SNOSDI4A March 2024 – December 2024 TLV1871 , TLV1872
PRODMIX
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
- 6 Detailed Description
- 7 Application and Implementation
- 8 Device and Documentation Support
- 9 Revision History
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DDF|8
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.1.1.2 Propagation Delay
There is a delay between from when the input crosses the reference voltage and the output responds. This is called the Propagation Delay. Propagation delay can be different between high-to low and low-to-high input transitions. This is shown as tpLH and tpHL in Figure 7-1 and is measured from the mid-point of the input to the midpoint of the output.
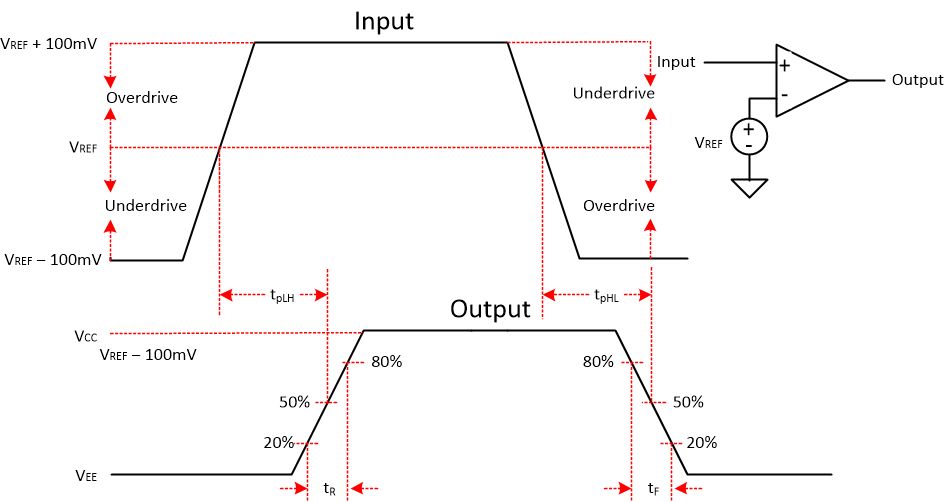 Figure 7-1 Comparator Timing Diagram
Figure 7-1 Comparator Timing Diagram