-
TLV237x-Q1 550-µA/Channel, 3-MHz Rail-to-Rail Input and Output Operational Amplifiers SGLS244B May 2004 – December 2016 TLV2371-Q1 , TLV2372-Q1 , TLV2374-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
-
TLV237x-Q1 550-µA/Channel, 3-MHz Rail-to-Rail Input and Output Operational Amplifiers
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
- IMPORTANT NOTICE
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- D|8
- DBV|5
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
TLV237x-Q1 550-µA/Channel, 3-MHz Rail-to-Rail Input and Output Operational Amplifiers
1 Features
- Qualified for Automotive Applications
- AEC-Q100 Qualified With the Following Results:
- Device Temperature Grade 1: –40°C to 125°C Ambient Operating Temperature Range
- Device HBM ESD Classification Level 2
- Device CDM ESD Classification Level C4B
- Rail-to-Rail Input and Output
- Wide Bandwidth: 3 MHz
- High Slew Rate: 2.4 V/µs
- Supply Voltage Range: 2.7 V to 16 V
- Supply Current: 550 µA/Channel
- Input Noise Voltage: 39 nV/√Hz
- Input Bias Current: 1 pA
- Ultra-Small Packaging:
- 5-Pin SOT-23 (TLV2371-Q1)
2 Applications
- Engine Control Units (ECU)
- Body Control Modules (BCM)
- Battery Management Systems
- HEV/EV Inverters
- Lane Departure Warning
- White Goods
3 Description
The TLV237x-Q1 devices are single-supply operational amplifiers providing rail-to-rail input and output capability. The TLV237x-Q1 takes the minimum operating supply voltage down to 2.7 V and up to 16 V over the extended automotive temperature range. Therefore, the wide voltage range can support both start-stop functionality and a connection directly to the typical 12-V battery. The rail-to-rail capabilities allow the device to maximize the output signal and avoid clipping.
The CMOS inputs enable high-impedance suitable for engine control units (ECU), body control modules (BCM), battery management systems (BMS), and HEV/EV inverters. This also allows the user to draw a lower offset voltage and maintain low power consumption to help meet overall system needs for quiescent current such as in infotainment or cluster, HEV/EV, and powertrain.
Additionally, the TLV237x-Q1 family supports a high common-mode rail to the supply voltage. This feature sets no gain limitations and can support the input at any level without the concern for any phase reversal.
Device Information(1)
| PART NUMBER | PACKAGE | BODY SIZE (NOM) |
|---|---|---|
| TLV2371-Q1 | SOT-23 (5) | 2.90 mm × 1.60 mm |
| SOIC (8) | 4.90 mm × 3.91 mm | |
| TLV2372-Q1 | SOIC (8) | 4.90 mm × 3.91 mm |
| TLV2374-Q1 | SOIC (14) | 8.65 mm × 3.91 mm |
| TSSOP (14) | 5.00 mm × 4.40 mm |
- For all available packages, see the orderable addendum at the end of the data sheet.
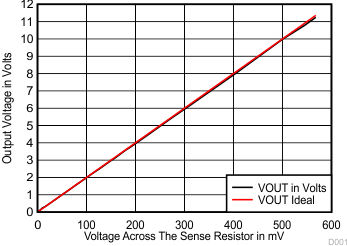
Output Voltage vs Differential Input
in High Current Sensing
4 Revision History
Changes from A Revision (June 2008) to B Revision
- Added ESD Ratings table, Feature Description section, Device Functional Modes, Application and Implementation section, Power Supply Recommendations section, Layout section, Device and Documentation Support section, and Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information sectionGo
- Deleted 8-Pin MSOP (TLV2372) because the TLV2372-Q1 is not available in MSOP; also removed all references throughout the data sheetGo
- Changed list items in Applications Go
- Removed Family Package and Available Options tables, see POA at the end of the data sheet Go
- Renamed Selection of Signal Amplifier Products table toDevice Comparison TableGo
- Changed SHUTDOWN for the TLV237x in the Device Comparison Table From: Yes To: —Go
- Changed IIB (pA) for the TLV246x in the Device Comparison Table From: 1300 To: 1.3Go
- Changed SHUTDOWN for the TLV237x in the Device Comparison Table From: Yes To: —Go
- Changed GND DESCRIPTION in Pin Functions: TLV2371-Q1 From: Ground connection To: Negative (lowest) power supplyGo
- Changed GND DESCRIPTION in Pin Functions: TLV2372-Q1 From: Ground connection To: Negative (lowest) power supplyGo
- Removed Typical Pin 1 Indicators image Go
- Changed GND DESCRIPTION in Pin Functions: TLV2374-Q1 From: Ground connection To: Negative (lowest) power supplyGo
- Deleted Lead temperature (260°C maximum)Go
- Added additional thermal values to all Thermal Information tablesGo
- Changed RθJA values in Thermal Information: TLV2371-Q1 From: 325.1 To: 228.5 (DBV) and From: 176 To: 138.4 (D)Go
- Changed RθJA value in Thermal Information: TLV2372-Q1 From: 176 To: 138.4 (D)Go
- Deleted entire DGK (MSOP) column from Thermal Information: TLV2372-Q1Go
- Changed RθJA values in Thermal Information: TLV2374-Q1 From: 122.3 To: 67 (D) and From: 173.6 To: 121 (PW)Go
- Deleted Maximum Power Dissipation vs Free-Air Temperature graphGo
5 Device Comparison Table
Typical values measured at 5 V and 25°C| DEVICE | VDD (V) | VIO (µV) | Iq/Ch (µA) | IIB (pA) | GBW (MHz) | SR (V/µs) | SHUTDOWN | RAIL-TO-RAIL | SINGLES, DUALS, QUADS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TLV237x-Q1 | 2.7 to 16 | 500 | 550 | 1 | 3 | 2.4 | — | I/O | S, D, Q |
| TLC227x-Q1 | 4 to 16 | 300 | 1100 | 1 | 2.2 | 3.6 | — | O | D, Q |
| TLV27x-Q1 | 2.7 to 16 | 500 | 550 | 1 | 3 | 2.4 | — | O | S, D, Q |
| TLV246x-Q1 | 2.7 to 6 | 150 | 550 | 1.3 | 6.4 | 1.6 | Yes | I/O | S, D, Q |
| TLV247x-Q1 | 2.7 to 6 | 250 | 600 | 2 | 2.8 | 1.5 | — | I/O | S, D, Q |
| TLV244x-Q1 | 2.7 to 10 | 300 | 725 | 1 | 1.8 | 1.4 | — | O | D, Q |
6 Pin Configuration and Functions


Pin Functions: TLV2371-Q1
| PIN | I/O | DESCRIPTION | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | SOT-23 | SOIC | ||
| GND | 2 | 4 | — | Negative (lowest) power supply |
| IN– | 4 | 2 | I | Negative (inverting) input |
| IN+ | 3 | 3 | I | Positive (noninverting) input |
| NC | — | 1, 5, 8 | — | No internal connection (can be left floating) |
| OUT | 1 | 6 | O | Output |
| VDD | 5 | 7 | — | Positive power supply |

Pin Functions: TLV2372-Q1
| PIN | I/O | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | ||
| 1IN– | 2 | I | Inverting input, channel 1 |
| 1IN+ | 3 | I | Noninverting input, channel 1 |
| 1OUT | 1 | O | Output, channel 1 |
| 2IN– | 6 | I | Inverting input, channel 2 |
| 2IN+ | 5 | I | Noninverting input, channel 2 |
| 2OUT | 7 | O | Output, channel 2 |
| GND | 4 | — | Negative (lowest) power supply |
| VDD | 8 | — | Positive power supply |

Pin Functions: TLV2374-Q1
| PIN | I/O | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | ||
| 1IN– | 2 | I | Inverting input, channel 1 |
| 1IN+ | 3 | I | Noninverting input, channel 1 |
| 1OUT | 1 | O | Output, channel 1 |
| 2IN– | 6 | I | Inverting input, channel 2 |
| 2IN+ | 5 | I | Noninverting input, channel 2 |
| 2OUT | 7 | O | Output, channel 2 |
| 3IN– | 9 | I | Inverting input, channel 3 |
| 3IN+ | 10 | I | Noninverting input, channel 3 |
| 3OUT | 8 | O | Output, channel 3 |
| 4IN– | 13 | I | Inverting input, channel 4 |
| 4IN+ | 12 | I | Noninverting input, channel 4 |
| 4OUT | 14 | O | Output, channel 4 |
| GND | 11 | — | Negative (lowest) power supply |
| VDD | 4 | — | Positive power supply |
7 Specifications
7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)(1)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supply voltage, VDD | 16.5 | V | ||
| Differential input voltage, VID | ±VDD | |||
| Input voltage, VI | –0.2 | VDD + 0.2 | V | |
| Input current, II | ±10 | mA | ||
| Output current, IO | ±100 | mA | ||
| Maximum junction temperature, TJ | 150 | °C | ||
| Storage temperature, Tstg | –65 | 150 | °C | |
7.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TLV2371-Q1 in DBV package | |||||
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human-body model (HBM), per AEC Q100-002(1) | All pins | ±2000 | V |
| Charged-device model (CDM), per AEC Q100-011 | All pins | ±500 | |||
| Corner pins (1, 3, 4, and 5) | ±750 | ||||
| TLV2371-Q1 in D package | |||||
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human-body model (HBM), per AEC Q100-002(1) | All pins | ±2000 | V |
| Charged-device model (CDM), per AEC Q100-011 | All pins | ±500 | |||
| Corner pins (1, 4, 5, and 8) | ±750 | ||||
| TLV2372-Q1 in D package | |||||
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human-body model (HBM), per AEC Q100-002(1) | All pins | ±2000 | V |
| Charged-device model (CDM), per AEC Q100-011 | All pins | ±500 | |||
| Corner pins (1, 4, 5, and 8) | ±750 | ||||
| TLV2374-Q1 in D and PW packages | |||||
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human-body model (HBM), per AEC Q100-002(1) | All pins | ±2000 | V |
| Charged-device model (CDM), per AEC Q100-011 | All pins | ±500 | |||
| Corner pins (1, 7, 8, and 14) | ±750 | ||||
7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VDD | Supply voltage | Single supply | 2.7 | 16 | V |
| Split supply | ±1.35 | ±8 | |||
| VICR | Common-mode input voltage | 0 | VDD | V | |
| V(ON) | Turnon voltage level (relative to GND pin voltage) | 2 | V | ||
| V(OFF) | Turnoff voltage level (relative to GND pin voltage) | 0.8 | V | ||
| TA | Operating free-air temperature (Q-suffix) | –40 | 125 | °C | |
7.4 Thermal Information: TLV2371-Q1
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | TLV2371-Q1 | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DBV (SOT-23) | D (SOIC) | |||
| 5 PINS | 8 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 228.5 | 138.4 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 99.1 | 89.5 | °C/W |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 54.6 | 78.6 | °C/W |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 7.7 | 29.9 | °C/W |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 53.8 | 78.1 | °C/W |
| RθJC(bot) | Junction-to-case (bottom) thermal resistance | — | — | °C/W |
7.5 Thermal Information: TLV2372-Q1
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | TLV2372-Q1 | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| D (SOIC) | |||
| 8 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 138.4 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 89.5 | °C/W |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 78.6 | °C/W |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 29.9 | °C/W |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 78.1 | °C/W |
| RθJC(bot) | Junction-to-case (bottom) thermal resistance | — | °C/W |
7.6 Thermal Information: TLV2374-Q1
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | TLV2374-Q1 | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D (SOIC) | PW (TSSOP) | |||
| 14 PINS | 14 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 67 | 121 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 24.1 | 49.4 | °C/W |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 22.5 | 62.8 | °C/W |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 2.2 | 5.9 | °C/W |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 22.1 | 62.2 | °C/W |
| RθJC(bot) | Junction-to-case (bottom) thermal resistance | — | — | °C/W |
7.7 Electrical Characteristics
at specified free-air temperature, VDD = 2.7 V, 5 V, and 15 V (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DC PERFORMANCE | ||||||||
| VIO | Input offset voltage | VIC = VDD/2, VO = VDD/2, RS = 50 Ω | TA = 25°C | 2 | 4.5 | mV | ||
| TA = –40°C to 125°C | 6 | |||||||
| αVIO | Offset voltage drift | VIC = VDD/2, VO = VDD/2, RS = 50 Ω, TA = 25°C | 2 | µV/°C | ||||
| CMRR | Common-mode rejection ratio | VDD = 2.7 V | VIC = 0 to VDD, RS = 50 Ω |
TA = 25°C | 50 | 68 | dB | |
| TA = –40°C to 125°C | 49 | |||||||
| VIC = 0 to VDD – 1.35 V, RS = 50 Ω |
TA = 25°C | 53 | 70 | |||||
| TA = –40°C to 125°C | 54 | |||||||
| VDD = 5 V | VIC = 0 to VDD, RS = 50 Ω |
TA = 25°C | 55 | 72 | ||||
| TA = –40°C to 125°C | 54 | |||||||
| VIC = 0 to VDD – 1.35 V, RS = 50 Ω |
TA = 25°C | 58 | 80 | |||||
| TA = –40°C to 125°C | 57 | |||||||
| VDD = 15 V | VIC = 0 to VDD, RS = 50 Ω |
TA = 25°C | 64 | 82 | ||||
| TA = –40°C to 125°C | 63 | |||||||
| VIC = 0 to VDD – 1.35 V, RS = 50 Ω |
TA = 25°C | 67 | 84 | |||||
| TA = –40°C to 125°C | 66 | |||||||
| AVD | Large-signal differential voltage amplification | VO(PP) = VDD/2, RS = 10 Ω |
VDD = 2.7 V | TA = 25°C | 95 | 106 | dB | |
| TA = –40°C to 125°C | 76 | |||||||
| VDD = 5 V | TA = 25°C | 80 | 110 | |||||
| TA = –40°C to 125°C | 82 | |||||||
| VDD = 15 V | TA = 25°C | 77 | 83 | |||||
| TA = –40°C to 125°C | 79 | |||||||
| INPUT | ||||||||
| IIO | Input offset current | VDD = 15 V, VIC = VDD/2, VO = VDD/2 | TA = 25°C | 1 | 60 | pA | ||
| TA = –40°C to 125°C | 500 | |||||||
| IIB | Input bias current | VDD = 15 V, VIC = VDD/2, VO = VDD/2 | TA = 25°C | 1 | 60 | pA | ||
| TA = –40°C to 125°C | 500 | |||||||
| ri(d) | Differential input resistance | TA = 25°C | 1000 | GΩ | ||||
| CIC | Common-mode input capacitance | f = 21 kHz, TA = 25°C | 8 | pF | ||||
| OUTPUT | ||||||||
| VOH | High-level output voltage | VIC = VDD/2, IOH = –1 mA, VID = 1 V |
VDD = 2.7 V | TA = 25°C | 2.55 | 2.58 | V | |
| TA = –40°C to 125°C | 2.48 | |||||||
| VDD = 5 V | TA = 25°C | 4.9 | 4.93 | |||||
| TA = –40°C to 125°C | 4.85 | |||||||
| VDD = 15 V | TA = 25°C | 14.92 | 14.96 | |||||
| TA = –40°C to 125°C | 14.9 | |||||||
| VIC = VDD/2, IOH = –5 mA, VID = 1 V |
VDD = 2.7 V | TA = 25°C | 1.88 | 2 | ||||
| TA = –40°C to 125°C | 1.42 | |||||||
| VDD = 5 V | TA = 25°C | 4.58 | 4.68 | |||||
| TA = –40°C to 125°C | 4.44 | |||||||
| VDD = 15 V | TA = 25°C | 14.7 | 14.8 | |||||
| TA = –40°C to 125°C | 14.6 | |||||||
| VOL | Low-level output voltage | VIC = VDD/2, IOH = 1 mA, VID = 1 V |
VDD = 2.7 V | TA = 25°C | 0.1 | 0.15 | V | |
| TA = –40°C to 125°C | 0.22 | |||||||
| VDD = 5 V | TA = 25°C | 0.05 | 0.1 | |||||
| TA = –40°C to 125°C | 0.15 | |||||||
| VDD = 15 V | TA = 25°C | 0.05 | 0.08 | |||||
| TA = –40°C to 125°C | 0.1 | |||||||
| VIC = VDD/2, IOH = 5 mA, VID = 1 V |
VDD = 2.7 V | TA = 25°C | 0.52 | 0.7 | ||||
| TA = –40°C to 125°C | 1.15 | |||||||
| VDD = 5 V | TA = 25°C | 0.28 | 0.4 | |||||
| TA = –40°C to 125°C | 0.54 | |||||||
| VDD = 15 V | TA = 25°C | 0.19 | 0.3 | |||||
| TA = –40°C to 125°C | 0.35 | |||||||
| POWER SUPPLY | ||||||||
| IDD | Supply current (per channel) |
VO = VDD/2 | VDD = 2.7 V | TA = 25°C | 470 | 560 | µA | |
| VDD = 5 V | TA = 25°C | 550 | 660 | |||||
| VDD = 15 V | TA = 25°C | 750 | 900 | |||||
| TA = –40°C to 125°C | 1200 | |||||||
| PSRR | Supply voltage rejection ratio (ΔVDD/ΔVIO) | VDD = 2.7 V to 15 V, VIC = VDD/2, no load |
TA = 25°C | 70 | 80 | dB | ||
| TA = –40°C to 125°C | 65 | |||||||
| DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE | ||||||||
| UGBW | Unity gain bandwidth | RL = 2 kΩ, CL = 10 pF | VDD = 2.7 V, TA = 25°C | 2.4 | MHz | |||
| VDD = 5 V to 15 V, TA = 25°C |
3 | |||||||
| SR | Slew rate at unity gain | VO(PP) = VDD/2, RL = 10 kΩ, CL = 50 pF |
VDD = 2.7 V | TA = 25°C | 1.4 | 2 | V/µs | |
| TA = –40°C to 125°C | 1 | |||||||
| VDD = 5 V | TA = 25°C | 1.4 | 2.4 | |||||
| TA = –40°C to 125°C | 1.2 | |||||||
| VDD = 15 V | TA = 25°C | 1.9 | 2.1 | |||||
| TA = –40°C to 125°C | 1.4 | |||||||
| φm | Phase margin | RL = 2 kΩ, CL = 100 pF, TA = 25°C | 65° | |||||
| Gain margin | RL = 2 kΩ, CL = 10 pF, TA = 25°C | 18 | dB | |||||
| ts | Settling time | VDD = 2.7 V, V(STEP)PP = 1 V, AV = –1, RL = 2 kΩ, CL = 10 pF, 0.1% at 25°C |
2.9 | µs | ||||
| VDD = 5 V or 15 V, V(STEP)PP = 1 V, AV = –1, RL = 2 kΩ, CL = 47 pF, 0.1% at 25°C |
2 | |||||||
| NOISE/DISTORTION PERFORMANCE | ||||||||
| THD+N | Total harmonic distortion plus noise | VDD = 2.7 V, VO(PP) = VDD/2 V, RL = 2 kΩ, f = 10 kHz, TA = 25°C |
AV = 1 | 0.02% | ||||
| AV = 10 | 0.05% | |||||||
| AV = 100 | 0.18% | |||||||
| VDD = 5 V or 15 V, VO(PP) = VDD/2 V, RL = 2 kΩ, f = 10 kHz, TA = 25°C |
AV = 1 | 0.02% | ||||||
| AV = 10 | 0.09% | |||||||
| AV = 100 | 0.5% | |||||||
| Vn | Equivalent input noise voltage | f = 1 kHz, TA = 25°C | 39 | nV√Hz | ||||
| f = 10 kHz, TA = 25°C | 35 | |||||||
| In | Equivalent input noise current | f = 1 kHz, TA = 25°C | 0.6 | fA√Hz | ||||
7.8 Typical Characteristics
Table 1. Table of Graphs
| FIGURE | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| VIO | Input offset voltage | vs Common-mode input voltage | Figure 1, Figure 2, Figure 3 |
| CMRR | Common-mode rejection ratio | vs Frequency | Figure 4 |
| Input bias and offset current | vs Free-air temperature | Figure 5 | |
| VOL | Low-level output voltage | vs Low-level output current | Figure 6, Figure 8, Figure 10 |
| VOH | High-level output voltage | vs High-level output current | Figure 7, Figure 9, Figure 11 |
| VO(PP) | Peak-to-peak output voltage | vs Frequency | Figure 12 |
| IDD | Supply current | vs Supply voltage | Figure 13 |
| PSRR | Power supply rejection ratio | vs Frequency | Figure 14 |
| AVD | Differential voltage gain & phase | vs Frequency | Figure 15 |
| Gain-bandwidth product | vs Free-air temperature | Figure 16 | |
| SR | Slew rate | vs Supply voltage | Figure 17 |
| vs Free-air temperature | Figure 18 | ||
| φm | Phase margin | vs Capacitive load | Figure 19 |
| Vn | Equivalent input noise voltage | vs Frequency | Figure 20 |
| Voltage-follower large-signal pulse response | Figure 21, Figure 22 | ||
| Voltage-follower small-signal pulse response | Figure 23 | ||
| Inverting large-signal response | Figure 24, Figure 25 | ||
| Inverting small-signal response | Figure 26 | ||
| Crosstalk | vs Frequency | Figure 27 | |
 Figure 1. Input Offset Voltage
Figure 1. Input Offset Voltagevs Common-Mode Input Voltage
 Figure 2. Input Offset Voltage
Figure 2. Input Offset Voltagevs Common-Mode Input Voltage
 Figure 3. Input Offset Voltage
Figure 3. Input Offset Voltagevs Common-Mode Input Voltage
 Figure 5. Input Bias and Offset Current
Figure 5. Input Bias and Offset Currentvs Free-Air Temperature
 Figure 7. High-Level Output Voltage
Figure 7. High-Level Output Voltagevs High-Level Output Current
 Figure 9. High-Level Output Voltage
Figure 9. High-Level Output Voltagevs High-Level Output Current
 Figure 11. High-Level Output Voltage
Figure 11. High-Level Output Voltagevs High-Level Output Current
 Figure 13. Supply Current vs Supply Voltage
Figure 13. Supply Current vs Supply Voltage
 Figure 15. Differential Voltage Gain and Phase
Figure 15. Differential Voltage Gain and Phasevs Frequency
 Figure 17. Slew Rate vs Supply Voltage
Figure 17. Slew Rate vs Supply Voltage
 Figure 19. Phase Margin vs Capacitive Load
Figure 19. Phase Margin vs Capacitive Load
 Figure 21. Voltage-Follower Large-Signal
Figure 21. Voltage-Follower Large-SignalPulse Response
 Figure 23. Voltage-Follower Small-Signal
Figure 23. Voltage-Follower Small-SignalPulse Response
 Figure 25. Inverting Large-Signal Response
Figure 25. Inverting Large-Signal Response
 Figure 27. Crosstalk vs Frequency
Figure 27. Crosstalk vs Frequency
 Figure 4. Common-Mode Rejection Ratio
Figure 4. Common-Mode Rejection Ratiovs Frequency
 Figure 6. Low-Level Output Voltage
Figure 6. Low-Level Output Voltagevs Low-Level Output Current
 Figure 8. Low-Level Output Voltage
Figure 8. Low-Level Output Voltagevs Low-Level Output Current
 Figure 10. Low-Level Output Voltage
Figure 10. Low-Level Output Voltagevs Low-Level Output Current
 Figure 12. Peak-to-Peak Output Voltage
Figure 12. Peak-to-Peak Output Voltagevs Frequency
 Figure 14. Power Supply Rejection Ratio
Figure 14. Power Supply Rejection Ratiovs Frequency
 Figure 16. Gain Bandwidth Product
Figure 16. Gain Bandwidth Productvs Free-Air Temperature
 Figure 18. Slew Rate vs Free-Air Temperature
Figure 18. Slew Rate vs Free-Air Temperature
 Figure 20. Equivalent Input Noise Voltage
Figure 20. Equivalent Input Noise Voltagevs Frequency
 Figure 22. Voltage-Follower Large-Signal
Figure 22. Voltage-Follower Large-SignalPulse Response
 Figure 24. Inverting Large-Signal Response
Figure 24. Inverting Large-Signal Response
 Figure 26. Inverting Small-Signal Response
Figure 26. Inverting Small-Signal Response
8 Detailed Description
8.1 Overview
The TLV237x-Q1 single-supply operational amplifiers provide rail-to-rail input and output capability with 3-MHz bandwidth. Consuming only 550 µA, the TLV237x-Q1 is the perfect choice for portable and battery-operated applications. The maximum recommended supply voltage is 16 V, which allows the devices to be operated from a variety of rechargeable cells (±8-V supplies down to ±1.35 V). The rail-to-rail inputs with high input impedance make the TLV237x-Q1 ideal for sensor signal-conditioning applications.
8.2 Functional Block Diagram

8.3 Feature Description
8.3.1 Rail-to-Rail Input Operation
The TLV237x-Q1 input stage consists of two differential transistor pairs, NMOS and PMOS, that operate together to achieve rail-to-rail input operation. The transition point between these two pairs can be seen in Figure 1 through Figure 3 for a 2.7-V, 5-V, and 15-V supply. As the common-mode input voltage approaches the positive supply rail, the input pair switches from the PMOS differential pair to the NMOS differential pair. This transition occurs approximately 1.35 V from the positive rail and results in a change in offset voltage due to different device characteristics between the NMOS and PMOS pairs. If the input signal to the device is large enough to swing between both rails, this transition results in a reduction in common-mode rejection ratio (CMRR). If the input signal does not swing between both rails, it is best to bias the signal in the region where only one input pair is active. This is the region in Figure 1 through Figure 3 where the offset voltage varies slightly across the input range and optimal CMRR can be achieved. This has the greatest impact when operating from a 2.7-V supply voltage.
8.3.2 Driving a Capacitive Load
When the amplifier is configured in this manner, capacitive loading directly on the output decreases the device’s phase margin, leading to high-frequency ringing or oscillations. Therefore, for capacitive loads of greater than
10 pF, TI recommends placing a resistor in series (RNULL) with the output of the amplifier, as shown in Figure 28. A minimum value of 20 Ω works well for most applications.
 Figure 28. Driving a Capacitive Load
Figure 28. Driving a Capacitive Load
8.3.3 Offset Voltage
The output offset voltage, (VOO) is the sum of the input offset volt age (VIO) and both input bias currents (IIB) times the corresponding gains. The schematic and formula in Figure 29 can be used to calculate the output offset voltage.
 Figure 29. Output Offset Voltage Model
Figure 29. Output Offset Voltage Model
8.3.4 General Configurations
When receiving low-level signals, limiting the bandwidth of the incoming signals into the system is often required. The simplest way to accomplish this is to place an RC filter at the noninverting terminal of the amplifier (see Figure 30).
 Figure 30. Single-Pole Low-Pass Filter
Figure 30. Single-Pole Low-Pass Filter
If even more attenuation is required, a multiple pole filter is required. The Sallen-Key filter can be used for this task (see Figure 31). For best results, the amplifier must have a bandwidth that is 8 to 10 times the filter frequency bandwidth. Failure to do this can result in phase shift of the amplifier.
 Figure 31. 2-Pole Low-Pass Sallen-Key Filter
Figure 31. 2-Pole Low-Pass Sallen-Key Filter
8.4 Device Functional Modes
The TLV2371-Q1, TLV2372-Q1, and TLV2374-Q1 have a single functional mode. These devices are operational as long as the power supply voltage is between 2.7 V (±1.35 V) and 16 V (±8 V).