SNOSDJ3 May 2024 TLV1812-EP
ADVANCE INFORMATION
- 1
- 1Features
- 2Applications
- 3Description
- Pin Configuration and Functions
- 4Specifications
- 5Detailed Description
-
6Application and Implementation
- 6.1 Application Information
- 6.2 Typical Applications
- 6.3 Power Supply Recommendations
- 6.4 Layout
- 7Device and Documentation Support
- 8Revision History
- 9Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DDF|8
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
6.1.2.2 Non-Inverting Comparator With Hysteresis
A non-inverting comparator with hysteresis requires a two-resistor network and a voltage reference (VREF) at the inverting input, as shown in Figure 6-5.
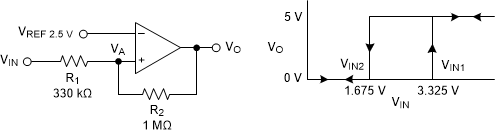 Figure 6-5 TLV1812-EP in a Non-Inverting Configuration With Hysteresis
Figure 6-5 TLV1812-EP in a Non-Inverting Configuration With HysteresisThe equivalent resistor networks when the output is high and low are shown in Figure 6-6.
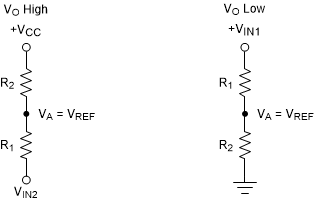 Figure 6-6 Non-Inverting Configuration Resistor Networks
Figure 6-6 Non-Inverting Configuration Resistor NetworksWhen VIN is less than VREF,, the output is low. For the output to switch from low to high, VIN must rise above the VIN1 threshold. Use Equation 4 to calculate VIN1.
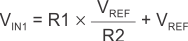
When VIN is greater than VREF, the output is high. For the comparator to switch back to a low state, VIN must drop below VIN2. Use Equation 5 to calculate VIN2.
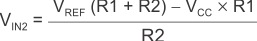
The hysteresis of this circuit is the difference between VIN1 and VIN2, as shown in Equation 6.
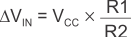
For more information, see the Inverting comparator with hysteresis circuit application note and the Non-Inverting Comparator With Hysteresis Circuit application note.