SNOSDC8D September 2022 – December 2024 TLV1811 , TLV1812 , TLV1814 , TLV1821 , TLV1822 , TLV1824
PRODMIX
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
- 6 Typical Characteristics
- 7 Detailed Description
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2 Typical Applications
- 8.3 Power Supply Recommendations
- 8.4 Layout
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Revision History
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RTE|16
Orderable Information
8.2.6 One-Shot Multivibrator
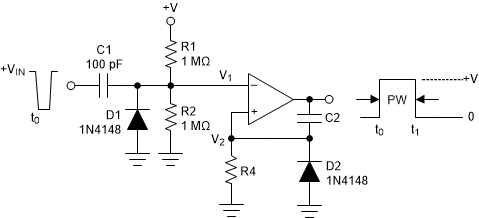 Figure 8-15 One-Shot Multivibrator
Figure 8-15 One-Shot MultivibratorA monostable multivibrator has one stable state in which the circuit can remain indefinitely. The circuit can be triggered externally to another quasi-stable state. A monostable multivibrator can thus be used to generate a pulse of desired width.
The desired pulse width is set by adjusting the values of C2 and R4. The resistor divider of R1 and R2 can be used to determine the magnitude of the input trigger pulse. The output changes state when V1 < V2. Diode D2 provides a rapid discharge path for capacitor C2 to reset at the end of the pulse. The diode also prevents the non-inverting input from being driven below ground.