SNOSDC8C September 2022 – September 2023 TLV1811 , TLV1812 , TLV1814 , TLV1821 , TLV1822 , TLV1824
PRODMIX
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Typical Characteristics
- 8 Detailed Description
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2 Typical Applications
- 9.3 Power Supply Recommendations
- 9.4 Layout
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
9.2.7 Bi-Stable Multivibrator
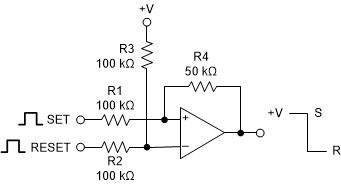 Figure 9-16 Bi-Stable Multivibrator
Figure 9-16 Bi-Stable MultivibratorA bi-stable multivibrator has two stable states. The reference voltage is set up by the voltage divider of R2 and R3. A pulse applied to the SET terminal will switch the output of the comparator high. The resistor divider of R1 and R4 now sets the non-inverting input to a voltage greater than the reference voltage. A pulse applied to RESET will now toggle the output low.