SGLS307Q July 2006 – August 2024 TLK2711-SP
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
5 Specifications
- 5.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 5.2 ESD Ratings
- 5.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 5.4 Thermal Information
- 5.5 TTL Input Electrical Characteristics
- 5.6 Transmitter/Receiver Electrical Characteristics
- 5.7 Reference Clock (TXCLK) Timing Requirements
- 5.8 TTL Output Switching Characteristics
- 5.9 Typical Characteristics
-
6 Detailed Description
- 6.1 Overview
- 6.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 6.3
Feature Description
- 6.3.1 Transmit Interface
- 6.3.2 Transmit Data Bus
- 6.3.3 Data Transmission Latency
- 6.3.4 8-Bit/10-Bit Encoder
- 6.3.5 Pseudo-Random Bit Stream (PRBS) Generator
- 6.3.6 Parallel to Serial
- 6.3.7 High-Speed Data Output
- 6.3.8 Receive Interface
- 6.3.9 Receive Data Bus
- 6.3.10 Data Reception Latency
- 6.3.11 Serial to Parallel
- 6.3.12 Comma Detect and 8-Bit/10-Bit Decoding
- 6.3.13 LOS Detection
- 6.3.14 PRBS Verification
- 6.3.15 Reference Clock Input
- 6.3.16 Operating Frequency Range
- 6.3.17 Testability
- 6.3.18 Loopback Testing
- 6.3.19 BIST
- 6.3.20 Power-On Reset
- 6.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7 Application and Implementation
- 8 Device and Documentation Support
- 9 Revision History
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- HFG|68
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
4 Pin Configuration and Functions
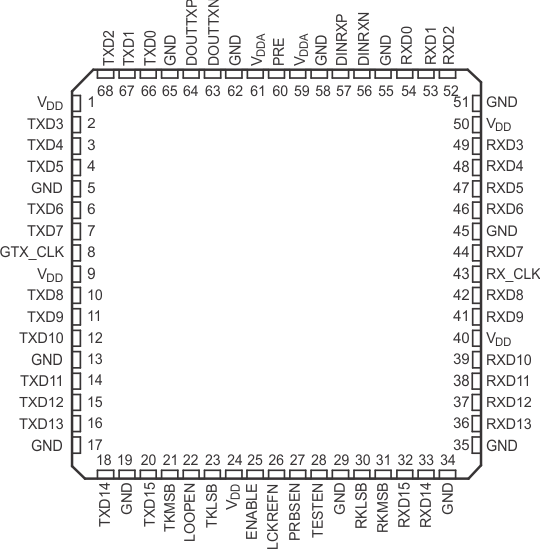 Figure 4-1 HFG Package68-Pin CFPTop View
Figure 4-1 HFG Package68-Pin CFPTop View| PIN | I/O | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | ||
| DOUTTXN DOUTTXP |
63 64 |
O | Serial transmit outputs. TXP and TXN are differential serial outputs that interface to copper or an optical I/F module. These pins transmit NRZ data at a rate of 20× the TXCLK value. TXP and TXN are put in a high-impedance state when LOOPEN is high and are active when LOOPEN is low. During power-on reset, these pins are high impedance. |
| ENABLE | 25 | I(1) | Device enable. When this pin is held low, the device is placed in power-down mode. Only the signal detect circuit on the serial receive pair is active. When in power-down mode, RKMSB will output the status of signal detect circuit (LOS). When asserted high while the device is in power-down mode, the transceiver is reset before beginning normal operation. |
| GND | 5, 13, 17, 19, 29, 34, 35, 45, 51, 55, 58, 62, 65 | — | Analog and digital logic ground. Provides a ground for the logic circuits, digital I/O buffers, and the high-speed analog circuits. |
| LCKREFN | 26 | I(1) |
Lock to reference. When LCKREFN is low, the receiver clock is frequency locked to TXCLK. This places the device in a transmit-only mode since the receiver is not tracking the data. When LCKREFN is asserted low, the receive data bus pins (RXD0 through RXD15, RXCLK, RKLSB, and RKMSB) are in a high-impedance state if device is enabled (ENABLE = H). If device is disabled (ENABLE = L), then RKMSB will output the status of the LOS detector (active low = LOS). All other receive outputs will remain high-impedance. When LCKREFN is deasserted high, the receiver is locked to the received data stream. LCKREFN must be deasserted to a high state during power-on reset. See Power-On Reset. |
| LOOPEN | 22 | I(2) | Loop enable. When LOOPEN is active high, the internal loopback path is activated. The transmitted serial data is directly routed internally to the inputs of the receiver. This provides a self-test capability in conjunction with the protocol device. The TXP and TXN outputs are held in a high-impedance state during the loopback test. LOOPEN is held low during standard operational state, with external serial outputs and inputs active. |
| PRE | 60 | I(2) | Preemphasis control. Selects the amount of preemphasis to be added to the high-speed serial output drivers. Left low or unconnected, 5% preemphasis is added. Pulled high, 20% preemphasis is added. |
| PRBSEN | 27 | I(2) | PRBS test enable. When asserted high, results of pseudo-random bit stream (PRBS) tests can be monitored on the RKLSB pin. A high on RKLSB indicates that valid PRBS is being received. |
| RKLSB | 30 | O | K-code indicator/PRBS test results. When RKLSB is asserted high, an 8-bit/10-bit K code was received and is indicated by data bits RXD0 through RXD7. When RKLSB is asserted low, an 8-bit/10-bit D code is received and is presented on data bits RXD0 through RXD7. When PRBSEN is asserted high, this pin is used to indicate status of the PRBS test results (high = pass). |
| RKMSB | 31 | O | K-code indicator. When RKMSB is asserted high an 8-bit/10-bit K code was received and is indicated by data bits RXD8 through RXD15. When RKMSB is asserted low an 8-bit/10-bit D code was received and is presented on data bits RXD8 through RXD15. If the differential signal on RXN and RXP drops below 200mV, RXD0–RXD15, RKLSB, and RKMSB are all asserted high. When device is disabled (ENABLE = L), RKMSB will output the status of LOS. Active low = LOS detected. |
| RXCLK RX_CLK |
43 | O | Recovered clock. Output clock that is synchronized to RXD0 through RXD9, RKLSB, and RKMSB. RXCLK is the recovered serial data rate clock divided by 20. RXCLK is held low during power-on reset. |
| RXD0 RXD1 RXD2 RXD3 RXD4 RXD5 RXD6 RXD7 RXD8 RXD9 RXD10 RXD11 RXD12 RXD13 RXD14 RXD15 |
54 53 52 49 48 47 46 44 42 41 39 38 37 36 33 32 |
O | Receive data bus. These outputs carry 16-bit parallel data output from the transceiver to the protocol device, synchronized to RXCLK. The data is valid on the rising edge of RXCLK as shown in Figure 6-4. These pins are in high-impedance state during power-on reset. |
| DINRXN DINRXP |
56 57 |
I | Serial receive inputs. RXP and RXN together are the differential serial input interface from a copper or an optical I/F module. |
| TESTEN | 28 | I(2) | Test mode enable. This pin should be left unconnected or tied low. |
| TKLSB | 23 | I(2) | K-code generator (LSB). When TKLSB is high, an 8-bit/10-bit K code is transmitted as controlled by data bits TXD0 through TXD7. When TKLSB is low, an 8-bit/10-bit D code is transmitted as controlled by data bits TXD0 through TXD7. |
| TKMSB | 21 | I(2) | K-code generator (MSB). When TKMSB is high, an 8-bit/10-bit K code is transmitted as controlled by data bits TXD8 through TXD15. When TKMSB is low, an 8-bit/10-bit D code is transmitted as controlled by data bits TXD8 through TXD15. |
| TXCLK GTX_CLK |
8 | I | Reference clock. TXCLK is a continuous external input clock that synchronizes the transmitter interface signals TKMSB, TKLSB, and TXD0–TXD15. The frequency range of TXCLK is 80 to 125MHz. The transmitter uses the rising edge of this clock to register the 16-bit input data TXD0 through TXD15 for serialization. |
| TXD0 TXD1 TXD2 TXD3 TXD4 TXD5 TXD6 TXD7 TXD8 TXD9 TXD10 TXD11 TXD12 TXD13 TXD14 TXD15 |
66 67 68 2 3 4 6 7 10 11 12 14 15 16 18 20 |
I | Transmit data bus. These inputs carry the 16-bit parallel data output from a protocol device to the transceiver for encoding, serialization, and transmission. This 16-bit parallel data is clocked into the transceiver on the rising edge of TXCLK as shown in Figure 6-1. |
| VDD | 1, 9, 24, 40, 50 | Digital logic power. Provides power for all digital circuitry and digital I/O buffers. | |
| VDDA | 59, 61 | Analog power. VDDA provides a supply reference for the high-speed analog circuits, receiver, and transmitter. | |