating disabled (Default 2’b00) | |||
| 01 | Gating enabled. LS_OK_OUT_A gated to LOW | |||
| 11 | Gating enabled. LS_OK_OUT_A gated to HIGH | |||
| 13:12 | LS_OK_IN_GATE[1:0] (G) |
R/W | LS_OK_IN_A gating control | |
| X0 | Gating disabled (Default 2’b00) | |||
| 01 | Gating enabled.LS_OK_IN_A gated to LOW | |||
| 11 | Gating enabled.LS_OK_IN_A gated to HIGH | |||
| 11:8 | RESERVED | R/W | For TI use only. (Default 4’b0011) | |
| 7 | HS_LOS_MASK (G) |
R/W | 0 | HS Serdes LOS status is used to generate HS channel synchronization status. If HS Serdes indicates LOS, channel synchronization indicates synchronization is not achieved |
| 1 | HS Serdes LOS status is not used to generate HS channel synchronization status (Default 1’b1) | |||
| 6 | RESERVED | R/W | For TI use only. Always reads 0. | |
| 5 | HS_CH_SYNC_OVERLAY (RXG) |
R/W | 0 | LOSA pin does not reflect receive channel loss of block lock (Default 1’b0) |
| 1 | Allows channel loss of block lock to be reflected on LOSA pin | |||
| 4 | HS_INVALID_CODE_OVERLAY (RXG) |
R/W | 0 | LOSA pin does not reflect receive channel invalid code word error (Default 1’b0) |
| 1 | Allows invalid code word error to be reflected on LOSA pin | |||
| 3 | HS_AGCLOCK_OVERLAY (RXG) |
R/W | 0 | 0 = LOSA pin does not reflect HS Serdes AGC unlock status (Default 1’b0) |
| 1 | Allows HS Serdes AGC unlock status to be reflected on LOSApin | |||
| 2 | HS_AZDONE_OVERLAY (RXG) |
R/W | 0 | LOSA pin does not reflect HS Serdes auto zero calibration not done status (Default 1’b0) |
| 1 | Allows auto zero calibration not done status to be reflected on LOSA pin | |||
| 1 | HS_PLL_LOCK_OVERLAY (RXG) |
R/W | 0 | LOSA pin does not reflect loss of HS Serdes PLL lock status (Default 1’b0) |
| R/W | 1 | Allows HS Serdes loss of PLL lock status to be reflected onLOSApin | ||
| 0 | HS_LOS_OVERLAY (RXG) |
R/W | 0 | LOSA pin does not reflect HS Serdes Loss of signal condition (Default 1’b0) |
| 1 | Allows HS Serdes Loss of signal condition to be reflected on LOSA pin |
7.5.2.11 LS_OVERLAY_CONTROL (register: 0x000A) (default: 0x4000)
(device address: 0x1E)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| RESERVED | LS_PLL_LOCK_OVERLAY (RXG) |
LS_CH_SYNC_OVERLAY_LN[3:0] (RXG) |
|||||
| R/W | R/W | R/W | |||||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| LS_INVALID_CODE_OVERLAY_LN[3:0] (RXG) |
LS_LOS_OVERLAY_LN[3:0] (RXG) |
||||||
| R/W | R/W | ||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-32 LS_OVERLAY_CONTROL Field Description
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:13 | RESERVED | R/W | For TI use only (Default 3’b010) | |
| 12 | LS_PLL_LOCK_OVERLAY (RXG) |
R/W | 0 | LOSA pin does not reflect loss of LS SERDES PLL lock status (Default 1’b0) |
| 1 | Allows LS SERDES loss of PLL lock status to be reflected on LOSA pin | |||
| 11:8 | LS_CH_SYNC_OVERLAY_LN[3:0] (RXG) |
R/W | [3] Corresponds to Lane 3, [2] Corresponds to Lane 2 [1] Corresponds to Lane 1, [0] Corresponds to Lane 0 |
|
| 0 | LOSA pin does not reflect LS Serdes lane loss of synchronization condition (Default 1’b0) | |||
| 1 | Allows LS Serdes lane loss of synchronization condition to be reflected on LOSA pin | |||
| 7:4 | LS_INVALID_CODE_OVERLAY_LN[3:0] (RXG) |
R/W | 0 | [3] Corresponds to Lane 3, [2] Corresponds to Lane 2 [1] Corresponds to Lane 1, [0] Corresponds to Lane 0 |
| 0 | LOSA pin does not reflect LS Serdes lane invalid code condition (Default 1’b0) | |||
| 1 | Allows LS Serdes lane invalid code condition to be reflected on LOSA pin | |||
| 3:0 | LS_LOS_OVERLAY_LN[3:0] (RXG) |
R/W | [3] Corresponds to Lane 3, [2] Corresponds to Lane 2 [1] Corresponds to Lane 1, [0] Corresponds to Lane 0 |
|
| R/W | 0 | LOSA pin does not reflect LS Serdes lane Loss of signal condition (Default 1’b0) | ||
| 1 | Allows LS Serdes lane Loss of signal condition to be reflected on LOSA pin |
7.5.2.12 LOOPBACK_TP_CONTROL (register: 0x000B) (default: 0x0D10) (device address: 0x1E)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| RESERVED | HS_TP_GEN_EN (RXG) |
HS_TP_ VERIFY_EN (RXG) |
LS_TEST_PATT _SEL[2] (RXG) |
HS_TEST_PATT _SEL[2:0] (RXG) |
|||
| R/W | R/W | R/W | R/W | R/W | |||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| LS_TP_GEN _EN (RXG) |
LS_TP_VERIFY _EN (RXG) |
LS_TEST_PATT_SEL[1:0] (RXG) |
DEEP_ REMOTE_LPBK (RXG) |
RESERVED | SHALLOW_ LOCAL_ LPBK (RXG) |
||
| R/W | R/W | R/W | R/W | R/W | R/W | ||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-33 LOOPBACK_TP_CONTROL Field Description
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:14 | RESERVED | R/W | For TI use only. (Default 2'b00) | |
| 13 | HS_TP_GEN_EN (RXG) |
R/W | 0 | Normal operation (Default 1’b0) |
| 1 | Activates test pattern generation selected by bits 1E.000B bits 10:8 | |||
| 12 | HS_TP_VERIFY_EN (RXG) |
R/W | 0 | Normal operation (Default 1’b0) |
| 1 | Activates test pattern verification selected by bits 1E.000B bits 10:8 | |||
| 11 | LS_TEST_PATT_SEL[2] (RXG) |
R/W | 0 | See selection in 1E.000B bits 5:4 |
| 10:8 | HS_TEST_PATT_SEL[2:0] (RXG) |
R/W | Test Pattern Selection. Refer to TLK100031 Bringup Procedure (a separate document) for more information. H/L/M/CRPAT valid in 1GKX/10G modes |
|
| 000 | High Frequency Test Pattern | |||
| 001 | Low Frequency Test Pattern | |||
| 010 | Mixed Frequency Test Pattern | |||
| 011 | CRPAT Long | |||
| 100 | CRPAT Short PRBS pattern valid in 1GKX/10G/10GKR modes |
|||
| 101 | 27 - 1 PRBS pattern (Default 3’b101) | |||
| 110 | 223 - 1 PRBS pattern | |||
| 111 | 231 - 1 PRBS pattern Errors can be checked by reading HS_ERROR_COUNT register. For KR standard pattern generation and verification, please refer to Register 03.002A |
|||
| 7 | LS_TP_GEN_EN (RXG) |
R/W | 0 = Normal operation (Default 1’b0) 1 = Activates test pattern generation selected by bits {1E.000B bit 11, 1E.000B bits 5:4} on the LS side |
|
| 6 | LS_TP_VERIFY_EN (RXG) |
R/W | 0 = Normal operation (Default 1’b0) 1 = Activates test pattern verification selected by bits {1E.000B bit 11, 1E.000B bits 5:4} on the LS side |
|
| 5:4 | LS_TEST_PATT_SEL[1:0] (RXG) |
R/W | LS Test Pattern Selection LS_TEST_PATT_SEL[2:0]. LS_TEST_PATT_SEL[2] is 1E.000B bit 11 | |
| 000 | High Frequency Test Pattern | |||
| 001 | Low Frequency Test Pattern | |||
| 010 | Mixed Frequency Test Pattern | |||
| 011 | CRPAT Long (In 1GKX mode only) | |||
| 100 | CRPAT Short (In 1GKX mode only) | |||
| 101 | 27 - 1 PRBS pattern (Default 3’b101) | |||
| 110 | 223 - 1 PRBS pattern | |||
| 111 | 231 - 1 PRBS pattern For XAUI standard test pattern generation and verification in KR mode, please refer register 01.8002 and 01.8003 |
|||
| 3 | DEEP_REMOTE_LPBK (RXG) |
R/W | 0 | 0 = Normal functional mode (Default 1’b0) |
| 1 | Enable deep remote loopback mode | |||
| 2:1 | RESERVED | R/W | For TI use only (Default 1’b0) | |
| 0 | SHALLOW_LOCAL_LPBK (RXG) |
R/W | 0 | Normal functional mode (Default 1’b0) |
| 1 | Enable shallow local loopback mode |
7.5.2.13 LS_CONFIG_CONTROL (register: 0x000C) (default: 0x0330) (device address: 0x1E)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| RESERVED | LS_STATUS_CFG[1:0] (RG) |
RESERVED | RESERVED | ||||
| R/W | R/W | R/W | R/W | ||||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| RESERVED | LS_LOS_MASK (G) |
LS_PLL_LOCK_MASK (G) |
RESERVED | FORCE_LM_REALIGN (G) |
RESERVED | ||
| R/W | R/W | R/W | R/W | R/W | R/W | ||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-34 LS_CONFIG_CONTROL Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:14 | RESERVED | R/W | For TI use only. (Default 2'b00) | |
| 13:12 | LS_STATUS_CFG[1:0] (RG) |
R/W | 0 | Selects selected lane status to be reflected in LS_STATUS_1 register 1E.0015 bit 14 |
| 00 | Lane 0 (Default 2’b00) | |||
| 01 | Lane 1 | |||
| 10 | Lane 2 | |||
| 11 | Lane 3 | |||
| 11:10 | RESERVED | R/W | For TI use only. Always reads 0. | |
| 9:8 | RESERVED | R/W | For TI use only. (Default 2’b11) | |
| 7:6 | RESERVED | R/W | For TI use only. | |
| 5 | LS_LOS_MASK (G) |
R/W | 0 | LS Serdes LOS status of enabled lanes is used to generate link status |
| 1 | LS Serdes LOS status of enabled lanes is not used to generate link status (Default 1’b1) | |||
| 4 | LS_PLL_LOCK_MASK (G) |
R/W | 0 | LS Serdes PLL Lock status is used to generate link status |
| 1 | LS Serdes PLL Lock status is not used to generate link status (Default 1’b1) | |||
| 3 | RESERVED | R/W | For TI use only. Always reads 0. | |
| 2 | FORCE_LM_REALIGN (G) |
R/W | 0 | Normal operation (Default 1’b0) |
| 1 | Force lane realignment in Link status monitor | |||
| 1:0 | RESERVED | R/W | For TI use only |
7.5.2.14 LS_CONFIG_CONTROL (register: 0x000C) (default: 0x0330) (device address: 0x1E)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| RESERVED | LS_STATUS_CFG[1:0] (RG) |
RESERVED | RESERVED | ||||
| R/W | R/W | R/W | R/W | ||||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| RESERVED | LS_LOS_MASK (G) |
LS_PLL_LOCK_MASK (G) |
RESERVED | FORCE_LM_REALIGN (G) |
RESERVED | ||
| R/W | R/W | R/W | R/W | R/W | R/W | ||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-35 LS_CONFIG_CONTROL Field Description
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:14 | RESERVED | R/W | For TI use only. (Default 2'b00) | |
| 13:12 | LS_STATUS_CFG[1:0] (RG) |
R/W | Selects selected lane status to be reflected in LS_STATUS_1 register 1E.0015 bit 14 | |
| 00 | Lane 0 (Default 2’b00) | |||
| 01 | Lane 1 | |||
| 10 | Lane 2 | |||
| 11 | Lane 3 | |||
| 11:10 | RESERVED | R/W | For TI use only. Always reads 0. | |
| 9:8 | RESERVED | R/W | For TI use only. (Default 2’b11) | |
| 7:6 | RESERVED | R/W | For TI use only. | |
| 5 | LS_LOS_MASK (G) |
R/W | 0 | LS Serdes LOS status of enabled lanes is used to generate link status |
| 1 | LS Serdes LOS status of enabled lanes is not used to generate link status (Default 1’b1) | |||
| 4 | LS_PLL_LOCK_MASK (G) |
R/W | 0 | LS Serdes PLL Lock status is used to generate link status |
| 1 | LS Serdes PLL Lock status is not used to generate link status (Default 1’b1) | |||
| 3 | RESERVED | R/W | For TI use only. Always reads 0. | |
| 2 | FORCE_LM_REALIGN (G) |
R/W | 0 | Normal operation (Default 1’b0) |
| 1 | Force lane realignment in Link status monitor | |||
| 1:0 | RESERVED | R/W | For TI use only |
7.5.2.15 CLK_CONTROL (register: 0x000D) (default: 0x2F80) (device address: 0x1E)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| RESERVED | CLKOUT_ EN (RXG) |
CLKOUT_POWERDOWN (RXG) |
RESERVED | ||||
| R/W | R/W | R/W | R/W | ||||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| CLKOUT_DIV[3:0] (RXG) |
RCLKOUT_SEL[3:0] (RXG) |
||||||
| R/W | R/W | ||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-36 CLK_CONTROL Field Description
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:14 | RESERVED | R/W | For TI use only. Always reads 0. | |
| 13 | CLKOUT_ EN (RXG) |
R/W | Output clock enable. | |
| 0 | Holds CLKOUTx_P/N output to a fixed value. | |||
| 1 | Allows CLKOUTx_P/N output to toggle normally. (Default 1’b1) | |||
| 12 | CLKOUT_POWERDOWN (RXG) |
R/W | 0 | Normal operation (Default 1’b0) |
| 1 | Enable CLKOUTx_P/N Power Down. | |||
| 11:8 | RESERVED | R/W | For TI use only. (Default 4'b1111) | |
| 7:4 | CLKOUT_DIV[3:0] (RXG) |
R/W | CLKOUT Output clock divide setting. This value is used to divide selected clock (Selected using CLKOUT_SEL) before giving it out onto respective channel CLKOUTA_P/N. | |
| 0000 | 0000 = Divide by 1 | |||
| 0001 | Reserved | |||
| 0010 | Reserved | |||
| 0011 | Reserved | |||
| 0100 | Divide by 2 | |||
| 0101 | Reserved | |||
| 0110 | Reserved | |||
| 0111 | Reserved | |||
| 1000 | Divide by 4 (Default 4'b1000) | |||
| 1001 | Divide by 8 | |||
| 1010 | Divide by 16 | |||
| 1011 | Reserved | |||
| 1100 | Divide by 5 | |||
| 1101 | Divide by 10 | |||
| 1110 | Divide by 20 | |||
| 1111 | Divide by 25 | |||
| 3:0 | CLKOUT_SEL[3:0] (RXG) |
R/W | CLKOUT Output clock select. Selects Recovered clock sent out on CLKOUTx_P/N pins (Default 4'b0000) | |
| 00x0 | Selects HS recovered byte clock as output clock | |||
| 00x1 | Selects HS transmit byte clock as output clock | |||
| 010x | Selects HSRX VCO divide by 4 clock as output clock | |||
| 0110 | Selects LS recovered byte clock as output clock | |||
| 0111 | Selects LS transmit byte clock as output clock | |||
| 10x0 | Reserved | |||
| 10x1 | Reserved | |||
| 110x | Reserved | |||
| 1110 | Reserved | |||
| 1111 | Reserved |
7.5.2.16 RESET_CONTROL (register: 0x000E) (default: 0x0000) (device address: 0x1E)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| RESERVED | |||||||
| R/W | |||||||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| RESERVED | DATAPATH_ RESET (RXG) |
TXFIFO_ RESET (G) |
RXFIFO_ RESET (G) |
RESERVED | |||
| R/W | R/W SC(1) |
R/W SC(1) |
R/W SC(1) |
R/W | |||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-37 RESET_CONTROL Field Description
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:8 | RESERVED | R/W | For TI use only. Always reads 0. | |
| 7:4 | RESERVED | R/W | For TI use only. (Default 4'b0000) | |
| 3 | DATAPATH_RESET (RXG) |
R/W SC | Channel datapath reset control. Required once the desired functional mode is configured. | |
| 0 | Normal operation. (Default 1’b0) | |||
| 1 | Resets channel logic excluding MDIO registers. (Resets both Tx and Rx datapath) | |||
| 2 | TXFIFO_RESET (G) |
R/W SC | Transmit FIFO reset control. Applicable in 10G mode only. Not required in 10GKR mode as 10GKR FIFO is self centering. | |
| 0 | Normal operation. (Default 1’b0) | |||
| 1 | Resets transmit datapath FIFO. | |||
| 1 | RXFIFO_RESET (G) |
R/W SC | Receive FIFO reset control. Applicable in 10G mode only. Not required in 10GKR mode as 10GKR FIFO is self centering. | |
| 0 | Normal operation. (Default 1’b0) | |||
| 1 | Resets receive datapath FIFO. | |||
| 0 | RESERVED | R/W | For TI use only. (Default 1'b0) |
7.5.2.17 CHANNEL_STATUS_1 (register: 0x000F) (default: 0x0000) (device address: 0x1E)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| HS_TP_STATUS (XG) |
LS_ALIGN_STATUS (RXG) |
HS_LOS (RXG) |
HS_AZ_DONE (RXG) |
HS_AGC_LOCKED (RXG) |
HS_CHANNEL_SYNC (RXG) |
RESERVED | HS_DECODE_INVALID (RXG) |
| R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R |
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| TX_FIFO_UNDERFLOW (RG) |
TX_FIFO_OVERFLOW (RXG) |
RX_FIFO_UNDERFLOW (RG) |
RX_FIFO_OVERFLOW (RXG) |
RX_LS_OK (G) |
TX_LS_OK (G) |
LS_PLL_LOCK (RXG) |
HS_PLL_LOCK (RXG) |
| R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R |
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-38 CHANNEL_STATUS_1 Field Description
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | HS_TP_STATUS (XG) |
R | Test Pattern status for High/Low/Mixed/CRPAT test patterns. Valid in 10G/1GKX modes. | |
| 0 | Alignment has not been determined | |||
| 1 | Alignment has achieved and correct pattern has been received. Any bit errors are reflected in HS_ERROR_COUNTER register (0x10) | |||
| 14 | LS_ALIGN_STATUS (RXG) |
R | Lane alignment status | |
| 0 | Lane alignment is achieved on the LS side | |||
| 1 | Lane alignment is not achieved on the LS side | |||
| 13 | HS_LOS (RXG) |
R | Loss of Signal Indicator. When high, indicates that a loss of signal condition is detected on HS serial receive inputs |
|
| 12 | HS_AZ_DONE (RXG) |
R | Auto zero complete indicator. When high, indicates auto zero calibration is complete |
|
| 11 | HS_AGC_LOCKED (RXG) |
R | Adaptive gain control loop lock indicator. When high, indicates AGC loop is in locked state |
|
| 10 | HS_CHANNEL_SYNC (RXG) |
R | Channel synchronization status indicator. When high, indicates channel synchronization has achieved |
|
| 9 | RESERVED | R | For TI use only. | |
| 8 | HS_DECODE_INVALID (RXG) |
R | Valid when decoder is enabled and during CRPAT test pattern verification. When high, indicates decoder received an invalid code word, or a 8b/10b disparity error. In functional mode, number of DECODE_INVALID errors are reflected in HS_ERROR_COUNTER register (0x10) | |
| 7 | TX_FIFO_UNDERFLOW (RG) |
R | Not applicable in 1GKX mode. When high, indicates underflow has occurred in the transmit datapath (CTC) FIFO. | |
| 6 | TX_FIFO_OVERFLOW (RXG) |
R | When high, in 10GKR and 10G modes indicates overflow has occurred in the transmit datapath (CTC) FIFO. | |
| 5 | RX_FIFO_UNDERFLOW (RG) |
R | Not applicable in 1GKX mode. When high, indicates underflow has occurred in the receive datapath (CTC) FIFO. | |
| 4 | RX_FIFO_OVERFLOW (RXG) |
R | In 10GKR and 10G modes, high indicates overflow has occurred in the receive datapath (CTC) FIFO. In 1G-KX mode, high indicates a FIFO error. | |
| 3 | RX_LS_OK (G) |
R | Receive link status indicator from system side. Applicable in 10G mode only When high, indicates receive link status is achieved on the system side . | |
| 2 | TX_LS_OK (G) |
R | Link status indicator from Lane alignment/Link training slave inside TLK10031. When high, indicates 10G Link align achieved sync and alignment . | |
| 1 | LS_PLL_LOCK (RXG) |
R | LS Serdes PLL lock indicator When high, indicates LS Serdes PLL achieved lock to the selected incoming REFCLK0/1_P/N |
|
| 0 | HS_PLL_LOCK (RXG) |
R | HS Serdes PLL lock indicator When high, indicates HS Serdes PLL achieved lock to the selected incoming REFCLK0/1_P/N |
7.5.2.18 HS_ERROR_COUNTER (register: 0x0010) (default: 0x0FFFD) (device address: 0x1E)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| HS_ERR_COUNT[15:0] (RXG) |
|||||||||||||||
| COR | |||||||||||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-39 HS_ERROR_COUNTER Field Description
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:0 | HS_ERR_COUNT[15:0] (RXG) |
COR | 0 | In functional mode, this counter reflects number of invalid code words (includes disparity errors) received by decoder. In 10GKR mode, reading this register also clears value in 03.0021 bits 7:0. In 10GKR mode, default value for this register is 16’h0000. In HS test pattern verification mode , this counter reflects error count for the test pattern selected through 1E.000B bits 10:8 When PRBS_EN pin is set, this counter reflects error count for selected PRBS pattern. Counter value cleared to 16’h0000 when read. |
7.5.2.19 LS_LN0_ERROR_COUNTER (register: 0x0011) (default: 0xFFFD) (device address: 0x1E)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| LS_LN0_ERR_COUNT[15:0] (RXG) |
|||||||||||||||
| COR | |||||||||||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-40 LS_LN0_ERROR_COUNTER Field Description
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:0 | LS_LN0_ERR_COUNT[15:0] (RXG) |
COR | 0 | Lane 0 Error counter In 10GKR/1GKX functional modes, this counter reflects number of invalid code words (includes disparity errors) received by decoder In 10G functional mode, this counter reflects number of invalid code words (includes disparity errors) received by decoder in lane alignment slave. In LS test pattern verification mode , this counter reflects error count for the test pattern selected through 1E.000B bits 5:4 Counter value cleared to 16’h0000 when read. |
7.5.2.20 LS_LN1_ERROR_COUNTER (register: 0x0012 ) (default: 0xFFFD) (device address: 0x1E)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| LS_LN1_ERR_COUNT[15:0] (RG) |
|||||||||||||||
| COR | |||||||||||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-41 LS_LN1_ERROR_COUNTER Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:0 | LS_LN1_ERR_COUNT[15:0] (RG) |
COR | Lane 1 Error counter In 10GKR/1GKX functional modes, this counter reflects number of invalid code words (includes disparity errors) received by decoder In 10G functional mode, this counter reflects number of invalid code words (includes disparity errors) received by decoder in lane alignment slave. In LS test pattern verification mode , this counter reflects error count for the test pattern selected through 1E.000B bits 5:4 Counter value cleared to 16’h0000 when read. |
7.5.2.21 LS_LN2_ERROR_COUNTER (register: 0x0013) (default: 0xFFFD) (device address: 0x1E)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| LS_LN2_ERR_COUNT[15:0] (RG) |
|||||||||||||||
| COR | |||||||||||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-42 LS_LN2_ERROR_COUNTER Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:0 | LS_LN2_ERR_COUNT[15:0] (RG) |
COR | 0 | Lane 2 Error counter In 10GKR/1GKX functional modes, this counter reflects number of invalid code words (includes disparity errors) received by decoder In 10G functional mode, this counter reflects number of invalid code words (includes disparity errors) received by decoder in lane alignment slave. In LS test pattern verification mode , this counter reflects error count for the test pattern selected through 1E.000B bits 5:4 Counter value cleared to 16’h0000 when read. |
7.5.2.22 LS_LN3_ERROR_COUNTER (register: 0x0014) (default: 0xFFFD) (device address: 0x1E)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| LS_LN3_ERR_COUNT[15:0] (RG) |
|||||||||||||||
| COR | |||||||||||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-43 LS_LN3_ERROR_COUNTER Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:0 | LS_LN3_ERR_COUNT[15:0] (RG) |
COR | 0 | Lane 3 Error counter In 10GKR/1GKX functional modes, this counter reflects number of invalid code words (includes disparity errors) received by decoder In 10G functional mode, this counter reflects number of invalid code words (includes disparity errors) received by decoder in lane alignment slave. In LS test pattern verification mode , this counter reflects error count for the test pattern selected through 1E.000B bits 5:4 Counter value cleared to 16’h0000 when read. |
7.5.2.23 LS_STATUS_1 (register: 0x0015) (default: 0x0000) (device address: 0x1E)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| RESERVED | LS_INVALID_DECODE (RXG) |
LS_LOS (RXG) |
LS_LN_ALIGN_FIFO_ERR (RG) |
LS_CH_SYNC_STATUS (RXG) |
|||
| RO | RO/LH | RO/LH | RO/LH | RO/LL | |||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| RESERVED | LS_CHSYNC_ROT[3:0] (RXG) | ||||||
| RO | RO | ||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-44 LS_STATUS_1 Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:12 | RESERVED | RO | For TI use only. | |
| 11 | LS_INVALID_DECODE (RXG) |
RO/LH | 0 | LS Invalid decode error for selected lane. Lane can be selected through LS_STATUS_CFG[1:0] (Register 1E.000C). Error count for each lane can also be monitored through respective LS_LNx_ERR_COUNT registers |
| 10 | LS_LOS (RXG) |
RO/LH | 0 | Loss of Signal Indicator. When high, indicates that a loss of signal condition is detected on LS serial receive inputs for selected lane. Lane can be selected through LS_STATUS_CFG[1:0] (Register 1E.000C) |
| 9 | LS_LN_ALIGN_FIFO_ERR (RG |
RO/LH | 0 | LS Lane alignment FIFO error status 1 = Lane alignment FIFO on LS side has error 0 = Lane alignment FIFO on LS side has no error |
| 8 | LS_CH_SYNC_STATUS (RXG) |
RO/LH | 0 | LS Channel sync status for selected lane. Lane can be selected through LS_STATUS_CFG[1:0] (Register 1E.000C) |
| 7:4 | RESERVED | RO | For TI use only. | |
| 3:0 | LS_CHSYNC_ROT[3:0] (RXG) |
RO/LH | 0 | Channel synchronization pointer on LS side. Required for latency measurement function. See Latency Measurement function section for more details. |
7.5.2.24 HS_STATUS_1 (register: 0x0016) (default: 0x0000) (device address: 0x1E)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| RESERVED | |||||||
| RO | |||||||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| RESERVED | HS_KR_CH_SYNC_ROT[6:4] (RXG) |
HS_KR_CH_SYNC_ROT[3:0] (RXG) |
|||||
| RO | RO | RO | |||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-45 HS_STATUS_1 Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:7 | RESERVED | RO | For TI use only. | |
| 6:4 | HS_KR_CH_SYNC_ROT[6:4] (RXG) |
RO | Channel synchronization pointer on HS side in 10GKR mode. Required for latency measurement function. See Latency Measurement function section for more details. In 10GKR mode, [6:4] reflects 3 MSB’s of 7 bit HS sync rotation. In 1GKX and 10G modes, indicates channel synchronization state on HS side. |
|
| 3:0 | HS_KR_CH_SYNC_ROT[3:0] (RXG) |
RO | Channel synchronization pointer on HS side. Required for latency measurement function. See Latency Measurement function section for more details. In 10GKR mode, reflects 4 LSB’s of 7 bit HS sync rotation. In 10G and 1GKX modes, reflects 4 bit HS sync rotation. |
7.5.2.25 DST_CONTROL_1 (register = 0x0017) (default = 0x2000) (device address: 0x1E)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| RESERVED | DST_PIN_SW_EN (RXG) |
DST_PIN_SW_SRC_1[1:0] (RXG) |
DST_PIN_SW_SRC_0[1:0] (RXG) |
||||
| RW | RW | RW | RW | ||||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| DST_OFF_SEL (RX) |
DST_ON_SEL (RX) |
DST_STUFF_SEL (RX) |
RESERVED | ||||
| RW | RW | RW | RW | ||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-46 DST_CONTROL_1 Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:13 | RESERVED | RW | For TI use only (Default 3'b001) | |
| 12 | DST_PIN_SW_EN (RXG) |
RW | 1 = Enable pin switch feature using top level pin. Ignore MDIO software switch. Requires setting PRTAD0_PIN_EN to high and setting PRTAD0_PIN_EN_SEL to control applicable channel Tx data switch. 0 = Disable pin switch feature. Only MDIO software switch is used (Default 1’b0) |
|
| 11:10 | DST_PIN_SW_SRC_1[1:0] (RXG) |
RW | Applicable when top level pin (PRTAD0) is assigned to control transmit data switch source input and if PRTAD0 is HIGH. 00 = Select LS input(Default 2’b00) 01 = Select HS input 10 = Reserved 11 = Reserved |
|
| 9:8 | DST_PIN_SW_SRC_0[1:0] (RXG) |
RW | Applicable when top level pin (PRTAD0) is assigned to control transmit data switch source input and if PRTAD0 is LOW. 00 = Select LS input(Default 2’b00) 01 = Select HS input 10 = Reserved 11 = Reserved |
|
| 7 | DST_OFF_SEL (RX) |
RW | Applicable only in KR & KX modes. Selects data pattern to trigger OFF condition (Default 1’b0) KR Mode: 1 = Local Fault (0x0100009c) 0 = IDLE (0x07 on all lanes) KX Mode: 1 = Match DST_OFF_CHAR specified in 1E.802AB 0 = IDLE (Either /I1/ or /I2/) |
|
| 6 | DST_ON_SEL (RX) |
RW | Applicable only in KR & KX modes. Selects data pattern to trigger ON condition (Default 1’b0) KR Mode: 1 = Local Fault (0x0100009c) 0 = IDLE (0x07 on all lanes) KX Mode: 1 = Match DST_ON_CHAR specified in 1E.802A 0 = IDLE (Either /I1/ or /I2/) |
|
| 5 | DST_STUFF_SEL (RX) |
RW | Applicable only in KR & KX modes. Selects data pattern to stuff the output during data switching (Default 1’b0) KR Mode: 1 = Local Fault (0x0100009c) 0 = IDLE (0x07 on all lanes) KX Mode: 1 = /V/ Error propagation (K30.7) 0 = /I2/ (/K28.5/D16.2/) |
|
| 4:0 | RESERVED | RW | For TI use only (Default 5’b00000) |
7.5.2.26 DST_CONTROL_2 (register = 0x0018 ) (default = 0x0C20) (device address: 0x1E)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| DST_DATA_SRC_SEL[1:0] (RXG) | DST_DATA_SW_MODE[1:0] (RXG) | RESERVED | |||||
| RW | RW | RW | |||||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| DST_MASK_CYCLES[7:0] (RXG) | |||||||
| RW | |||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-47 DST_CONTROL_2 Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:14 | DST_DATA_SRC_SEL[1:0] (RXG) |
RW | Data selection for transmit data switch source input. Applicable when DST_PIN_SW_EN is LOW. 00 = Select LS input(Default 2’b00) 01 = Select HS input 10 = Reserved 11 = Reserved |
|
| 13:12 | DST_DATA_SW_MODE[1:0] (RXG) |
RW | Selects condition to trigger data switch for the selected ON/OFF condition. (Default 2’b00) OFF condition: 00 = Wait for OFF trigger 01 = Any data 10 = Any data 11 = Wait for OFF trigger ON condition: 00 = Wait for ON trigger 01 = Wait for ON trigger 10 = Any data 11 = Any data |
|
| 11:8 | RESERVED | RW | For TI use only (Default 4’b1100) | |
| 7:0 | DST_MASK_CYCLES[7:0] (RXG) |
RW | Duration of clock cycles that the data-switch output data is masked with the data pattern selected through DST_STUFF_SEL. (Default 8’b0010_0000) |
7.5.2.27 DSR_CONTROL_1 (register = 0x0019) (default = 0x2500) (device address: 0x1E)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| RESERVED | DSR_PIN_SW_ EN (RXG) |
DSR_PIN_SW_SRC_1[1:0] (RXG) |
DSR_PIN_SW_SRC_0[1:0] (RXG) |
||||
| RW | RW | RW | RW | ||||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| DSR_OFF_ SEL (RX) |
DSR_ON_SEL (RX) |
DSR_STUFF_SEL (RX) |
RESERVED | ||||
| RW | RW | RW | RW | ||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-48 DSR_CONTROL_1 Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:13 | RESERVED | RW | For TI use only (Default 3'b001) | |
| 12 | DSR_PIN_SW_EN (RXG) |
RW | 1 = Enable pin switch feature using top level pin. Ignore MDIO software switch. Requires setting PRTAD0_PIN_EN to high and setting PRTAD0_PIN_EN_SEL to control Rx data switch. 0 = Disable pin switch feature. Only MDIO software switch is used (Default 1’b0) |
|
| 11:10 | DSR_PIN_SW_SRC_1[1:0] (RXG) |
RW | Applicable when top level pin (PRTAD0) is assigned to control receive data switch source input and if PRTAD0 is HIGH. 00 = Select LS input 01 = Select HS input(Default 2’b01) 10 = Reserved 11 = Reserved |
|
| 9:8 | DSR_PIN_SW_SRC_0[1:0] (RXG) |
RW | Applicable when top level pin (PRTAD0) is assigned to control receive data switch source input and if PRTAD0 is LOW. 00 = Select LS input 01 = Select HS input(Default 2’b01) 10 = Reserved 11 = Reserved |
|
| 7 | DSR_OFF_SEL (RX) |
RW | Applicable only in KR & KX modes. Selects data pattern to trigger OFF condition (Default 1’b0) KR Mode: 1 = Local Fault (0x0100009c) 0 = IDLE (0x07 on all lanes) KX Mode: 1 = Match DSR_OFF_CHAR specified in 1E.802E 0 = IDLE (Either /I1/ or /I2/) |
|
| 6 | DSR_ON_SEL (RX) |
RW | Applicable only in KR & KX modes. Selects data pattern to trigger ON condition (Default 1’b0) KR Mode: 1 = Local Fault (0x0100009c) 0 = IDLE (0x07 on all lanes) KX Mode: 1 = Match DSR_ON_CHAR specified in 1E.802D 0 = IDLE (Either /I1/ or /I2/) |
|
| 5 | DSR_STUFF_SEL (RX) |
RW | Applicable only in KR & KX modes. Selects data pattern to stuff the output during data switching (Default 1’b0) KR Mode: 1 = Local Fault (0x0100009c) 0 = IDLE (0x07 on all lanes) KX Mode: 1 = /V/ Error propagation (K30.7) 0 = /I2/ (/K28.5/D16.2/) |
|
| 4:0 | RESERVED | RW | For TI use only (Default 5’b00000) |
7.5.2.28 DSR_CONTROL_2 (register = 0x001A) (default = 0x4C20) (device address: 0x1E)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| DSR_DATA_SRC_SEL[1:0] (RXG) | SR_DATA_SW_MODE[1:0] (RXG) | RESERVED | |||||
| RW | RW | RW | |||||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| DSR_MASK_CYCLES[7:0] (RXG) | |||||||
| RW | |||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-49 DSR_CONTROL_2 Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:14 | DSR_DATA_SRC_SEL[1:0] (RXG) |
RW | Data selection for receive data switch source input. Applicable when DST_PIN_SW_EN is LOW. 00 = Select LS input 01 = Select HS input(Default 2’b01) 10 = Reserved 11 = Reserved |
|
| 13:12 | DSR_DATA_SW_MODE[1:0] (RXG) |
RW | Selects condition to trigger data switch for the selected ON/OFF condition. (Default 2’b00) OFF condition: 00 = Wait for OFF trigger 01 = Any data 10 = Any data 11 = Wait for OFF trigger ON condition: 00 = Wait for ON trigger 01 = Wait for ON trigger 10 = Any data 11 = Any data |
|
| 11:8 | RESERVED | RW | For TI use only (Default 4’b1100) |
7.5.2.29 DATA_SWITCH_STATUS (register = 0x001B) (default = 0x1020) (device address: 0x1E)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| DST_EN[3:0] (RXG) |
DST_SW_PENDING (RXG) |
DST_SW_DONE (RXG) |
DST_ON (RXG) |
DST_OFF (RXG) |
|||
| RO | RO | RO | RO | RO | |||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| DSR_EN[3:0] (RXG) |
DSR_SW_PENDING (RXG) |
DSR_SW_DONE (RXG) |
DSR_ON (RXG) |
DSR_OFF (RXG) |
|||
| RO | RO | RO | RO | RO | |||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-50 DATA_SWITCH_STATUS Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:12 | DST_EN[3:0] (RXG) |
RO | Source input data selection status on transmit side. 0001 = LS data 0010 = HS data 0100 = Reserved 1000 = Reserved |
|
| 11 | DST_SW_PENDING (RXG) |
RO | When HIGH, indicates data switching event is pending to be completed in the transmit side based on selected data source input | |
| 10 | DST_SW_DONE (RXG) |
RO | When HIGH, indicates data switching event has occurred in the transmit side based on selected data source input | |
| 9 | DST_ON (RXG) |
RO | ON condition indicator from transmit data switch. When HIGH, indicates an ON condition has occurred in transmit data switch | |
| 8 | DST_OFF (RXG) |
RO | OFF condition indicator from transmit data switch. When HIGH, indicates an OFF condition has occurred in transmit data switch. | |
| 7:4 | DSR_EN[3:0] (RXG) |
RO | Source input data selection status on receive side. 0001 = LS data 0010 = HS data 0100 = Reserved 1000 = Reserved |
|
| 3 | DSR_SW_PENDING (RXG) |
RO | When HIGH, indicates data switching event is pending to be completed in the receive side based on selected data source input | |
| 2 | DSR_SW_DONE (RXG) |
RO | When HIGH, indicates data switching event has occurred in the receive side based on selected data source input | |
| 1 | DSR_ON (RXG) |
RO | ON condition indicator from receive data switch. When HIGH, indicates an ON condition has occurred in receive data switch. | |
| 0 | DSR_OFF (RXG) |
RO | OFF condition indicator from receive data switch. When HIGH, indicates an OFF condition has occurred in receive data switch. |
7.5.2.30 LS_CH_CONTROL_1 (register =0x001C) (default =0x0000) (device address: 0x1E)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| RESERVED | |||||||
| RW | |||||||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| RESERVED | RESERVED | RESERVED | LS_CH_SYNC_HYS_SEL[1:0] (RG) |
||||
| RW | RW | RW | RW | ||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-51 LS_CH_CONTROL_1 Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:7 | RESERVED | RW | For TI use only. Always reads 0. | |
| 6 | RESERVED | RW | For TI use only. (Default 1'b0) | |
| 5:2 | RESERVED | RW | For TI use only. (Default 4'b0000) | |
| 1:0 | LS_CH_SYNC_HYS_SEL[1:0] (RG) |
RW | LS Channel synchronization hysteresis selection for selected lane. Lane can be selected in LS_SERDES_CONTROL_1. 00 = The channel synchronization, when in the synchronization state, performs the Ethernet standard specified hysteresis to return to the LOS state (Default 2’b00) 01 = A single 8b/10b invalid decode error or disparity error causes the channel synchronization state machine to immediately transition from sync to LOS 10 = Two adjacent 8b/10b invalid decode errors or disparity errors cause the channel synchronization state machine to immediately transition from sync to LOS 11 = Three adjacent 8b/10b invalid decode errors or disparity errors cause the channel synchronization state machine to immediately transition from sync to LOS |
7.5.2.31 HS_CH_CONTROL_1 (register = 0x001D) (default = 0x0000) (device address: 0x1E)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| RESERVED | REFCLK_FREQ_SEL_1 (RX) |
REFCLK_FREQ_SEL_0 (RXG) |
RX_CTC_BYPASS (RX) |
TX_CTC_BYPASS (RX) |
RESERVED | ||
| RW | RW | RW | RW | RW | RW | ||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| RESERVED | HS_ENC_BYPASS (RXG) |
HS_DEC_BYPASS (RXG) |
HS_CH_SYNC_HYSTERESIS[1:0] (RXG) |
||||
| RW | RW | RW | RW | ||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-52 HS_CH_CONTROL_1 Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:14 | RESERVED | RW | For TI use only (Default 2’b00) | |
| 13 | REFCLK_FREQ_SEL_1 (RX) |
RW | Input REFCLK frequency selection MSB. When set, HS_PLL_MULT, LS_MPY and HS/LS TX/RX RATE settings can be set through related control bits specified in registers 1E.0002, 1E.0003, 1E.0006 0 = HS_PLL_MULT, LS_MPY and HS/LS TX/RX RATE are set automatically based on input REFCLK frequency as specified in REFCLK_FREQ_SEL_0(1E.001D bit 12) (Default 1’b0) 1 = Set this value if HS_PLL_MULT, LS_MPY and HS/LS TX/RX RATE values are NOT to be set automatically. |
|
| 12 | REFCLK_FREQ_SEL_0 (RXG) |
RW | Input REFCLK frequency selection LSB. Applicable when REFCLK_FREQ_SEL_1(1E.001D bit 13) is set to 0. 0 = Set this value if REFCLK frequency is 156.25 MHz (Default 1’b0) 1 = Set this value if REFCLK frequency is 312.5 MHz |
|
| 11 | RX_CTC_BYPASS (RX) |
RW | 0 = Normal operation. (Default 1’b0) 1 = Disables RX CTC operation. |
|
| 10 | TX_CTC_BYPASS (RX) |
RW | 0 = Normal operation. (Default 1’b0) 1 = Disables TX CTC operation. |
|
| 9:4 | RESERVED | RW | For TI use only (Default 4’b0000) | |
| 3 | HS_ENC_BYPASS (RXG) |
RW | 0 = Normal operation. (Default 1’b0) 1 = Disables 8B/10B encoder on HS side. |
|
| 2 | HS_DEC_BYPASS (RXG) |
RW | 0 = Normal operation. (Default 1’b0) 1 = Disables 8B/10B decoder on HS side. |
|
| 1:0 | HS_CH_SYNC_HYSTERESIS[1:0] (RXG) |
RW | Channel synchronization hysteresis control on the HS receive channel. 00 = The channel synchronization, when in the synchronization state, performs the Ethernet standard specified hysteresis to return to the unsynchronized state (Default 2’b00) 01 = A single 8b/10b invalid decode error or disparity error causes the channel synchronization state machine to immediately transition from sync to unsync 10 = Two adjacent 8b/10b invalid decode errors or disparity errors cause the channel synchronization state machine to immediately transition from sync to unsync 11 = Three adjacent 8b/10b invalid decode errors or disparity errors cause the channel synchronization state machine to immediately transition from sync to unsync |
7.5.2.32 EXT_ADDRESS_CONTROL (register = 0x001E) (default = 0x0000) (device address: 0x1E)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| EXT_ADDR_CONTROL[15:0] (XG) |
|||||||||||||||
| RW | |||||||||||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-53 EXT_ADDRESS_CONTROL Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:0 | EXT_ADDR_CONTROL[15:0] (XG) |
RW | Applicable in Clause 22 mode only. This register should be written with the extended register address to be written/read. Contents of address written in this register can be accessed from Reg 1E.0x001F (Default 16’h0000) |
7.5.2.33 EXT_ADDRESS_DATA (register = 0x001F) (default = 0x0000) (device address: 0x1E)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| EXT_ADDR_DATA[15:0] (XG) |
|||||||||||||||
| RW | |||||||||||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-54 EXT_ADDRESS_DATA Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:0 | EXT_ADDR_DATA[15:0] (XG) |
RW | Applicable in Clause 22 mode only. This register contains the data associated with the register address written in Register 1E.0x001E |
The registers below can be accessed directly through Clause 45 or indirectly through Clause 22. Contains mode specific control/status registers.
7.5.2.34 VS_10G_LN_ALIGN_ACODE_P (register =0x8003) (default = 0x0283)
(device address: 0x1E)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| RESERVED | LN_ALIGN_ACODE_P[9:0] (G) | ||||||||||||||
| RW | RW | ||||||||||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-55 VS_10G_LN_ALIGN_ACODE_P Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:10 | RESERVED | RW | For TI use only. Always reads 0. | |
| 9:0 | LN_ALIGN_ACODE_P[9:0] (G) |
RW | 10 bit Alignment character to be matched (Default 10’h283) |
7.5.2.35 VS_10G_LN_ALIGN_ACODE_N (register =0x8004 ) (default = 0x017C)
(device address: 0x1E)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| RESERVED | LN_ALIGN_ACODE_N[9:0] (G) |
||||||||||||||
| RW | RW | ||||||||||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-56 VS_10G_LN_ALIGN_ACODE_N Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:10 | RESERVED | RW | For TI use only. Always reads 0. | |
| 9:0 | LN_ALIGN_ACODE_N[9:0] (G) |
RW | 10 bit Alignment character to be matched (Default 10’h17C) |
7.5.2.36 MC_AUTO_CONTROL (register = 0x8021) (default = 0x000F) (device address: 0x1E)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| RESERVED | |||||||
| RW | |||||||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| RESERVED | HS_PLL_LOCK_CHECK_ DISABLE (RXG) |
HS_LOS_CHECK_ DISABLE (RXG) |
SYNC_STATUS_CHECK _DISABLE (RXG) |
CLKOUT_EN_AUTO _DISABLE (RXG) |
RESERVED | ||
| RW | RW | RW | RW | RW | RW | ||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-57 MC_AUTO_CONTROL Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:7 | RESERVED | RW | For TI use only. Always reads 0. | |
| 6 | HS_PLL_LOCK_CHECK_DISABLE (RXG) |
RW | 1 = Disable auto HS PLL lock status check. 0 = Enable auto HS PLL lock status check (Default 1’b0) |
|
| 5 | HS_LOS_CHECK_DISABLE (RXG) |
RW | 1 = Disable auto HS LOS status check 0 = Enable auto HS LOS sync status check (Default 1’b0) |
|
| 4 | SYNC_STATUS_CHECK_DISABLE (RXG) |
RW | This bit needs to be set to 1 for PRBS testing. 1 = Disable auto sync status check. 0 = Enable auto sync status check (Default 1'b0) |
|
| 3 | CLKOUT_EN_AUTO_DISABLE (RXG) |
RW | This bit controls the signal which flat lines CLKOUT and applicable only when CLKOUT is selected to have HS Recovered byte clock 1 = CLKOUT clock flat lined if HS LOS is detected (Default 1’b1) 0 = CLKOUT clock not flat lined if HS LOS is detected |
|
| 2:0 | RESERVED | RW | For TI use only (Default 3’b111) |
7.5.2.37 DST_ON_CHAR_CONTROL (register = 0x802A) (default = 0x02FD)
(device address: 0x1E)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| RESERVED | DST_ON_CHAR[9:0] (XG) |
||||||||||||||
| RW | RW | ||||||||||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-58 DST_ON_CHAR_CONTROL Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:10 | RESERVED | RW | For TI use only. Always reads 0. | |
| 9:0 | DST_ON_CHAR[9:0] (XG) |
RW | Applicable only in 1GKX and 10G modes. 10 bit data pattern to trigger ON condition if matched on transmit side (Default 10’h2FD) |
7.5.2.38 DST_OFF_CHAR_CONTROL (register = 0x802B ) (default = 0x02FD)
(device address: 0x1E)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| RESERVED | DST_OFF_CHAR[9:0] (XG) | ||||||||||||||
| RW | RW | ||||||||||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-59 DST_OFF_CHAR_CONTROL Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:10 | RESERVED | RW | For TI use only. Always reads 0. | |
| 9:0 | DST_OFF_CHAR[9:0] (XG) |
RW | Applicable only in 1GKX and 10G modes. 10 bit data pattern to trigger OFF condition if matched on transmit side (Default 10’h2FD) |
7.5.2.39 DST_STUFF_CHAR_CONTROL (register = 0x802C) (default = 0x0207)
(device address: 0x1E)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| RESERVED | DST_STUFF_CHAR[9:0] (G) |
||||||||||||||
| RW | RW | ||||||||||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-60 DST_STUFF_CHAR_CONTROL Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:10 | RESERVED | RW | For TI use only. Always reads 0. | |
| 9:0 | DST_STUFF_CHAR[9:0] (G) |
RW | Applicable only in 10G mode. 10 bit data pattern to stuff the output of data switch on transmit side (Default 10’h207) |
7.5.2.40 DSR_ON_CHAR_CONTROL (register = 0x802D) (default = 0x02FD)
(device address: 0x1E)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| RESERVED | DSR_ON_CHAR[9:0] (XG) |
||||||||||||||
| RW | RW | ||||||||||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-61 DSR_ON_CHAR_CONTROL Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:10 | RESERVED | RW | For TI use only. Always reads 0. | |
| 9:0 | DSR_ON_CHAR[9:0] (XG) |
RW | Applicable only in 1GKX and 10G modes. 10 bit data pattern to trigger ON condition if matched on receive side (Default 10’h2FD) |
7.5.2.41 DSR_OFF_CHAR_CONTROL (register = 0X802E) (default = 0x02FD)
(device address: 0x1E)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| RESERVED | DSR_OFF_CHAR[9:0] (XG) |
||||||||||||||
| RW | RW | ||||||||||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-62 DSR_OFF_CHAR_CONTROL Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:10 | RESERVED | RW | For TI use only. Always reads 0. | |
| 9:0 | DSR_OFF_CHAR[9:0] (XG) |
RW | Applicable only in 1GKX and 10G modes. 10 bit data pattern to trigger OFF condition if matched on receive side (Default 10’h2FD) |
7.5.2.42 DSR_STUFF_CHAR_CONTROL (register = 0x802F) (default = 0x0207)
(device address: 0x1E)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| RESERVED | DSR_STUFF_CHAR[9:0] (G) |
||||||||||||||
| RW | RW | ||||||||||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-63 DSR_STUFF_CHAR_CONTROL Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:10 | RESERVED | RW | For TI use only. Always reads 0. | |
| 9:0 | DSR_STUFF_CHAR[9:0] (G) |
RW | Applicable only in 10G mode. 10 bit data pattern to stuff the output of data switch on receive side (Default 10’h207) |
7.5.2.43 LATENCY_MEASURE_CONTROL (register = 0x8040) (default = 0x0000)
(device address: 0x1E)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| RESERVED | |||||||
| RW | |||||||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| LATENCY_MEAS_STOP_SEL[1: 0] (RXG) |
LATENCY_MEAS_CLK_DIV[1:0 ] (RXG) |
LATENCY_MEAS_START_SEL[ 1:0] (RXG) |
LATENCY_MEAS_EN (RXG) |
LATENCY_MEAS_CLK_SEL (RXG) |
|||
| RW | RW | RW | RW | ||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-64 LATENCY_MEASURE_CONTROL Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:8 | RESERVED | RW | For TI use only. Always reads 0. | |
| 7:6 | LATENCY_MEAS_STOP_SEL[1: 0] (RXG) |
RW | Latency measurement stop point selection 00 = Selects LS RX as stop point (Default 2 ’b00) 01 = Selects HS TX as stop point 1x = Selects external pin (PRTAD0) as stop point |
|
| 5:4 | LATENCY_MEAS_CLK_DIV[1:0 ] (RXG) |
RW | Latency measurement clock divide control. Valid only when bit 1E.8040 bit 2 is 0. Divides clock to needed resolution. Higher the divide value, lesser the latency measurement resolution. Divider value should be chosen such that the divided clock doesn’t result in clock slower than the high speed byte clock. 00 = Divide by 1 (Default 2’b00) (Most Accurate Measurement) 01 = Divide by 2 10 = Divide by 4 11 = Divide by 8 (Longest Measurement Capability) |
|
| 3:2 | LATENCY_MEAS_START_SEL[ 1:0] (RXG) |
RW | Latency measurement start point selection 00 = Selects LS TX as start point (Default 2’b00) 01 = Selects HS RX as start point 1x = Selects external pin (PRTAD0) as start point |
|
| 1 | LATENCY_MEAS_EN (RXG) |
RW | Latency measurement enable 0 = Disable Latency measurement (Default ’b0) 1 = Enable Latency measurement |
|
| 0 | LATENCY_MEAS_CLK_SEL (RXG) |
RW | Latency measurement clock selection. 0 = Selects VCO clock as per Latency measurement table. Bits 1E.8040 bits 5:4 can be used to divide this clock to achieve needed resolution. (Default 1’b0) 1 = Selects recovered byte clock |
7.5.2.44 LATENCY_COUNTER_2 (register = 0x8041) (default =0x0000)
(device address: 0x1E)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| LATENCY_MEAS_START_COMMA[3:0] (RXG) |
LATENCY_MEAS_STOP_COMMA[3:0] (RXG) |
||||||
| RO/LH | RO/LH | ||||||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| RESERVED | LATENCY_ MEAS_READY (RXG) |
LATENCY_MEAS_COUNT[19:16] (RXG) |
|||||
| RO/LH | RO | ||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-65 LATENCY_COUNTER_2 Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:12 | LATENCY_MEAS_START_COMMA[3:0] (RXG) |
RO/LH | Latency measurement start comma location status. “1” indicates start comma location found. If LS TX is selected as start point (1E.8040 bit 7 = 0), [3:0] indicates status for lane3, lane2, lane1, lane0. If HS RX is selected as start point (1E.8040 bit 7 = 1), [0] indicates status for data[9:0], [1] indicates status for data[19:10]. [3:2] is unused. Reading this register will clear Latency stopwatch status specified in LATENCY_COUNTER_1 & LATENCY_COUNTER_2 registers. Below sequence of reads needs to be performed for accurate and repeat stopwatch measurements. See Latency measurement procedure more information. READ 0x8041 READ 0x8042 |
|
| 11:8 | LATENCY_MEAS_STOP_COMMA[3:0] (RXG) |
RO/LH | Latency measurement stop comma location status. “1” indicates stop comma location found. If LS RX is selected as stop point (1E.8040 bit 6 = 0), [3:0] indicates status for lane3, lane2, lane1, lane0. If HS TX is selected as stop point (1E.8040 bit 6 = 1), [0] indicates status for data[9:0], [1] indicates status for data[19:10]. [3:2] is unused. | |
| 7:5 | RESERVED | RO/LH | ||
| 4 | LATENCY_ MEAS_READY (RXG) |
RO/LH | Latency measurement ready indicator 0 = Indicates latency measurement not complete. 1 = Indicates latency measurement is complete and value in latency measurement counter (LATENCY_MEAS_COUNT[19:0]) is ready to be read. |
|
| 3:0 | LATENCY_MEAS_COUNT[19:16] (RXG) |
RO/LH | Bits[19:16] of 20 bit wide latency measurement counter. Latency measurement counter value represents the latency in number of clock cycles. Each clock cycle is half of the period of the measurement clock as determined by register 1E.8040 bits 5:4 and 1E.8040 bit 0. This counter will return 20’h00000 if it’s read before rx comma is received. If latency is more than 20’hFFFFF clock cycles then this counter returns 20’hFFFFF. |
7.5.2.45 LATENCY_COUNTER_1 (register = 0x8042) (default = 0x0000) (device address: 0x1E)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| LATENCY_MEAS_COUNT[15:0] (RXG) |
|||||||||||||||
| COR(1) | |||||||||||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-66 LATENCY_COUNTER_1 Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:0 | LATENCY_MEAS_COUNT[15:0] (RXG) |
COR | Bits[15:0] of 20 bit wide latency measurement counter. Below sequence of reads needs to be performed for accurate and repeat stopwatch measurements. READ 0x8041 READ 0x8042 |
7.5.2.46 TRIGGER_LOAD_CONTROL (register =0x8100) (default = 0x0000)
(device address: 0x1E)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| RESERVED | RESERVED | ||||||
| RW | RW | ||||||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| RESERVED | DEFAULT_ TX_LOAD_ TRIGGER (RXG) |
RESERVED | |||||
| RW | RW | RW | |||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-67 TRIGGER_LOAD_CONTROL Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:11 | RESERVED | RW | For TI use only. Always reads 0. | |
| 10:3 | RESERVED | RW | For TI use only. (Default 8'b00000000) | |
| 2 | DEFAULT_TX_LOAD_TRIGGER (RXG) |
RW | Valid only when DEFAULT_TX_TRIGGER_EN is HIGH 1 = Trigger loading default HS TX setting values 0 = Normal operation (Default 1'b0) This bit needs to be written HIGH and then LOW to load the HS Tx default values. Applicable when link training is enabled. |
|
| 1:0 | RESERVED | RW | For TI use only. (Default 2'b00) |
7.5.2.47 TRIGGER_EN_CONTROL (register = 0x8101) (default = 0x0000) (device address: 0x1E)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| RESERVED | RESERVED | ||||||
| RW | RW | ||||||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| RESERVED | DEFAULT_ TX_LOAD_ TRIGGER_EN (RXG) |
RESERVED | |||||
| RW | RW | RW | |||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-68 TRIGGER_EN_CONTROL Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:11 | RESERVED | RW | For TI use only. Always reads 0. | |
| 10:3 | RESERVED | RW | For TI use only. (Default 8'b00000000) | |
| 2 | DEFAULT_TX_TRIGGER_EN (RXG) |
RW | 1 = Enable loading of Tx default values through DEFAULT_TX_LOAD_TRIGGER 0 = Normal operation (Default 1'b0) |
|
| 1:0 | RESERVED | RW | For TI use only. (Default 2'b00) |
7.5.3 PMA/PMD Registers
The registers below can be accessed only in Clause 45 mode and with device address field set to 0x01 (DA[4:0] = 5’b00001).
NOTE: Link training registers can also be accessed in Clause 22 mode using indirect address method and in Clause 45 mode with device address field set to 0x1E (DA[4:0] = 5’b11110). Link training registers are also applicable in 10G and 1GKX modes.
7.5.3.1 PMA_CONTROL_1 (register = 0x0000) (default = 0x0000) (device address: 0x01)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| RESET (RX) |
RESERVED | POWERDOWN (RX) |
RESERVED | ||||
| RW/SC | RW | RW | RW | ||||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| RESERVED | LOOPBACK (RX) |
||||||
| RW | RW | ||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-69 PMA_CONTROL_1 Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | RESET (RX) |
RW/SC | 1 = Global reset. Resets datapath and MDIO registers. Equivalent to asserting RESET_N. 0 = Normal operation (Default 1’b0) |
|
| 14:12 | RESERVED | RW | For TI use only. Always reads 0. | |
| 11 | POWERDOWN (RX) |
RW | 1 = Enable power down mode 0 = Normal operation (Default 1’b0) |
|
| 10:1 | RESERVED | RW | For TI use only. Always reads 0. | |
| 0 | LOOPBACK (RX) |
RW | 1 = Enables loopback on HS side. LS data traverses through entire Tx datapath excluding HS serdes and will be available at LS output side 0 = Normal operation (Default 1’b0) |
7.5.3.2 PMA_STATUS_1 (register = 0x0001) (default = 0x0002) (device address: 0x01)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| RESERVED | |||||||
| RO | |||||||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| FAULT (RX) | RESERVED | RX_LINK (RX) |
LOW_ POWER_ ABILITY (RX) |
RESERVED | |||
| RO | RO | RO/LL | RO | RO | |||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-70 PMA_STATUS_1 Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:8 | RESERVED | For TI use only. | ||
| 7 | FAULT (RX) |
RO | 1 = Fault condition detected on either Tx or Rx side 0 = No fault condition detected This bit is cleared after Register 01.0008 is read and no fault condition occurs after 01.0008 is read. |
|
| 6:3 | RESERVED | For TI use only. | ||
| 2 | RX_LINK (RX) |
RO/LL | 1 = Receive link is up 0 = Receive link is down |
|
| 1 | LOW_POWER_ABILITY (RX) |
RO | Always reads 1. 1 = Supports low power mode 0 = Does not support low power mode |
7.5.3.3 PMA_DEV_IDENTIFIER_1 (register = 0x0002) (default = 0x4000) (device address: 0x01)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| DEV_IDENTIFIER[31:16] (RX) |
|||||||||||||||
| RO | |||||||||||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-71 PMA_DEV_IDENTIFIER_1 Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:0 | DEV_IDENTIFIER[31:16] (RX) |
RO | 16 MSB of 32 bit unique device identifier. See Table 7-73 for identifier code details. |
7.5.3.4 PMA_DEV_IDENTIFIER_2 (register = 0x0003) (default = 0x5100) (device address: 0x01)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| DEV_IDENTIFIER[15:0] (RX) | |||||||||||||||
| RO | |||||||||||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-72 PMA_DEV_IDENTIFIER_2 Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:0 | DEV_IDENTIFIER[31:16] (RX) |
RO | 16 MSB of 32 bit unique device identifier. See Table 7-73 for identifier code details. |
Table 7-73 UNIQUE DEVICE IDENTIFIER (1)
| Register address | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 01.0002 bits 15:0 | 16’b0100_0000_0000_0000 | OUI[3-18] |
| 01.0003 bits 15:10 | 6’b010100 | OUI[19-24] |
| 01.0003 bits 9:4 | 6’b010000 | 6-bit Manufacturer device model number |
| 01.0003 bits 3:0 | 4’b0000 | 4-bit Manufacturer device revision number |
7.5.3.5 PMA_SPEED_ABILITY (register = 0x0004) (default = 0x0011) (device address: 0x01)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| RESERVED | |||||||
| RO | |||||||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| RESERVED | SPEED_1G (RX) |
RESERVED | SPEED_10G (RX) |
||||
| RO | RO | RO | RO | ||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-74 PMA_SPEED_ABILITY Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:5 | RESERVED | For TI use only. | ||
| 4 | SPEED_1G (RX) |
RO | Always reads 1. 1 = Capable of operating at 1000 Mb/s 0 = Not capable of operating at 1000 Mb/s |
|
| 3:1 | RESERVED | For TI use only. | ||
| 0 | SPEED_10G (RX) |
RO | Always reads 1. 1 = Capable of operating at 10 Gb/s 0 = Not capable of operating at 10 Gb/s |
7.5.3.6 PMA_DEV_PACKAGE_1 (register = 0x0005) (default = 0x000B) (device address: 0x01)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| RESERVED | |||||||
| RO | |||||||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| RESERVED | PCS_ PRESENT (RX) |
RESERVED | PMA_PMD_PRESENT (RX) |
CL22_PRESENT (RX) |
|||
| RO | RO | RO | RO | RO | |||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-75 PMA_DEV_PACKAGE_1 Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:4 | RESERVED | RO | For TI use only. | |
| 3 | PCS_ PRESENT (RX) |
RO | Always reads 1. 1 = PCS present in the package 0 = PCS not present in the package |
|
| 2 | RESERVED | RO | For TI use only. | |
| 1 | PMA_PMD_PRESENT (RX) |
RO | Always reads 1. 1 = PMA/PMD present in the package 0 = PMA/PMD not present in the package |
|
| 0 | CL22_PRESENT (RX) |
RO | Always reads 1. 1 = Clause 22 registers present in the package 0 = Clause 22 registers not present in the package |
7.5.3.7 PMA_DEV_PACKAGE_2 (register = 0x0006) (default = 0x4000) (device address: 0x01)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| VS_DEV2_ PRESENT (RX) |
VS_DEV1_ PRESENT (RX) |
RESERVED | |||||
| RO | RO | RO | |||||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| RESERVED | |||||||
| RO | |||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-76 PMA_DEV_PACKAGE_2 Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | VS_DEV2_PRESENT (RX) |
RO | Always reads 0. 1 = Vendor specific device 2 present in the package 0 = Vendor specific device 2 not present in the package |
|
| 14 | VS_DEV1_PRESENT (RX) |
RO | Always reads 1. 1 = Vendor specific device 1 present in the package 0 = Vendor specific device 1 not present in the package |
|
| 13:0 | RESERVED | For TI use only. |
7.5.3.8 PMA_DEV_PACKAGE_2 (register = 0x0006) (default = 0x4000) (device address: 0x01)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| DEV_PRESENT (RX) |
TX_FAULT_ABILITY (RX) |
RX_FAULT_ABILITY (RX) |
TX_FAULT (RX) |
RX_FAULT (RX) |
RESERVED | TX_DISABLE_ABILITY (RX) |
|
| RO | RO | RO | RO.LH | RO/LH | RO | ||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| RESERVED | |||||||
| RO | |||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-77 PMA_DEV_PACKAGE_2 Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:14 | DEV_PRESENT (RX) |
RO | Always reads 2’b10 0x = No device responding at this address 10 = Device responding at this address 11 = No device responding at this address |
|
| 13 | TX_FAULT_ABILITY (RX) |
RO | Always reads 1’b1. 1 = Able to detect fault condition on Tx path 0 = Not able to detect fault condition on Tx path |
|
| 12 | RX_FAULT_ABILITY (RX) |
RO | Always reads 1’b1. 1 = Able to detect fault condition on Rx path 0 = Not able to detect fault condition on Rx path |
|
| 11 | TX_FAULT (RX) |
RO/LH | 1 = Fault condition detected on transmit path 0 = No fault condition detected on transmit path |
|
| 10 | RX_FAULT (RX) |
RO/LH | 1 = Fault condition detected on receive path 0 = No fault condition detected on receive path |
|
| 9 | RESERVED | For TI use only. | ||
| 8 | TX_DISABLE_ABILITY (RX) |
RO | Always reads 1’b0. 1 = Able to perform transmit disable function 0 = Not able to perform transmit disable function |
|
| 7:0 | RESERVED | For TI use only. |
7.5.3.9 PMA_RX_SIGNAL_DET_STATUS (register = 0x000A) (default = 0x0000)
(device address: 0x01)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| RESERVED | |||||||
| RO | |||||||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| RESERVED | RX_SIGNAL_DET (RX) |
||||||
| RO | RO | ||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-78 PMA_RX_SIGNAL_DET_STATUS Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:1 | RESERVED | RO | For TI use only. | |
| 0 | RX_SIGNAL_DET (RX) |
RO | 1 = Signal detected on serial Rx pins 0 = Signal not detected on serial Rx pins |
7.5.3.10 PMA_EXTENDED_ABILITY (register = 0x000B) (default = 0x0050) (device address: 0x01)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| RESERVED | |||||||
| RO | |||||||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| RESERVED | KX_ABILITY (RX) |
RESERVED | KR_ABILITY (RX) |
RESERVED | |||
| RO | RO | RO | RO | RO | |||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-79 PMA_EXTENDED_ABILITY Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Value | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:7 | RESERVED | For TI use only. | ||
| 6 | KX_ABILITY (RX) |
RO | Always reads 1’b11 = Able to perform 1000BASE-KX 0 = Not able to perform 1000BASE-KX |
|
| 5 | RESERVED | For TI use only. | ||
| 4 | KR_ABILITY (RX) |
RO | Always reads 1’b11 = Able to perform 10GBASE-KR 0 = Not able to perform 10GBASE-KR |
|
| 3:0 | RESERVED | For TI use only. |
7.5.3.11 LT_TRAIN_CONTROL (register =0x0096) (default = 0x0002) (device address: 0x01)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| RESERVED | |||||||
| RW | |||||||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| RESERVED | LT_TRAINING_ ENABLE (RXG) |
LT_RESTART_TRAINING (RXG) |
|||||
| RW | RW | RW/SC | |||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-80 LT_TRAIN_CONTROL Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:2 | RESERVED | RW | For TI use only. Always reads 0. | |
| 1 | LT_TRAINING_ENABLE (RXG) |
RW | 1 = Enable start-up protocol as per 10GBASE-KR standard(Default 1’b1) 0 = Disable start-up protocol This bit should be set to HIGH for autotrain mode to function correctly |
|
| 0 | LT_RESTART_TRAINING (RXG) |
RW/SC | 1 = Reset link/auto train 0 = Normal operation (Default 1’b0) |
7.5.3.12 LT_TRAIN_STATUS (register = 0x0097) (default = 0x0000) (device address: 0x01)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| RESERVED | |||||||
| RO | |||||||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| RESERVED | LT_TRAINING_FAIL (RXG) |
LT_START_PROTOCOL (RXG) |
LT_FRAME_LOCK (RXG) |
LT_RX_STATUS (RXG) |
|||
| RO | RO | RO | RO | RO | |||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-81 LT_TRAIN_STATUS Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:4 | RESERVED | For TI use only. | ||
| 3 | LT_TRAINING_FAIL (RXG) |
RO | 1 = Training failure has been detected 0 = Training failure has not been detected |
|
| 2 | LT_START_PROTOCOL (RXG) |
RO | 1 = Start up protocol in progress 0 = Start up protocol complete |
|
| 1 | LT_FRAME_LOCK (RXG) |
RO | 1 = Training frame delineation detected 0 = Training frame delineation not detected |
|
| 0 | LT_RX_STATUS (RXG) |
RO | 1 = Receiver trained and ready to receive data 0 = Receiver training in progress |
7.5.3.13 LT_LINK_PARTNER_CONTROL (register = 0x0098) (default = 0x0000)
(device address: 0x01)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| RESERVED | LT_LP_PRESET (RXG) |
LT_LP_INITIALIZE (RXG) |
RESERVED | LT_LP_COEFF_SWG (RXG) |
RESERVED | ||
| RO | RO | RO | |||||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| LT_LP_COEFF_PS2 (RXG) |
RESERVED | LT_LP_COEFF_P1 (RXG) |
RESERVED | LT_LP_COEFF_0 (RXG) |
RESERVED | LT_LP_COEFF_M1 (RXG) |
RESERVED |
| RO | RO | RO | RO | ||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-82 LT_LINK_PARTNER_CONTROL Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:14 | RESERVED | For TI use only. | ||
| 13 | LT_LP_PRESET (RXG) |
RO | 1 = KR preset coefficients 0 = Normal operation |
|
| 12 | LT_LP_INITIALIZE (RXG) |
RO | 1 = Initialize KR coefficients 0 = Normal operation |
|
| 11:10 | RESERVED | For TI use only. | ||
| 9 | LT_LP_COEFF_SWG (RXG) |
RO | Swing update 11 = Reserved 01 = Increment 10 = Decrement 00 = Hold |
|
| 8 | RESERVED | For TI use only. | ||
| 7 | LT_LP_COEFF_PS2 (RXG) |
RO | Post2 tap control update 11 = Reserved01 = Increment 10 = Decrement 00 = Hold |
|
| 6 | RESERVED | For TI use only. | ||
| 5 | LT_LP_COEFF_P1 (RXG) |
RO | Coefficient K(+1) update 11 = Reserved 01 = Increment 10 = Decrement 00 = Hold |
|
| 4 | RESERVED | For TI use only. | ||
| 3 | LT_LP_COEFF_0 (RXG) |
RO | Coefficient K(0) update 11 = Reserved 01 = Increment 10 = Decrement 00 = Hold |
|
| 2 | RESERVED | For TI use only. | ||
| 1 | LT_LP_COEFF_M1 (RXG) |
RO | Coefficient K(-1) update 11 = Reserved 01 = Increment 10 = Decrement 00 = Hold (Default 2’b00) |
|
| 0 | RESERVED | For TI use only. |
7.5.3.14 LT_LINK_PARTNER_STATUS (register = 0x0099) (default = 0x0000)
(device address: 0x01)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| LT_LP_RX_READY (RXG) |
RESERVED | LT_LP_COEFF_SWG_STAT (RXG) |
|||||
| RO | RO | RO | |||||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| LT_LP_COEFF_PS2_STAT (RXG) |
LT_LP_COEFF_P1_STAT (RXG) |
LT_LP_COEFF_0_STAT (RXG) |
LT_LP_COEFF_M1_STAT (RXG) |
||||
| RO | RO | RO | RO | ||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-83 LT_LINK_PARTNER_STATUS Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | LT_LP_RX_READY (RXG) |
RO | 1 = LP receiver has determined that training is complete and prepared to receive data 0 = LP receiver is requesting that training continue |
|
| 14:10 | RESERVED | For TI use only. | ||
| 9:8 | LT_LP_COEFF_SWG_STAT (RXG) |
RO | Swing update 11 = Maximum 01 = Updated 10 = Minimum 00 = Not updated |
|
| 7:6 | LT_LP_COEFF_PS2_STAT (RXG) |
RO | Post2 tap control update 11 = Maximum 01 = Updated 10 = Minimum 00 = Not updated |
|
| 5:4 | LT_LP_COEFF_P1_STAT (RXG) |
RO | Coefficient K(+1) update 11 = Maximum 01 = Updated 10 = Minimum 00 = Not updated |
|
| 3:2 | LT_LP_COEFF_0_STAT (RXG) |
RO | Coefficient K(0) update 11 = Maximum 01 = Updated 10 = Minimum 00 = Not updated |
|
| 1:0 | LT_LP_COEFF_M1_STAT (RXG) |
RO | Coefficient K(-1) update 11 = Maximum 01 = Updated 10 = Minimum 00 = Not updated |
7.5.3.15 LT_LOCAL_DEVICE_CONTROL (register = 0x009A) (default = 0x0000)
(device address: 0x01)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| RESERVED | LT_LD_PRESET (RXG) |
LT_ LD_INITIALIZE (RXG) |
RESERVED | LT_LD_COEFF_SWG (RXG) |
|||
| RO | RO | RO | RO | RO | |||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| LT_LD_COEFF_PS2 (RXG) |
LT_ LD_COEFF_P1 (RXG) |
LT_ LD_COEFF_0 (RXG) |
LT_ LD_COEFF_M1 (RXG |
||||
| RO | RO | RO | RO | ||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-84 LT_LOCAL_DEVICE_CONTROL Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:14 | RESERVED | RO | For TI use only. Always reads 0. | |
| 13 | LT_LD_PRESET (RXG) |
RO | 1 = KR preset coefficients 0 = Normal operation (Default 1’b0) |
|
| 12 | LT_ LD_INITIALIZE (RXG) |
RO | 1 = Initialize KR coefficients 0 = Normal operation (Default 1’b0) |
|
| 11:10 | RESERVED | RO | For TI use only. Always reads 0. | |
| 9:8 | LT_LD_COEFF_SWG (RXG) |
RO | Swing update 11 = Reserved 01 = Increment 10 = Decrement 00 = Hold (Default 2’b00) |
|
| 7:6 | LT_LD_COEFF_PS2 (RXG) |
RO | Post2 tap control update 11 = Reserved01 = Increment 10 = Decrement 00 = Hold (Default 2’b00) |
|
| 5:4 | LT_ LD_COEFF_P1 (RXG) |
RO | Coefficient K(+1) update 11 = Reserved01 = Increment 10 = Decrement 00 = Hold (Default 2’b00) |
|
| 3:2 | LT_ LD_COEFF_0 (RXG) |
RO | Coefficient K(0) update 11 = Reserved 01 = Increment 10 = Decrement 00 = Hold (Default 2’b00) |
|
| 1:0 | LT_ LD_COEFF_M1 (RXG) |
RO | Coefficient K(-1) update 11 = Reserved 01 = Increment 10 = Decrement 00 = Hold (Default 2’b00) |
7.5.3.16 LT_LOCAL_DEVICE_STATUS (register = 0x009B) (default = 0x0000)
(device address: 0x01)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| LT_LD_RX_ READY (RXG) |
RESERVED | ||||||
| RO | RO | ||||||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| RESERVED | LT_ LD_COEFF_P1_STAT (RXG) |
LT_ LD_COEFF_0_STAT (RXG) |
LT_ LD_COEFF_M1_STAT (RXG) |
||||
| RO | RO | RO | |||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-85 LT_LOCAL_DEVICE_STATUS Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | LT_ LD_RX_READY (RXG) |
RO | 1 = LD receiver has determined that training is complete and prepared to receive data 0 = LD receiver is requesting that training continue |
|
| 14:5 | RESERVED | RO | For TI use only. | |
| 4 | LT_ LD_COEFF_P1_STAT (RXG) |
RO | Coefficient K(+1) update 11 = Maximum 01 = Updated 10 = Minimum 00 = Not updated |
|
| 3:2 | LT_ LD_COEFF_0_STAT (RXG) |
RO | Coefficient K(0) update 11 = Maximum 01 = Updated 10 = Minimum 00 = Not updated |
|
| 1:0 | LT_ LD_COEFF_M1_STAT (RXG) |
RO | Coefficient K(-1) update 11 = Maximum 01 = Updated 10 = Minimum 00 = Not updated |
7.5.3.17 KX_STATUS (register = 0x00A1) (default = 0x3000) (device address: 0x01)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| RESERVED | KX_TX_FAULT_ABILITY (X) |
KX_RX_FAULT_ABILITY (X) |
KX_TX_FAULT (X) |
KX_RX_FAULT (X) |
RESERVED | ||
| RO | RO | RO | RO/LH | RO/LH | RO | ||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| RESERVED | KX_RX_SIGNAL_DETECT (X) |
||||||
| RO | RO | ||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-86 KX_STATUS Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:14 | RESERVED | RO | For TI use only. | |
| 13 | KX_TX_FAULT_ABILITY (X) |
RO | Always reads 1. 1 = Able to detect fault condition on transmit path 0 = Not able to detect fault condition on transmit path |
|
| 12 | KX_RX_FAULT_ABILITY (X) |
RO | Always reads 1. 1 = Able to detect fault condition on receive path 0 = Not able to detect fault condition on receive path |
|
| 11 | KX_TX_FAULT (X) |
RO/LH | 1 = Fault condition detected on transmit path 0 = No fault condition detected on transmit path |
|
| 10 | KX_RX_FAULT (X) |
RO/LH | 1 = Fault condition detected on receive path 0 = No fault condition detected on receive path |
|
| 9:1 | RESERVED | RO | For TI use only. | |
| 0 | KX_RX_SIGNAL_DETECT (X) |
RO | 1 = Signal detected 0 = Signal not detected |
7.5.3.18 KR_FEC_ABILITY (register = 0x00AA) (default = 0x0003) (device address: 0x01)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| RESERVED | |||||||
| RO | |||||||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| RESERVED | KR_FEC_ERR_ABILITY (R) |
KR_FEC_ABILITY (R) |
|||||
| RO | RO | RO | |||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-87 KR_FEC_ABILITY Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:2 | RESERVED | RO | For TI use only. | |
| 1 | KR_FEC_ERR_ABILITY (R) |
RO | Always reads 1. 1 = Device supports 10GBASE-R FEC error indication to PCS 0 = Device does not support 10GBASE-R FEC function error indication tx PCS |
|
| 0 | KR_FEC_ABILITY (R) |
RO | Always reads 1. 1 = Device supports 10GBASE-R FEC function 0 = Device does not support 10GBASE-R FEC function |
7.5.3.19 KR_FEC_CONTROL (register = 0x00AB) (default = 0x0000) (device address: 0x01)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| RESERVED | |||||||
| RW | |||||||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| RESERVED | KR_FEC_ERR_INDEN (R) |
KR_FEC_EN (R) |
|||||
| RW | RW | RW | |||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-88 KR_FEC_CONTROL Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:2 | RESERVED | RW | For TI use only. Always reads 0. | |
| 1 | KR_FEC_ERR_IND_EN (R) |
RW | 1 = Enable FEC decoder to indicate errors to PCS 0 = Disable FEC decoder error indication to PCS (Default 1’b0) |
|
| 0 | KR_FEC_EN (R) |
RW | 1 = Enable 10GBASE-R FEC function 0 = Disable 10GBASE-R FEC function (Default 1’b0) |
7.5.3.20 KR_FEC_C_COUNT_1 (register = 0x00AC) (default = 0x0000) (device address: 0x01)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| KR_FEC_C_COUNT[15:0] (R) |
|||||||||||||||
| COR | |||||||||||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-89 KR_FEC_C_COUNT_1(1) Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:0 | KR_FEC_C_COUNT[15:0] (R) |
COR | Lower 16 bits of FEC corrected blocks counter |
7.5.3.21 KR_FEC_C_COUNT_2 (register = 0x00AD) (default = 0x0000) (device address: 0x01)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| KR_FEC_C_COUNT[31:16] (R) |
|||||||||||||||
| COR | |||||||||||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-90 KR_FEC_C_COUNT_2 Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:0 | KR_FEC_C_COUNT[31:16] (R) |
COR | Upper 16 bits of FEC corrected blocks counter |
7.5.3.22 KR_FEC_UC_COUNT_1 (register = 0x00AE) (default = 0x0000)
(device address: 0x01)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| KR_FEC_UC_COUNT[15:0] (R) |
|||||||||||||||
| COR | |||||||||||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-91 KR_FEC_UC_COUNT_1(1) Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:0 | KR_FEC_UC_COUNT[15:0] (R) |
COR | Lower 16 bits of FEC Uncorrected blocks counter |
7.5.3.23 KR_FEC_UC_COUNT_2 (register = 0x00AF) (default = 0x0000)
(device address: 0x01)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| KR_FEC_UC_COUNT[31:16] (R) |
|||||||||||||||
| COR | |||||||||||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-92 KR_FEC_UC_COUNT_2 Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:0 | KR_FEC_UC_COUNT[31:16] (R) |
COR | Lower 16 bits of FEC Uncorrected blocks counter |
7.5.3.24 KR_VS_FIFO_CONTROL_1 (register = 0x8001) (default = 0xCC4C)
(device address: 0x01)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| RESERVED | RX_FIFO_DEPTH[2:0] (R) |
RX_CTC_WMK_SEL[1:0] (R) |
RX_Q_CNT_ IPG (R) |
RX_CTC_Q_ DROP_EN (R) |
|||
| RW | |||||||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| XMIT_IDLE (R) |
TX_FIFO_DEPTH[2:0] (R) |
TX_CTC_WMK_SEL[1:0] (R) |
TX_Q_CNT_ IPG (R) |
TX_CTC_Q_DROP _EN (R) |
|||
| RW | RW | RW | RW | RW | |||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-93 KR_VS_FIFO_CONTROL_1 Field Descriptions
| Bit | Name | Type | Reset | Description | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | RESERVED | RW | For TI use only (Default 1’b1) | |||||||
| 14:12 | RX_FIFO_DEPTH[2:0] (R) |
RW | Rx CTC FIFO depth selection 1xx = 32 deep (Default 3’b100) 011 = 24 deep 010 = 16 deep 001 = 12 deep 000 = 8 deep (No CTC function) |
|||||||
| 11:10 | RX_CTC_WMK_SEL[1:0] (R) |
RW | Water mark selection for receive CTC Works in conjunction with RX_FIFO_DEPTH_SEL setting (Default 2’b11) |
|||||||
| Depth-> | 32 | 24 | 26 | 12/8 | ||||||
| 11 | High | High | High | NA | ||||||
| 10 | Mid-high | Mid | High | |||||||
| 01 | Mid | Low | Low | |||||||
| 00 | Low | Low | Low | |||||||
| 9 | RX_Q_CNT_IPG (R) |
RW | 0 = Normal operation. (Default 1’b0) 1 = Sequence columns are counted as IPG. |
|||||||
| 8 | RX_CTC_Q_DROP_EN (R) |
RW | 0 = Normal operation. (Default 1’b0) 1 = Enable Q column drop in RX CTC. |
|||||||
| 7 | XMIT_IDLE (R) |
RW | 1 = Transmit idle pattern onto LS side 0 = Normal operation (Default 1’b0) |
|||||||
| 6:4 | TX_FIFO_DEPTH[2:0] (R) |
RW | Tx CTC FIFO depth selection 1xx = 32 deep (Default 3’b100)011 = 24 deep 010 = 16 deep001 = 12 deep 000 = 8 deep (No CTC function) |
|||||||
| 3:2 | TX_CTC_WMK_SEL[1:0] (R) |
RW | Water mark selection for receive CTC Works in conjunction with TX_FIFO_DEPTH_SEL setting (Default 2’b11) |
|||||||
| Depth-> | 32 | 24 | 26 | 12/8 | ||||||
| 11 | High | High | High | NA | ||||||
| 10 | Mid-high | Mid | High | |||||||
| 01 | Mid | Low | Low | |||||||
| 00 | Low | Low | Low | |||||||
| 1 | TX_Q_CNT_IPG (R) |
RW | 0 = Normal operation. (Default 1’b0) 1 = Sequence columns are counted as IPG. |
|||||||
| 0 | TX_CTC_Q_DROP_EN (R) |
RW | 0 = Normal operation. (Default 1’b0) 1 = Enable Q column drop in TX CTC |
|||||||
7.5.3.25 KR_VS_TP_GEN_CONTROL (register =0x8002) (default = 0x0000)
(device address: 0x01)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| RESERVED | |||||||
| RW | |||||||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| RESERVED | RX_TPG_HLM_TEST_SEL[1:0] (R) |
RX_TPG_CRPAT_TEST_EN (R) |
RX_TPG_CJPAT_TEST_EN (R) |
RX_TPG_10GFC_TEST_EN (R) |
RX_TPG_HLM_TEST_EN (R) |
||
| RW | RW | RW | RW | RW | RW | ||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-94 KR_VS_TP_GEN_CONTROL Field Descriptions
| Bit | Name | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:6 | RESERVED | For TI use only. Always reads 0. | ||
| 5:4 | RX_TPG_HLM_TEST_SEL[1:0] (R) |
RW | XAUI based test pattern selection on LS side. See Test pattern procedures for more information. 00 = High Frequency test pattern(Default 2’b00) 01 = Low Frequency test pattern 10 = Mixed Frequency test pattern 11 = Normal operation |
|
| 3 | RX_TPG_CRPAT_TEST_EN (R) |
RW | XAUI based test pattern selection on LS side. See Test pattern procedures for more information. 0 = Normal operation. (Default 1’b0) 1 = Enables CRPAT test pattern generation |
|
| 2 | RX_TPG_CJPAT_TEST_EN (R) |
RW | XAUI based test pattern selection on LS side. See Test pattern procedures for more information. 0 = Normal operation. (Default 1’b0) 1 = Enables CJPAT test pattern generation |
|
| 1 | RX_TPG_10GFC_TEST_EN (R) |
RW | XAUI based test pattern selection on LS side. See Test pattern procedures for more information. 0 = Normal operation. (Default 1’b0) 1 = Enables 10 GFC CJPAT test pattern generation |
|
| 0 | RX_TPG_HLM_TEST_EN (R) |
RW | XAUI based test pattern selection on LS side. See Test pattern procedures for more information. 0 = Normal operation. (Default 1’b0) 1 = Enables H/L/M test pattern generation |
7.5.3.26 KR_VS_TP_VER_CONTROL (register = 0x8003) (default = 0x0000)
(device address: 0x01)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| RESERVED | TX_TPV_HLM_TEST_SEL[1:0] (R) |
TX_TPV_CRPAT_TEST_EN (R) |
TX_TPV_CJPAT_TEST_EN (R) |
TX_TPV_10GFC_TEST_EN (R) |
TX_TPV_HLM_TEST_EN (R) |
||
| RW | RW | RW | RW | RW | RW | ||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| RESERVED | |||||||
| RW | |||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-95 KR_VS_TP_VER_CONTROL Field Descriptions
| Bit | Name | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:14 | RESERVED | RW | For TI use only. Always reads 0. | |
| 13:12 | TX_TPV_HLM_TEST_SEL[1:0] (R) |
RW | XAUI based test pattern selection on LS side. See Test pattern procedures for more information. 00 = High Frequency test pattern(Default 2’b00) 01 = Low Frequency test pattern 10 = Mixed Frequency test pattern 11 = Normal operation |
|
| 11 | TX_TPV_CRPAT_TEST_EN (R) |
RW | XAUI based test pattern selection on LS side. See Test pattern procedures for more information. 0 = Normal operation. (Default 1’b0) 1 = Enables CRPAT test pattern verification |
|
| 10 | TX_TPV_CJPAT_TEST_EN (R) |
RW | XAUI based test pattern selection on LS side. See Test pattern procedures for more information. 0 = Normal operation. (Default 1’b0) 1 = Enables CJPAT test pattern verification |
|
| 9 | TX_TPV_10GFC_TEST_EN (R) |
RW | XAUI based test pattern selection on LS side. See Test pattern procedures for more information. 0 = Normal operation. (Default 1’b0) 1 = Enables 10 GFC CJPAT test pattern verification |
|
| 8 | TX_TPV_HLM_TEST_EN (R) |
RW | XAUI based test pattern selection on LS side. See Test pattern procedures for more information. 0 = Normal operation. (Default 1’b0) 1 = Enables HL/M test pattern verification |
|
| 7:0 | RESERVED | RW | For TI use only(Default 8’b00000000) |
7.5.3.27 KR_VS_CTC_ERR_CODE_LN0 (register = 0x8005) (default = 0xCE00)
(device address: 0x01)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| KR_CTC_ERR_CODE_LN0 (R) |
RESERVED | ||||||||||||||
| RW | RW | ||||||||||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-96 KR_VS_CTC_ERR_CODE_LN0 Field Descriptions
| Bit | Name | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:7 | KR_CTC_ERR_CODE_LN0 (R) |
RW | Applicable in 10G-KR mode only. XGMII code to be transmitted in case of error condition. This applies to both TX and RX data paths. The msb is the control bit; remaining 8 bits constitute the error code. The default value for lane 0 corresponds to 8’h9C with the control bit being 1’b1. The default values for lanes 0~3 correspond to ||LF|| | |
| 6:0 | RESERVED | RW | For TI use only. Always reads 0. |
7.5.3.28 KR_VS_CTC_ERR_CODE_LN1 (register = 0x8006) (default =0x0000)
(device address: 0x01)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| KR_CTC_ERR_CODE_LN1 (R) |
RESERVED | ||||||||||||||
| RW | RW | ||||||||||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-97 KR_VS_CTC_ERR_CODE_LN1 Field Descriptions
| Bit | Name | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:7 | KR_CTC_ERR_CODE_LN1 (R) |
RW | Applicable in 10G-KR mode only. XGMII code to be transmitted in case of error condition. This applies to both TX and RX data paths. The msb is the control bit; remaining 8 bits constitute the error code. The default value for lane 1 corresponds to 8’h00 with the control bit being 1’b0. The default values for lanes 0~3 correspond to ||LF|| | |
| 6:0 | RESERVED | RW | For TI use only. Always reads 0. |
7.5.3.29 KR_VS_CTC_ERR_CODE_LN2 (register = 0x8007) (default = 0x0000)
(device address: 0x01)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| KR_CTC_ERR_CODE_LN2 (R) |
RESERVED | ||||||||||||||
| RW | RW | ||||||||||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-98 KR_VS_CTC_ERR_CODE_LN2 Field Descriptions
| Bit(s) | Name | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:7 | KR_CTC_ERR_CODE_LN2 (R) |
RW | Applicable in 10G-KR mode only. XGMII code to be transmitted in case of error condition. This applies to both TX and RX data paths. The msb is the control bit; remaining 8 bits constitute the error code. The default value for lane 2 corresponds to 8’h00 with the control bit being 1’b0. The default values for lanes 0~3 correspond to ||LF|| | |
| 6:0 | RESERVED | RW | For TI use only. Always reads 0. |
7.5.3.30 KR_VS_CTC_ERR_CODE_LN3 (register = 0x8008) (default = 0x0080)
(device address: 0x01)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| KR_CTC_ERR_CODE_LN3 (R) |
RESERVED | ||||||||||||||
| RW | RW | ||||||||||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-99 KR_VS_CTC_ERR_CODE_LN3 Field Descriptions
| Bit | Name | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:7 | KR_CTC_ERR_CODE_LN3 (R) |
RW | Applicable in 10G-KR mode only. XGMII code to be transmitted in case of error condition. This applies to both TX and RX data paths. The msb is the control bit; remaining 8 bits constitute the error code. The default value for lane 3 corresponds to 8’h01 with the control bit being 1’b0. The default values for lanes 0~3 correspond to ||LF|| | |
| 6:0 | RESERVED | RW | For TI use only. Always reads 0. |
7.5.3.31 KR_VS_LN0_EOP_ERROR_COUNTER (register = 0x8010) (default = 0xFFFD) (device address: 0x01)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| KR_LN0_EOP_ERR_COUNT (R) |
|||||||||||||||
| COR | |||||||||||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-100 KR_VS_LN0_EOP_ERROR_COUNTER Field Descriptions
| Bit | Name | Type | Reset | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:0 | KR_LN0_EOP_ERR_COUNT (R) |
COR | Lane 0 End of packet Error counter. End of packet error is detected when Terminate character is in lane 0 and 1 or both of the following holds: |
||
| ● | Terminate character is not followed by /K/ characters in lanes 1, 2 & 3 | ||||
| ● | The column following the terminate column is neither ||K|| nor ||A||. | ||||
| Counter value cleared to 16’h0000 when read. | |||||
7.5.3.32 KR_VS_LN1_EOP_ERROR_COUNTER (register = 0x8011) (default = 0xFFFD) (device address: 0x01)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| KR_LN1_EOP_ERR_COUNT (R) |
|||||||||||||||
| COR | |||||||||||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-101 KR_VS_LN1_EOP_ERROR_COUNTER Field Descriptions
| Bit | Name | Type | Reset | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:0 | KR_LN1_EOP_ERR_COUNT (R) |
COR | Lane 1 End of packet Error counter. End of packet error is detected when Terminate character is in lane 1 and one or both of the following holds: |
||
| ● | Terminate character is not followed by /K/ characters in lanes 1, 2 & 3 | ||||
| ● | The column following the terminate column is neither ||K|| nor ||A||. | ||||
| Counter value cleared to 16’h0000 when read. | |||||
7.5.3.33 KR_VS_LN2_EOP_ERROR_COUNTER (register = 0x8012) (default = 0xFFFD) (device address: 0x01)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| KR_LN2_EOP_ERR_COUNT (R) |
|||||||||||||||
| COR | |||||||||||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-102 KR_VS_LN2_EOP_ERROR_COUNTER Field Descriptions
| Bit | Name | Type | Reset | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:0 | KR_LN1_EOP_ERR_COUNT (R) |
COR | Lane 2 End of packet Error counter. End of packet error is detected when Terminate character is in lane 2 and 1 or both of the following holds: |
||
| ● | Terminate character is not followed by /K/ characters in lanes 1, 2 & 3 | ||||
| ● | The column following the terminate column is neither ||K|| nor ||A||. | ||||
| Counter value cleared to 16’h0000 when read. | |||||
7.5.3.34 KR_VS_LN3_EOP_ERROR_COUNTER (register =0x8013 ) (default = 0xFFFD) (device address: 0x01)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| KR_LN3_EOP_ERR_COUNT (R) |
|||||||||||||||
| COR | |||||||||||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-103 KR_VS_LN3_EOP_ERROR_COUNTER Field Descriptions
| Bit(s) | Name | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:0 | KR_LN3_EOP_ERR_COUNT (R) |
COR | Lane 3 End of packet Error counter. End of packet error is detected when Terminate character is in lane 3 and the column following the terminate column is neither ||K|| nor ||A||. Counter value cleared to 16’h0000 when read. |
7.5.3.35 KR_VS_TX_CTC_DROP_COUNT (register = 0x8014) (default = 0xFFFD) (device address: 0x01)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| TX_CTC_DROP_COUNT (R) |
|||||||||||||||
| COR | |||||||||||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-104 KR_VS_TX_CTC_DROP_COUNT Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:0 | TX_CTC_DROP_COUNT (R) |
COR | Counter for number of idle drops in the transmit CTC. |
7.5.3.36 KR_VS_TX_CTC_INSERT_COUNT (register = 0x8015) (default = 0xFFFD)
(device address: 0x01)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| TX_CTC_INS_COUNT (R) |
|||||||||||||||
| COR | |||||||||||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-105 KR_VS_TX_CTC_INSERT_COUNT Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:0 | TX_CTC_INS_COUNT (R) |
COR | Counter for number of idle inserts in the transmit CTC. |
7.5.3.37 KR_VS_RX_CTC_DROP_COUNT (register = 0x8016) (default = 0xFFFD)
(device address: 0x01)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| RX_CTC_DROP_COUNT (R) |
|||||||||||||||
| COR | |||||||||||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-106 KR_VS_RX_CTC_DROP_COUNT Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:0 | RX_CTC_DROP_COUNT (R) |
COR | Counter for number of idle drops in the receive CTC. |
7.5.3.38 KR_VS_RX_CTC_INSERT_COUNT (register = 0x8017) (default = 0xFFFD)
(device address: 0x01)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| RX_CTC_INS_COUNT (R) |
|||||||||||||||
| COR | |||||||||||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-107 KR_VS_RX_CTC_INSERT_COUNT Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:0 | RX_CTC_INS_COUNT (R) |
COR | Counter for number of idle inserts in the receive CTC. |
7.5.3.39 KR_VS_STATUS_1 (register = 0x8018) (default = 0x0000) (device address: 0x01)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| TX_TPV_TP_ SYNC (R) |
RESERVED | ||||||
| RO | RO | ||||||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| RESERVED | INVALID_S_ COL_ERR (R) |
INVALID_T_ COL_ERR (R) |
INVALID_XGMII_LN3 (R) |
INVALID_XGMII_LN2 (R) |
INVALID_XGMII_LN1 (R) |
INVALID_XGMII_LN0 (R) |
|
| RO | RO/LH | RO/LH | RO/LH | RO/LH | RO/LH | RO/LH | |
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-108 KR_VS_STATUS_1 Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | TX_TPV_TP_SYNC (R) |
RO | 0 = Test pattern sync is not achieved on on Tx side 1 = Test pattern sync is achieved on on Tx side |
|
| 14:6 | RESERVED | RO | For TI use only | |
| 5 | INVALID_S_COL_ERR (R) |
RO/LH | 1 = Indicates invalid start (S) column error detected | |
| 4 | INVALID_T_COL_ERR (R) |
RO/LH | 1 = Indicates invalid terminate (T) column error detected | |
| 3 | INVALID_XGMII_LN3 (R) |
RO/LH | 1 = Indicates invalid XGMII character detected in Lane 3 | |
| 2 | INVALID_XGMII_LN2 (R) |
RO/LH | 1 = Indicates invalid XGMII character detected in Lane 2 | |
| 1 | INVALID_XGMII_LN1 (R) |
RO/LH | 1 = Indicates invalid XGMII character detected in Lane 1 | |
| 0 | INVALID_XGMII_LN0 (R) |
RO/LH | 1 = Indicates invalid XGMII character detected in Lane 0 |
7.5.3.40 KR_VS_TX_CRCJ_ERR_COUNT_1 (register = 0x8019) (default = 0xFFFF)
(device address: 0x01)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| TX_TPV_CR_CJ_ERR_COUNT[31:16] (R) |
|||||||||||||||
| COR | |||||||||||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-109 KR_VS_TX_CRCJ_ERR_COUNT_1 Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:0 | TX_TPV_CR_CJ_ERR_COUNT[31:16] (R) |
COR | Error Counter for CR/CJ test pattern verification on Tx side. MSBs [31:16] |
7.5.3.41 KR_VS_TX_CRCJ_ERR_COUNT_2 (register = 0x801A) (default = 0xFFFD)
(device address: 0x01)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| TX_TPV_CR_CJ_ERR_COUNT[15:0] (R) |
|||||||||||||||
| COR | |||||||||||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-110 KR_VS_TX_CRCJ_ERR_COUNT_2 Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:0 | TX_TPV_CR_CJ_ERR_COUNT[15:0] (R) |
COR | Error Counter for CR/CJ test pattern verification on Tx side. MSBs [15:0] |
7.5.3.42 KR_VS_TX_LN0_HLM_ERR_COUNT (register = 0x801B) (default = 0xFFFD)
(device address: 0x01)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| TX_TPV_LN0_ERR_COUNT[15:0] (R) |
|||||||||||||||
| COR | |||||||||||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-111 KR_VS_TX_LN0_HLM_ERR_COUNT Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Value | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:0 | TX_TPV_LN0_ERR_COUNT[15:0] (R) |
COR | Error Counter for H/L/M test pattern verification on Lane 0 of Tx side |
7.5.3.43 KR_VS_TX_LN1_HLM_ERR_COUNT (register = 0x801C) (default = 0xFFFD)
(device address: 0x01)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| TX_TPV_LN1_ERR_COUNT[15:0] (R) |
|||||||||||||||
| COR | |||||||||||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-112 KR_VS_TX_LN1_HLM_ERR_COUNT Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Value | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:0 | TX_TPV_LN1_ERR_COUNT[15:0] (R) |
COR | Error Counter for H/L/M test pattern verification on Lane 1 of Tx side |
7.5.3.44 KR_VS_TX_LN2_HLM_ERR_COUNT (register = 0x801D) (default = 0xFFFD)
(device address: 0x01)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| TX_TPV_LN2_ERR_COUNT[15:0] (R) |
|||||||||||||||
| COR | |||||||||||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-113 KR_VS_TX_LN2_HLM_ERR_COUNT Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:0 | TX_TPV_LN2_ERR_COUNT[15:0] (R) |
COR | Error Counter for H/L/M test pattern verification on Lane 2 of Tx side |
7.5.3.45 KR_VS_TX_LN3_HLM_ERR_COUNT (register = 0x801E) (default = 0xFFFD) (device address: 0x01)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| TX_TPV_LN3_ERR_COUNT[15:0] (R) |
|||||||||||||||
| COR | |||||||||||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-114 KR_VS_TX_LN3_HLM_ERR_COUNT Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:0 | TX_TPV_LN3_ERR_COUNT[15:0] (R) |
COR | Error Counter for H/L/M test pattern verification on Lane 3 of Tx side |
7.5.3.46 LT_VS_CONTROL_2 (register = 0x9001) (default = 0x0000) (device address: 0x01)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| RESERVED | RESERVED | AP_SEARCH_MODE [2:0] (RXG) |
RESERVED | ||||||||||||
| RW | RW/SC | RW | RW | ||||||||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-115 LT_VS_CONTROL_2 Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:14 | RESERVED | RW | For TI use only (Default 2'b00) | |
| 13:12 | RESERVED | RW/SC | For TI use only (Default 2'b00) | |
| 11:9 | AP_SEARCH_MODE[2:0] (RXG) |
RW | 000 = Auto search, autotrain disabled (Default 3'b000) 001 = Full region search, autotrain disabled 010 = Auto search, autotrain enabled 011 = Full region search, autotrain enabled 1xx = Manual search |
|
| 8:0 | RESERVED | RW | For TI use only (Default 9'b000000000) |
7.5.4 PCS Registers
The registers below can be accessed only in Clause 45 mode and with device address field set to 0x03 (DEVADD [4:0] = 5’b00011). Valid only when device is in 10GBASE-KR mode.
7.5.4.1 PCS_CONTROL (register = 0x0000) (default = 0x0000) (device address: 0x03)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| PCS_RESET (R) |
PCS_LOOPBACK (R) |
RESERVED | PCS_LP_MODE (R) |
RESERVED | |||
| RW/SC | RW | RW | RW | RW | |||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| RESERVED | |||||||
| RW | |||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-116 PCS_CONTROL Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | PCS_RESET (R) |
RW/SC | 1 = Resets datapath and MDIO registers. Equivalent to asserting RESET_N. 0 = Normal operation (Default 1’b0) |
|
| 14 | PCS_LOOPBACK (R) |
RW | 1 = Enables PCS loopback 0 = Normal operation (Default 1’b0) Requires Auto Negotiation and Link Training to be disabled. |
|
| 13:12 | RESERVED | RW | For TI use only. Always reads 0. | |
| 11 | PCS_LP_MODE (R) |
RW | 1 = Enable power down mode 0 = Normal operation (Default 1’b0) |
|
| 10:0 | RESERVED | RW | For TI use only. Always reads 0. |
7.5.4.2 PCS_STATUS_1 (register = 0x0001) (default = 0x0002) (device address: 0x03)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| RESERVED | |||||||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| PCS_FAULT (R) |
RESERVED | PCS_RX_LINK (R) |
PCS_LP_ABILITY (R) |
RESERVED | |||
| RO | RO/LL | RO | |||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-117 PCS_STATUS_1 Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | TYPE | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:8 | RESERVED | For TI use only. | ||
| 7 | PCS_FAULT (R) |
RO | 1 = Fault condition detected on either PCS TX or PCS RX 0 = No fault condition detected This bit is cleared after Register 03.0008 is read and no fault condition occurs after 03.0008 is read. |
|
| 6:3 | RESERVED | For TI use only. | ||
| 2 | PCS_RX_LINK (R) |
RO/LL | 1 = PCS receive link is up 0 = PCS receive link is down |
|
| 1 | PCS_LP_ABILITY (R) |
RO | Always reads 1. 1 = Supports low power mode 0 = Does not support low power mode |
|
| 0 | RESERVED | For TI use only. |
7.5.4.3 PCS_STATUS_2 (register = 0x0008) (default = 0x8001) (device address: 0x03)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| DEV_PRESENT (R) |
RESERVED | PCS_TX_FAULT (R) |
PCS_RX_FAULT (R) |
RESERVED | |||
| RO | RO/LH | RO/LH | |||||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| RESERVED | PCS_10GBASER_CAPABLE (R) |
||||||
| RO | |||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-118 PCS_STATUS_2 Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:14 | DEV_PRESENT (R) |
RO | Always reads 2’b10. 0x = No device responding at this address 10 = Device responding at this address 11 = No device responding at this address |
|
| 13:12 | RESERVED | For TI use only. | ||
| 11 | PCS_TX_FAULT (R) |
RO/LH | 1 = Fault condition detected on transmit path 0 = No fault condition detected on transmit path |
|
| 10 | PCS_RX_FAULT (R) |
RO/LH | 1 = Fault condition detected on receive path 0 = No fault condition detected on receive path |
|
| 9:1 | RESERVED | For TI use only. | ||
| 0 | PCS_10GBASER_CAPABLE (R) |
RO | Always reads 1. 1 = PCS is able to support 10GBASE-R PCS type 0 = PCS not able to support 10GBASE-R PCS type |
7.5.4.4 KR_PCS_STATUS_1 (register = 0x0020) (default = 0x0004) (device address: 0x03)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| RESERVED | PCS_RX_LINK_STATUS (R) |
RESERVED | |||||
| RO | RO | ||||||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| RESERVED | PCS_PRBS31_ABILITY (R) |
PCS_HI_BER (R) |
PCS_BLOCK_LOCK (R) |
||||
| RO | RO | RO | RO | ||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-119 KR_PCS_STATUS_1 Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:13 | RESERVED | RO | For TI use only. | |
| 12 | PCS_RX_LINK_STATUS (R) |
RO | 1 = 10GBASE-R PCS receive link up 0 = 10GBASE-R PCS receive link down |
|
| 11:3 | RESERVED | RO | For TI use only. | |
| 2 | PCS_PRBS31_ABILITY (R) |
RO | Always reads 1. 1 = PCS is able to support PRBS31 pattern testing 0 = PCS is not able to support PRBS31 testing |
|
| 1 | PCS_HI_BER (R) |
RO | 1 = High BER condition detected 0 = High BER condition not detected |
|
| 0 | PCS_BLOCK_LOCK (R) |
RO | 1 = PCS locked to receive blocks 0 = PCS not locked to receive blocks |
7.5.4.5 KR_PCS_STATUS_2 (register = 0x0021) (default = 0x0000) (device address: 0x03)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| PCS_BLOCK_ LOCK_LL (R) |
PCS_HI_BER_LH (R) |
PCS_BER_COUNT[5:0] (R) |
|||||
| RO/LL | RO/LH | COR | |||||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| PCS_ERR_BLOCK_COUNT[7:0] (R) |
|||||||
| COR | |||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-120 KR_PCS_STATUS_2 Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | PCS_BLOCK_LOCK_LL (R) |
RO/LL | 1 = PCS locked to receive blocks 0 = PCS not locked to receive blocks |
|
| 14 | PCS_HI_BER_LH (R) |
RO/LL | 1 = High BER condition detected 0 = High BER condition not detected |
|
| 13:8 | PCS_BER_COUNT[5:0] (R) |
COR | Value indicating number of times BER state machine enters BER_BAD_SH state | |
| 7:0 | PCS_ERR_BLOCK_COUNT[7:0] (R) |
COR | Value indicating number of times RX decode state machine enters RX_E state. Same value is also reflected in 1E.0010 and reading either register clears the counter value. |
7.5.4.6 PCS_TP_SEED_A0 (register = 0x0022) (default = 0x0000) (device address: 0x03)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| PCS_TP_SEED_A[15:0] (R) |
|||||||||||||||
| RW | |||||||||||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-121 PCS_TP_SEED_A0 Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:0 | PCS_TP_SEED_A[15:0] (R) |
RW | Test pattern seed A bits 15-0 |
7.5.4.7 PCS_TP_SEED_A1 (register = 0x0023) (default = 0x0000) (device address: 0x03)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| PCS_TP_SEED_A[31:16] (R) |
|||||||||||||||
| RW | |||||||||||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-122 PCS_TP_SEED_A1 Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:0 | PCS_TP_SEED_A[31:16] (R) |
RW | Test pattern seed A bits 31-16 |
7.5.4.8 PCS_TP_SEED_A2 (register = 0x0024) (default = 0x0000) (device address: 0x03)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| PCS_TP_SEED_A[47:32] (R) |
|||||||||||||||
| RW | |||||||||||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-123 PCS_TP_SEED_A2 Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:0 | PCS_TP_SEED_A[47:32] (R) |
RW | Test pattern seed A bits 47-32 |
7.5.4.9 PCS_TP_SEED_A3 (register = 0x0025) (default = 0x0000) (device address: 0x03)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| RESERVED | PCS_TP_SEED_A[57:48] (R) |
||||||||||||||
| RW | RW | ||||||||||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-124 PCS_TP_SEED_A3 Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:10 | RESERVED | RW | For TI use only. Always reads 0. | |
| 9:0 | PCS_TP_SEED_A[57:48] (R) |
RW | Test pattern seed A bits 57-48 |
7.5.4.10 PCS_TP_SEED_B0 (register = 0x0026) (default = 0x0000) (device address: 0x03)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| PCS_TP_SEED_B[15:0] (R) |
|||||||||||||||
| RW | |||||||||||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-125 PCS_TP_SEED_B0 Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:0 | PCS_TP_SEED_B[15:0] (R) |
RW | Test pattern seed B bits 15-0 |
7.5.4.11 PCS_TP_SEED_B1 (register = 0x0027) (default = 0x0000) (device address: 0x03)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| PCS_TP_SEED_B[31:16] (R) |
|||||||||||||||
| RW | |||||||||||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-126 PCS_TP_SEED_B1 Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:0 | PCS_TP_SEED_B[31:16] (R) |
RW | Test pattern seed B bits 31-16 |
7.5.4.12 PCS_TP_SEED_B2 (register = 0x0028) (default = 0x0000) (device address: 0x03)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| PCS_TP_SEED_B[47:32] (R) |
|||||||||||||||
| RW | |||||||||||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-127 PCS_TP_SEED_B2 Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:0 | PCS_TP_SEED_B[47:32] (R) |
RW | Test pattern seed B bits 47-32 |
7.5.4.13 PCS_TP_SEED_B3 (register = 0x0029) (default = 0x0000) (device address: 0x03)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| RESERVED | PCS_TP_SEED_B[57:48] (R) |
||||||||||||||
| RW | RW | ||||||||||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-128 PCS_TP_SEED_B3 Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:10 | RESERVED | RW | For TI use only. Always reads 0. | |
| 9:0 | PCS_TP_SEED_B[57:48] (R) |
RW | Test pattern seed B bits 57-48 |
7.5.4.14 PCS_TP_CONTROL (register = 0x002A) (default = 0x0000) (device address: 0x03)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| RESERVED | |||||||
| RW | |||||||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| RESERVED | PCS_PRBS31_RX_TP_EN (R) |
PCS_PRBS31_TX_TP_EN (R) |
PCS_TX_TP_EN (R) |
PCS_RX_TP_EN (R) |
PCS_TP_SEL (R) |
PCS_DP_SEL (R) |
|
| RW | RW | RW | RW | RW | RW | RW | |
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-129 PCS_TP_CONTROL Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:6 | RESERVED | RW | For TI use only. Always reads 0. | |
| 5 | PCS_PRBS31_RX_TP_EN (R) |
RW | 1 = Enable PRBS31 test pattern verification on receive path 0 = Normal operation (Default 1’b0) |
|
| 4 | PCS_PRBS31_TX_TP_EN (R) |
RW | 1 = Enable PRBS31 test pattern generation on transmit path 0 = Normal operation (Default 1’b0) |
|
| 3 | PCS_TX_TP_EN (R) |
RW | 1 = Enable transmit test pattern generation 0 = Normal operation (Default 1’b0) |
|
| 2 | PCS_RX_TP_EN (R) |
RW | 1 = Enable receive test pattern verification 0 = Normal operation (Default 1’b0) |
|
| 1 | PCS_TP_SEL (R) |
RW | 1 = Square wave test pattern 0 = Pseudo random test pattern (Default 1’b0) |
|
| 0 | PCS_DP_SEL (R) |
RW | 1 = 0’S data pattern 0 = LF data pattern (Default 1’b0) |
7.5.4.15 PCS_TP_ERR_COUNT (register = 0x002B) (default = 0x0000) (device address: 0x03)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| PCS_TP_ERR_COUNT[15:0] (R) |
|||||||||||||||
| COR | |||||||||||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-130 PCS_TP_ERR_COUNT Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:0 | PCS_TP_ERR_COUNT[15:0] (R) |
COR | Test pattern error counter. This counter reflects number of errors occurred during the test pattern mode selected through PCS_TP_CONTROL. In PRBS31 test pattern verification mode, counter value indicates the number of received bytes that have 1 or more bit errors. |
7.5.4.16 PCS_VS_CONTROL (register = 0x8000) (default = 0x00B0) (device address: 0x03)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| RESERVED | |||||||
| RW | |||||||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| PCS_SQWAVE_N (R) |
RESERVED | PCS_RX_DEC_CTRL_CHAR (R) |
PCS_DESCR_DISABLE (R) |
PCS_SCR_DISABLE (R) |
|||
| RW | RW | RW | RW | RW | |||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-131 PCS_VS_CONTROL Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:8 | RESERVED | RW | For TI use only. Always reads 0. | |
| 7:4 | PCS_SQWAVE_N (R) |
RW | Sets number of repeating 0’s followed by repeating 1’s during square wave test pattern generation mode (Default 4’1011) | |
| 3 | RESERVED | RW | For TI use only (Default 1’b0) | |
| 2 | PCS_RX_DEC_CTRL_CHAR (R) |
RW | PCS RX Decode control character selection. Determines what control characters are passed 0 = A/K/R control characters are changed to Idles. Reserved characters passed through (Default 1’b0) 1 = A/K/R control characters are passed through as is RW |
|
| 1 | PCS_DESCR_DISABLE (R) |
RW | De-scrambler control in 10GKR RX PCS 1 = Disable descrambler 0 = Enable descrambler (Default 1’b0) |
|
| 0 | PCS_SCR_DISABLE (R) |
RW | Scrambler control in 10GKR TX PCS 1 = Disable scrambler 0 = Enable scrambler (Default 1’b0) |
7.5.4.17 PCS_VS_STATUS (register = 0x8010) (default = 0x00FD) (device address: 0x03)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| RESERVED | UNCORR_ERR_STATUS (R) |
CORR_ERR_STATUS (R) |
RESERVED | PCS_TP_ERR (R) |
|||
| RO/LF | RO/LF | RO/LF | RO/LF | ||||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| RESERVED | |||||||
| COR | |||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-132 PCS_VS_STATUS Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:14 | RESERVED | RO/LF | For TI use only. | |
| 13 | UNCORR_ERR_STATUS (R) |
RO/LF | 1 = Uncorrectable block error found | |
| 12 | CORR_ERR_STATUS (R) |
RO/LF | 1 = Correctable block error found | |
| 11:9 | RESERVED | COR | For TI use only. | |
| 8 | PCS_TP_ERR (R) |
RO/LF | PCS test pattern verification status PCS_SCR_DISABLE 1 = Error occurred during pseudo random test pattern verification Number of errors can be checked by reading PCS_TP_ERR_COUNT (03.002B) register |
|
| 7:0 | RESERVED | COR | For TI use only. |
7.5.5 Auto-Negotiation Registers
The registers below can be accessed only in Clause 45 mode and with device address field set to 0x07 (DA[4:0] = 5’b00111)
7.5.5.1 AN_CONTROL (register = 0x0000) (default = 0x3000) (device address: 0x07)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| AN_RESET (RX) |
RESERVED | AN_ENABLE (RX) |
RESERVED | AN_RESTART (RX) |
RESERVED | ||
| RW/SC | RW | RW | RW | RW/SC(1) | RW | ||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| RESERVED | |||||||
| RW | |||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-133 AN_CONTROL Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | AN_RESET (RX) |
RW/SC | 1 = Resets Auto Negotiation 0 = Normal operation (Default 1’b0) |
|
| 14 | RESERVED | RW | For TI use only. Always reads 0. | |
| 13 | RESERVED | RW | For TI use only (Default 1’b1) | |
| 12 | AN_ENABLE (RX) |
RW | 1 = Enable Auto Negotiation (Default 1’b1) 0 = Disable Auto Negotiation |
|
| 11:10 | RESERVED | RW | For TI use only. Always reads 0. | |
| 9 | AN_RESTART (RX) |
RW/SC | 1 = Restart Auto Negotiation 0 = Normal operation (Default 1’b0) If set, a read of this register is required to clear AN_RESTART bit. |
|
| 8:0 | RESERVED | RW | For TI use only. Always reads 0. |
7.5.5.2 AN_STATUS (register = 0x0001) (default = 0x0088) (device address: 0x07)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| RESERVED | AN_PAR_DET_FAULT (RX) |
RESERVED | |||||
| RO/LH | RO | ||||||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| AN_EXP_NP_STATUS (RX) |
AN_PAGE_RCVD (RX) |
AN_COMPLETE (RX) |
REMOTE_FAULT (RX) |
AN_ABILITY (RX) |
LINK_STATUS (RX) |
RESERVED | AN_LP_ABILITY (RX) |
| RO | RO/LH | RO | RO/LH | RO | RO/LL | RO | |
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-134 AN_STATUS Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:10 | RESERVED | RO | For TI use only. | |
| 9 | AN_PAR_DET_FAULT (RX) |
RO/LH | 1 = Fault has been detected via parallel detection function 0 = Fault has not been detected via parallel detection function |
|
| 8 | RESERVED | RO | For TI use only. | |
| 7 | AN_EXP_NP_STATUS (RX) |
RO/LH | 1 = Extended next page is used 0 = Extended next page is not allowed |
|
| 6 | AN_PAGE_RCVD (RX) |
RO | 1 = A page has been received 0 = A page has not been received |
|
| 5 | AN_COMPLETE (RX) |
RO/LH | 1 = Auto Negotiation process is completed 0 = Auto Negotiation process not completed |
|
| 4 | REMOTE_FAULT (RX) |
RO/LH | 1 = Remote fault detected by AN 0 = Remote fault not detected by AN |
|
| 3 | AN_ABILITY (RX) |
RO | Always reads 1. 1 = Device is able to perform Auto Negotiation 0 = Device not able to perform Auto Negotiation |
|
| 2 | LINK_STATUS (RX) |
RO/LH | 1 = Link is up 0 = Link is down |
|
| 1 | RESERVED | RO | For TI use only. | |
| 0 | AN_LP_ABILITY (RX) |
RO | 1 = LP is able to perform Auto Negotiation 0 = LP not able to perform Auto Negotiation |
7.5.5.3 AN_DEV_PACKAGE (register = 0x0005) (default = 0x0080) (device address: 0x07)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| RESERVED | |||||||
| RO | |||||||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| AN_ PRESENT (RX) |
RESERVED | ||||||
| RO | RO | ||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-135 AN_DEV_PACKAGE Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:8 | RESERVED | RO | For TI use only. | |
| 7 | AN_PRESENT (RX) |
RO | Always reads 1 1 = Auto Negotiation present in the package 0 = Auto Negotiation not present in the package |
|
| 6:0 | RESERVED | RO | For TI use only. |
7.5.5.4 AN_ADVERTISEMENT_1 (register = 0x0010) (default = 0x1001) (device address: 0x07)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| AN_NEXT_PAGE (RX) |
AN_ACKNOWLEDGE (RX) |
AN_REMOTE_FAULT (RX) |
AN_CAPABILITY[2:0] (RX) |
AN_ECHO_NONCE[4:0] (RX) |
|||
| RW | RO | RW | RW | RW | |||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| AN_ECHO_NONCE[4:0] (RX) |
AN_SELECTOR[4:0] (RX) |
||||||
| RW | RW | ||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-136 AN_ADVERTISEMENT_1 Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | AN_NEXT_PAGE (RX) |
RW | NP bit (D15) in base link codeword 1 = Next page available 0 = Next page not available (Default 1’b0) |
|
| 14 | AN_ACKNOWLEDGE (RX) |
RO | Acknowledge bit (D14) in base link codeword. Always reads 0. | |
| 13 | AN_REMOTE_FAULT (RX) |
RW | RF bit (D13) in base link codeword 1 = Sets RF bit to 1 0 = Normal operation (Default 1’b0) |
|
| 12:10 | AN_CAPABILITY[2:0] (RX) |
RW | Value to be set in D12:D10 bits of the base link codeword. Consists of abilities like PAUSE, ASM_DIR (Default 3’b100) | |
| 9:5 | AN_ECHO_NONCE[4:0] (RX) |
RW | Value to be set in D9:D5 bits of the base link codeword. Consists of Echo nonce value. Transmitted in base page only until local device and link Partner have exchanged unique Nonce values, at which time transmitted Echoed Nonce will change to Link Partner's Nonce value. Read value always reflects the value written, not the actual Echoed Nonce. (Default 5’b00000) | |
| 4:0 | AN_SELECTOR[4:0] (RX) |
RW | Value to be set in D4:D0 bits of the base link codeword. Consists of selector field value (Default 5’b00001) |
7.5.5.5 AN_ADVERTISEMENT_2 (register = 0x0011) (default = 0x0080)
(device address: 0x07)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| AN_ABILITY[10:3] (RX) |
|||||||
| RW | |||||||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| AN_ABILITY[2] (RX) |
AN_ABILITY[1] (RX) |
AN_ABILITY[0] (RX) |
AN_TRANS_NONCE_ FIELD[4:0] (RX) |
||||
| RW | RW | RW | RW | ||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-137 AN_ADVERTISEMENT_2 Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Value | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:8 | AN_ABILITY[10:3] (RX) |
RW | Value to be set in D31:D24 bits of the base link codeword. Consists of technology ability field bits [10:3] (Default 9’b000000000) | |
| 7 | AN_ABILITY[2] (RX) |
RW | Value to be set in D23 bits of the base link codeword. Consists of technology ability field bits [2]. When set, indicates device supports 10GBASE-KR (Default 1’b1) | |
| 6 | AN_ABILITY[1] (RX) |
RW | Value to be set in D22 bits of the base link codeword. Consists of technology ability field bits [1]. Always set to 0 (Default 1’b0) | |
| 5 | AN_ABILITY[0] (RX) |
RW | Value to be set in D21 bits of the base link codeword. Consists of technology ability field bit [0]. When set, indicates device supports 1000BASE-KX (Default 1’b0) | |
| 4:0 | AN_TRANS_NONCE_ FIELD[4:0] (RX) |
RW | Not used. Transmitted Nonce field is generated by hardware random number generator. Read value always reflects value written, not the actual Transmitted Nonce (Default 5’b00000) |
7.5.5.6 AN_ADVERTISEMENT_3 (register = 0x0012) (default = 0x4000)
(device address: 0x07)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| AN_FEC_REQUESTED (RX) |
AN_FEC_ABILITY (RX) |
AN_ABILITY[24:11] (RX) |
|||||
| RW | RW | RW | |||||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| AN_ABILITY[24:11] (RX) |
|||||||
| RW | |||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-138 AN_ADVERTISEMENT_3 Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | AN_FEC_REQUESTED (RX) |
RW | Value to be set in D47 bits of the base link codeword. When set, indicates a request to enable FEC on the link (Default 1’b0) | |
| 14 | AN_FEC_ABILITY (RX) |
RW | Value to be set in D46 bits of the base link codeword. When set, indicates 10GBASE-KR has FEC ability (Default 1’b1) | |
| 13:0 | AN_ABILITY[24:11] (RX) |
RW | Value to be set in D45:D32 bits of the base link codeword. Consists of technology ability field bits [24:11] (Default 14’b00000000000000) |
7.5.5.7 AN_LP_ADVERTISEMENT_1 (register = 0x0013) (default = 0x0001)
(device address: 0x07)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| AN_LP_NEXT_PAGE (RX) |
AN_LP_ACKNOWLEDGE (RX) |
AN_LP_REMOTE_FAULT (RX) |
AN_ LP_CAPABILITY (RX) |
AN_ LP_ECHO_NONCE (RX) |
|||
| RO | RO | RO | RO | RO | |||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| AN_ LP_ECHO_NONCE (RX) |
AN_LP_SELECTOR[4:0] (RX) |
||||||
| RO | RO | ||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-139 AN_LP_ADVERTISEMENT_1(1) Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | AN_LP_NEXT_PAGE (RX) |
RO | NP bit (D15) in link partner base page 1 = Next page available in link partner 0 = Next page not available in link partner |
|
| 14 | AN_LP_ACKNOWLEDGE (RX) |
RO | Acknowledge bit (D14) in link partner base page. | |
| 13 | AN_LP_REMOTE_FAULT (RX) |
RO | RF bit (D13) in link partner base page 1 = Remote fault detected in link partner 0 = Remote fault not detected in link partner |
|
| 12:10 | AN_ LP_CAPABILITY (RX) |
RO | D12:D10 bits of the link partner base page. Consists of abilities like PAUSE, ASM_DIR | |
| 9:5 | AN_ LP_ECHO_NONCE (RX) |
RO | D9:D5 bits of the link partner base page. Consists of Echo nonce value | |
| 4:0 | AN_LP_SELECTOR[4:0] (RX) |
RO | D4:D0 bits of the link partner base page. Consists of selector field value Always reads 5’b00001 |
7.5.5.8 AN_LP_ADVERTISEMENT_2 (register = 0x0014) (default = 0x0000)
(device address: 0x07)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| AN_ LP_ABILITY[10:3] (RX) |
|||||||
| RO | |||||||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| AN_LP_ABILITY[2] (RX) |
AN_LP_ABILITY[1] (RX) |
AN_LP_ABILITY[0] (RX) |
AN_LP_TRANS_NONCE_FIELD (RX) |
||||
| RO | RO | RO | RO | ||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-140 AN_LP_ADVERTISEMENT_2 Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:8 | AN_ LP_ABILITY[10:3] (RX) |
RO | D31:D24 bits of the link partner base page. Consists of technology ability field bits [10:3] | |
| 7 | AN_LP_ABILITY[2] (RX) |
RO | D23 bits of the link partner base page. Consists of technology ability field bits [2]. When high, indicates link partner supports 10GBASE-KR | |
| 6 | AN_LP_ABILITY[1] (RX) |
RO | D22 bits of the link partner base page. Consists of technology ability field bits [1]. | |
| 5 | AN_LP_ABILITY[0] (RX) |
RO | D21 bits of the link partner base page. Consists of technology ability field bit [0]. When high, indicates link partner supports 1000BASE-KX | |
| 4:0 | AN_LP_TRANS_NONCE_FIELD (RX) |
RO | D20:D16 bits of the link partner base page. Consists of transmitted nonce value |
7.5.5.9 AN_LP_ADVERTISEMENT_3 (register = 0x0015) (default = 0x0000)
(device address: 0x07)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| AN_LP_FEC_REQUESTED (RX) |
AN_LP_FEC_ABILITY (RX) |
AN_LP_ABILITY[24:11] (RX) |
|||||
| RO | RO | RO | |||||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| AN_LP_ABILITY[24:11] (RX) |
|||||||
| RO | |||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-141 AN_LP_ADVERTISEMENT_3 Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | AN_LP_FEC_REQUESTED (RX) |
RO | D47 bits of the link partner base page. When high, indicates link partner request to enable FEC on the link | |
| 14 | AN_LP_FEC_ABILITY (RX) |
RO | D46 bits of the link partner base page. When high, indicates link partner has FEC ability | |
| 13:0 | AN_LP_ABILITY[24:11] (RX) |
RO | D45:D32 bits of the link partner base page. Consists of link partner technology ability field bits [24:11] |
7.5.5.10 AN_XNP_TRANSMIT_1 (register = 0x0016) (default = 0x2000) (device address: 0x07)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| AN_XNP_NEXT_PAGE (RX) |
RESERVED | AN_MP (RX) |
AN_ACKNOWLEDGE_2 (RX) |
AN_TOGGLE (RX) |
AN_CODE_FIELD (RX) |
||
| RW | RO | RW | RW | RW | RW | ||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| AN_CODE_FIELD (RX) |
|||||||
| RW | |||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-142 AN_XNP_TRANSMIT_1 Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | AN_XNP_NEXT_PAGE (RX) |
RW | NP bit (D15) in next page code word 1 = Next page available 0 = Next page not available (Default 1’b0) |
|
| 14 | RESERVED | RO | Always reads 0. | |
| 13 | AN_MP (RX) |
RW | Message page bit (D13) in next page code word 1 = Sets MP bit to 1 indicating next page is a message page (Default 1’b1) 0 = Sets MP bit to 0 indicating next page is unformatted next page |
|
| 12 | AN_ACKNOWLEDGE_2 (RX) |
RW | Value to be set in D12 bit of the next page code word. When set, indicates device is able to act on the information defined in the message (Default 1’b0) | |
| 11 | AN_TOGGLE (RX) |
RW | Not used. Toggle value is generated by hardware. Read value always reflects value written, not the actual Toggle field (Default 1’b0) | |
| 10:0 | AN_CODE_FIELD (RX) |
RW | Value to be set in D10:D0 bits of the next page code word. Consists of Message/Unformatted code field value (Default 11’b00000000000) |
7.5.5.11 AN_XNP_TRANSMIT_2 (register = 0x0017) (default = 0x0000) (device address: 0x07)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| AN_MSG_CODE_1 (RX) |
|||||||||||||||
| RW | |||||||||||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-143 AN_XNP_TRANSMIT_2 Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Value | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:0 | AN_MSG_CODE_1 (RX) |
RW | Value to be set in D31:D16 bits of the next page code word. Consists of Message/Unformatted code field value (Default 16’b0000000000000000) |
7.5.5.12 AN_XNP_TRANSMIT_3 (register = 0x0018) (default = 0x0000) (device address: 0x07)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| AN_MSG_CODE_2 (RX) |
|||||||||||||||
| RW | |||||||||||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-144 AN_XNP_TRANSMIT_3 Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:0 | AN_MSG_CODE_2 (RX) |
RW | Value to be set in D47:D32 bits of the next page code word. Consists of Message/Unformatted code field value (Default 16’b0000000000000000) |
7.5.5.13 AN_LP_XNP_ABILITY_1 (register = 0x0019) (default = 0x0000)
(device address: 0x07)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| AN_LP_XNP_NEXT_PAGE (RX) |
AN_LP_XNP_ACKNOWLEDGE (RX) |
AN_LP_MP (RX) |
AN_LP_ACKNOWLEDGE_2 (RX) |
AN_LP_TOGGLE (RX) |
AN_ LP_CODE_FIELD (RX) |
||
| RO | RO | RO | RO | RO | RO | ||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| AN_ LP_CODE_FIELD (RX) |
|||||||
| RO | |||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-145 AN_LP_XNP_ABILITY_1(1) Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | AN_LP_XNP_NEXT_PAGE (RX) |
RO | NP bit (D15) in next page code word 1 = Next page available 0 = Next page not available (Default 1’b0) |
|
| 14 | AN_LP_XNP_ACKNOWLEDGE (RX) |
RO | Value in D14 bit of the next page code word. When set, indicates device is able to act on the information defined in the message (Default 1’b0) | |
| 13 | AN_LP_MP (RX) |
RO | Message page bit (D13) in next page code word 1 = Sets MP bit to 1 indicating next page is a message page 0 = Sets MP bit to 0 indicating next page is unformatted next page (Default 1’b0) |
|
| 12 | AN_LP_ACKNOWLEDGE_2 (RX) |
RO | Value in D12 bit of the next page code word. When set, indicates device is able to act on the information defined in the message (Default 1’b0) | |
| 11 | AN_LP_TOGGLE (RX) |
RO | Value of D11 bit of the next page code word. Consists of Toggle field value(Default 1’b0) | |
| 10:0 | AN_ LP_CODE_FIELD (RX) |
RO | Value in D10:D0 bits of the next page code word. Consists of Message/Unformatted code field value (Default 11’b00000000000) |
7.5.5.14 AN_LP_XNP_ABILITY_2 (register = 0x001A) (default = 0x0000)
(device address: 0x07)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| AN_LP_MSG_CODE_2 (RX) |
|||||||||||||||
| RO | |||||||||||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-146 AN_LP_XNP_ABILITY_2 Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:0 | AN_LP_MSG_CODE_1 (RX) |
RO | Value to be set in D31:D16 bits of the next page code word. Consists of Message/Unformatted code field value (Default 16’b0000000000000000) |
7.5.5.15 AN_LP_XNP_ABILITY_3 (register = 0x001B) (default = 0x0000)
(device address: 0x07)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| AN_LP_MSG_CODE_2 (RX) |
|||||||||||||||
| RO | |||||||||||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-147 AN_LP_XNP_ABILITY_3 Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:0 | AN_LP_MSG_CODE_2 (RX) |
RO | Value to be set in D47:D32 bits of the next page code word. Consists of Message/Unformatted code field value (Default 16’b0000000000000000) |
7.5.5.16 AN_BP_STATUS (register = 0x0030) (default = 0x0001) (device address: 0x07)
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| RESERVED | |||||||
| RO | |||||||
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| RESERVED | AN_10G_KR_FEC (RX) |
AN_10G_KR (RX) |
RESERVED | AN_1G_KX (RX) |
AN_BP_AN_ABILITY (RX) |
||
| RO | RO | RO | RO | RO | RO | ||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 7-148 AN_BP_STATUS Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:5 | RESERVED | RO | For TI use only. | |
| 4 | AN_10G_KR_FEC (RX) |
RO | 1 = PMA/PMD is negotiated to perform 10GBASE-KR FEC | |
| 3 | AN_10G_KR (RX) |
RO | 1 = PMA/PMD is negotiated to perform 10GBASE-KR | |
| 2 | RESERVED | RO | For TI use only. | |
| 1 | AN_1G_KX (RX) |
RO | 1 = PMA/PMD is negotiated to perform 1000BASE-KX | |
| 0 | AN_BP_AN_ABILITY (RX) |
RO | Always reads 1. 1 = Indicates 1000BASE-KX, 10GBASE-KR is implemented |
Table 7-149 TI_Reserved Control and Status Registers
| Register Name | Register Address | Default Value | Access | Register Name | Register Address | Default Value | Access | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TI_RESERVED_CONTROL | 1E.8000 | 0x04C0 | RW | TI_RESERVED_STATUS | 1E.A014 | 0x0000 | RO | |
| TI_RESERVED_CONTROL | 1E.8001 | 0x0207 | RW | TI_RESERVED_STATUS | 1E.A015 | 0x0000 | RO | |
| TI_RESERVED_CONTROL | 1E.8002 | 0x02FE | RW | TI_RESERVED_STATUS | 1E.A016 | 0x0000 | RO | |
| TI_RESERVED_CONTROL | 1E.8005 | 0x0000 | RW | TI_RESERVED_STATUS | 1E.A017 | 0x0000 | RO | |
| TI_RESERVED_CONTROL | 1E.8006 | 0x0000 | RW | TI_RESERVED_STATUS | 1E.A018 | 0x0000 | RO | |
| TI_RESERVED_CONTROL | 1E.8007 | 0x8000 | RW | TI_RESERVED_CONTROL | 1E.A116 | 0x0000 | RW | |
| TI_RESERVED_CONTROL | 1E.8008 | 0x0000 | RW | TI_RESERVED_CONTROL | 1E.A117 | 0x0000 | RW | |
| TI_RESERVED_CONTROL | 1E.8009 | 0xFC00 | RW | TI_RESERVED_STATUS | 1E.A118 | 0x0000 | RO | |
| TI_RESERVED_CONTROL | 1E.800A | 0xBC3C | RW | TI_RESERVED_STATUS | 1E.A119 | 0x0000 | RO | |
| TI_RESERVED_CONTROL | 1E.800B | 0x0000 | RW | TI_RESERVED_CONTROL | 01.8000 | 0x4800 | RW | |
| TI_RESERVED_CONTROL | 1E.800C | 0x0000 | RW | TI_RESERVED_STATUS | 01.801F | 0xFFFD | COR | |
| TI_RESERVED_CONTROL | 1E.800D | 0x01FC | RW | TI_RESERVED_STATUS | 01.8020 | 0xFFFD | COR | |
| TI_RESERVED_CONTROL | 1E.800E | 0x0000 | RW | TI_RESERVED_STATUS | 01.8021 | 0xFFFD | COR | |
| TI_RESERVED_CONTROL | 1E.800F | 0x00C0 | RW | TI_RESERVED_STATUS | 01.8022 | 0xFFFD | COR | |
| TI_RESERVED_CONTROL | 1E.8011 | 0x7F00 | RW | TI_RESERVED_STATUS | 01.8023 | 0xFFFF | COR | |
| TI_RESERVED_STATUS | 1E.8012 | 0xFFFD | COR | TI_RESERVED_STATUS | 01.8024 | 0xFFFD | COR | |
| TI_RESERVED_STATUS | 1E.8013 | 0xFFFD | COR | TI_RESERVED_CONTROL | 01.9000 | 0x0249 | RW | |
| TI_RESERVED_STATUS | 1E.8014 | 0x0000 | RO/LH | TI_RESERVED_CONTROL | 01.9002 | 0x1335 | RW | |
| TI_RESERVED_STATUS | 1E.8015 | 0x0000 | RO | TI_RESERVED_CONTROL | 01.9003 | 0x5E29 | RW | |
| TI_RESERVED_CONTROL | 1E.8019 | 0xFC00 | RW | TI_RESERVED_CONTROL | 01.9004 | 0x007F | RW | |
| TI_RESERVED_CONTROL | 1E.801A | 0xBC3C | RW | TI_RESERVED_CONTROL | 01.9005 | 0x1C00 | RW | |
| TI_RESERVED_CONTROL | 1E.801C | 0x0000 | RW | TI_RESERVED_CONTROL | 01.9006 | 0x0000 | RW | |
| TI_RESERVED_CONTROL | 1E.801D | 0x01FC | RW | TI_RESERVED_CONTROL | 01.9007 | 0x5120 | RW | |
| TI_RESERVED_CONTROL | 1E.801E | 0x0000 | RW | TI_RESERVED_CONTROL | 01.9008 | 0xC018 | RW | |
| TI_RESERVED_CONTROL | 1E.801F | 0x00C0 | RW | TI_RESERVED_CONTROL | 01.9009 | 0xE667 | RW | |
| TI_RESERVED_CONTROL | 1E.8020 | 0x0200 | RW | TI_RESERVED_CONTROL | 01.900A | 0x5E8F | RW | |
| TI_RESERVED_CONTROL | 1E.8022 | 0x0000 | RW | TI_RESERVED_CONTROL | 01.900B | 0xAFAF | RW | |
| TI_RESERVED_CONTROL | 1E.8023 | 0x0000 | RW | TI_RESERVED_CONTROL | 01.900C | 0x0800 | RW | |
| TI_RESERVED_CONTROL | 1E.8024 | 0x0000 | RW | TI_RESERVED_CONTROL | 01.900D | 0x461A | RW | |
| TI_RESERVED_CONTROL | 1E.8025 | 0xF000 | RW | TI_RESERVED_CONTROL | 01.900E | 0x1723 | RW | |
| TI_RESERVED_STATUS | 1E.8030 | 0x0000 | RO | TI_RESERVED_CONTROL | 01.900F | 0x7003 | RW | |
| TI_RESERVED_STATUS | 1E.8031 | 0x0000 | RO | TI_RESERVED_CONTROL | 01.9010 | 0x0851 | RW | |
| TI_RESERVED_STATUS | 1E.8032 | 0x0000 | RO | TI_RESERVED_CONTROL | 01.9011 | 0x1EFF | RW | |
| TI_RESERVED_STATUS | 1E.8033 | 0x0000 | RO | TI_RESERVED_STATUS | 01.9020 | 0x0000 | RO | |
| TI_RESERVED_STATUS | 1E.8034 | 0x0000 | RO | TI_RESERVED_STATUS | 01.9021 | 0xFFFD | COR | |
| TI_RESERVED_STATUS | 1E.8035 | 0x0000 | RO | TI_RESERVED_STATUS | 01.9022 | 0x0000 | RO | |
| TI_RESERVED_CONTROL | 1E.8050 | 0x0000 | RW | TI_RESERVED_STATUS | 01.9023 | 0x0000 | RO | |
| TI_RESERVED_CONTROL | 1E.8102 | 0xF280 | RW | TI_RESERVED_STATUS | 01.9024 | 0x0000 | RO | |
| TI_RESERVED_CONTROL | 1E.A000 | 0x0000 | RW | TI_RESERVED_STATUS | 01.9025 | 0x0000 | RO | |
| TI_RESERVED_STATUS | 1E.A010 | 0x0000 | RO | TI_RESERVED_STATUS | 01.9026 | 0x0000 | RO | |
| TI_RESERVED_STATUS | 1E.A011 | 0x0000 | RO | TI_RESERVED_STATUS | 01.9027 | 0x0000 | RO | |
| TI_RESERVED_STATUS | 1E.A012 | 0x0000 | RO | TI_RESERVED_STATUS | 01.9028 | 0x0000 | RO | |
| TI_RESERVED_STATUS | 1E.A013 | 0x0000 | RO | TI_RESERVED_STATUS | 01.9029 | 0x0000 | RO |