SLAS548D October 2008 – September 2015 TLV320ADC3001
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description (continued)
- 6 Device Comparison Table
- 7 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
8 Specifications
- 8.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 8.2 ESD Ratings
- 8.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 8.4 Thermal Information
- 8.5 Electrical Characteristics
- 8.6 Dissipation Ratings
- 8.7 I2S/LJF/RJF Timing in Master Mode
- 8.8 DSP Timing in Master Mode
- 8.9 I2S/LJF/RJF Timing in Slave Mode
- 8.10 DSP Timing in Slave Mode
- 8.11 Typical Characteristics
- 9 Parameter Measurement Information
-
10Detailed Description
- 10.1 Overview
- 10.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 10.3
Feature Description
- 10.3.1 Hardware Reset
- 10.3.2 PLL Start-up
- 10.3.3 Software Power Down
- 10.3.4 miniDSP
- 10.3.5 Audio Data Converters
- 10.3.6 Digital Audio Data Serial Interface
- 10.3.7 Audio Clock Generation
- 10.3.8 Stereo Audio ADC
- 10.3.9 Audio Analog Inputs
- 10.3.10 Input Impedance and VCM Control
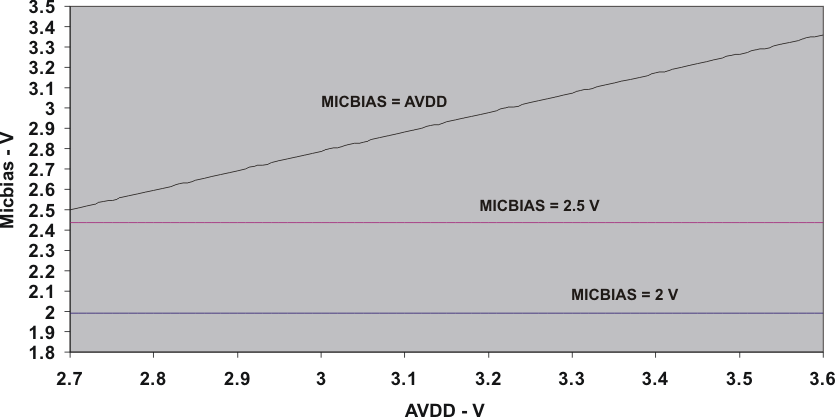
- 10.3.11 MICBIAS Generation
- 10.3.12
ADC Decimation Filtering and Signal Processing
- 10.3.12.1 Processing Blocks
- 10.3.12.2
Processing Blocks - Details
- 10.3.12.2.1 First-Order IIR, AGC, Filter A
- 10.3.12.2.2 Five Biquads, First-Order IIR, AGC, Filter A
- 10.3.12.2.3 25-Tap FIR, First-Order IIR, AGC, Filter A
- 10.3.12.2.4 First-Order IIR, AGC, Filter B
- 10.3.12.2.5 Three Biquads, First-Order IIR, AGC, Filter B
- 10.3.12.2.6 20-Tap FIR, First-Order IIR, AGC, Filter B
- 10.3.12.2.7 First-Order IIR, AGC, Filter C
- 10.3.12.2.8 Five Biquads, First-Order IIR, AGC, Filter C
- 10.3.12.2.9 25-Tap FIR, First-Order IIR, AGC, Filter C
- 10.3.12.3 User-Programmable Filters
- 10.3.12.4 Decimation Filter
- 10.4 Device Functional Modes
- 10.5 Programming
- 10.6
Register Maps
- 10.6.1 Control Registers
- 10.6.2 Control Registers, Page 0: Clock Multipliers and Dividers, Serial Interfaces, Flags, Interrupts and Programming of GPIOs
- 10.6.3 CONTROL REGISTERS Page 1: ADC Routing, PGA, Power-Controls, Etc.
- 10.6.4 Control Registers, Page 4: ADC Digital Filter Coefficients
- 10.6.5 Control Registers, Page 5: ADC Programmable Coefficients RAM (65:127)
- 10.6.6 Control Registers, Page 32: ADC DSP Engine Instruction RAM (0:31)
- 10.6.7 Control Registers, Page 33 Through Page 47: ADC DSP Engine Instruction RAM (32:63) Through (480:511)
- 11Application and Implementation
- 12Power Supply Recommendations
- 13Layout
- 14Device and Documentation Support
- 15Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- YZH|16
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8 Specifications
8.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)(1)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AVDD to AVSS | –0.3 | 3.9 | V | |
| IOVDD to DVSS | –0.3 | 3.9 | V | |
| DVDD to DVSS | –0.3 | 2.5 | V | |
| Digital input voltage to DVSS | –0.3 | IOVDD + 0.3 | V | |
| Analog input voltage to AVSS | –0.3 | AVDD + 0.3 | V | |
| Operating temperature | –40 | 85 | °C | |
| TJ Max | Junction temperature | 105 | °C | |
| Power dissipation | (TJ Max – TA) / θJA | W | ||
| Tstg | Storage temperature | –65 | 125 | °C |
(1) Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under Recommended Operating Conditions is not implied. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
8.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001(1) | ±2500 | V |
| Charged-device model (CDM), per JEDEC specification JESD22-C101(2) | ±1000 | |||
(1) JEDEC document JEP155 states that 500-V HBM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
(2) JEDEC document JEP157 states that 250-V CDM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
8.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AVDD(1) | Analog supply voltage | 2.6 | 3.3 | 3.6 | V |
| DVDD(1) | Digital core supply voltage | 1.65 | 1.8 | 1.95 | V |
| IOVDD(1) | Digital I/O supply voltage | 1.1 | 1.8 | 3.6 | V |
| VI | Analog full-scale 0-dB input voltage (AVDD = 3.3 V) | 0.707 | Vrms | ||
| Digital output load capacitance | 10 | pF | |||
| TA | Operating free-air temperature | –40 | 85 | °C | |
(1) Analog voltage values are with respect to AVSS; digital voltage values are with respect to DVSS.
8.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | TLV320ADC3001 | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| YZH (DSBGA) | |||
| 16 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 70.9 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 0.3 | °C/W |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 13.7 | °C/W |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 1.7 | °C/W |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 13.7 | °C/W |
| RθJC(bot) | Junction-to-case (bottom) thermal resistance | — | °C/W |
(1) For more information about traditional and new thermal metrics, see the Semiconductor and IC Package Thermal Metrics application report, SPRA953.
8.5 Electrical Characteristics
At 25°C, AVDD = 3.3 V, IOVDD = 1.8 V, DVDD = 1.8 V, fS = 48-kHz, 16-bit audio data (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUDIO ADC | |||||||
| Input signal level (0-dB) | Single-ended input | 0.707 | Vrms | ||||
| Input common-mode voltage | Single-ended input | 1.35 | Vrms | ||||
| Signal-to-noise ratio, A-weighted(1)(2) |
fS = 48 kHz, 0-dB PGA gain, IN1 inputs selected and AC-shorted to ground |
80 | 92 | dB | |||
| Dynamic range, A-weighted(1)(2) |
fS = 48 kHz, 1-kHz –60-dB full-scale input applied at IN1 inputs, 0-dB PGA gain | 92 | dB | ||||
| THD | Total harmonic distortion | fS = 48 kHz, 1-kHz –2-dB full-scale input applied at IN1 inputs, 0-dB PGA gain |
–90 | –75 | dB | ||
| 0.003% | 0.017% | ||||||
| Power-supply rejection ratio | 234 Hz, 100 mVPP on AVDD, single-ended input | 46 | dB | ||||
| 234 Hz, 100 mVPP on AVDD, differential input | 68 | ||||||
| ADC channel separation | 1 kHz, –2 dB IN1L to IN1R | –73 | dB | ||||
| ADC gain error | 1-kHz input, 0-dB PGA gain | 0.7 | dB | ||||
| ADC programmable-gain amplifier maximum gain | 1-kHz input tone, RSOURCE < 50 Ω | 40 | dB | ||||
| ADC programmable-gain amplifier step size | 0.502 | dB | |||||
| Input resistance | IN1 inputs, routed to single ADC Input mix attenuation = 0 dB |
35 | kΩ | ||||
| IN2 inputs, input mix attenuation = 0 dB | 35 | ||||||
| IN1 inputs, input mix attenuation = –6 dB | 62.5 | ||||||
| IN2 inputs, input mix attenuation = –6 dB | 62.5 | ||||||
| Input capacitance | 10 | pF | |||||
| Input level control minimum attenuation setting | 0 | dB | |||||
| Input level control maximum attenuation setting | 6 | dB | |||||
| Input level control attenuation step size | 6 | dB | |||||
| ADC DIGITAL DECIMATION FILTER | fS = 48 kHz | ||||||
| Filter gain from 0 to 0.39 fS | Filter A, AOSR = 128 or 64 | ±0.1 | dB | ||||
| Filter gain from 0.55 fS to 64 fS | Filter A, AOSR = 128 or 64 | –73 | dB | ||||
| Filter group delay | Filter A, AOSR = 128 or 64 | 17/fS | s | ||||
| Filter gain from 0 to 0.39 fS | Filter B, AOSR = 64 | ±0.1 | dB | ||||
| Filter gain from 0.60 fS to 32 fS | Filter B, AOSR = 64 | -46 | dB | ||||
| Filter group delay | Filter B, AOSR = 64 | 11/fS | s | ||||
| Filter gain from 0 to 0.39 fS | Filter C, AOSR = 32 | ±0.033 | dB | ||||
| Filter gain from 0.28 fS to 16 fS | Filter C, AOSR = 32 | -60 | dB | ||||
| Filter group delay | Filter C, AOSR = 32 | 11/fS | s | ||||
| MICROPHONE BIAS | |||||||
| Bias voltage | Programmable settings, load = 750 Ω | 2 | V | ||||
| 2.25 | 2.5 | 2.75 | |||||
| AVDD – 0.2 | |||||||
| Current sourcing | 2.5 V setting | 4 | mA | ||||
| Integrated noise | BW = 20 Hz to 20 kHz, A-weighted, 1-µF capacitor between MICBIAS and AGND | 3.3 | µVrms | ||||
| DIGITAL I/O | |||||||
| VIL | Input low level | IIL = 5 μA | –0.3 | 0.3 × IOVDD | V | ||
| VIH | Input high level(3) | IIH = 5 μA | 0.7 × IOVDD | V | |||
| VOL | Output low level | IIH = 2 TTL loads | 0.1 × IOVDD | V | |||
| VOH | Output high level | IOH = 2 TTL loads | 0.8 × IOVDD | V | |||
| SUPPLY CURRENT | fS = 48 kHz, AVDD = 3.3 V, DVDD = IOVDD = 1.8 V | ||||||
| Mono record | AVDD | PLL and AGC off | 2 | mA | |||
| DVDD | 1.9 | ||||||
| Stereo record | AVDD | PLL and AGC off | 4 | mA | |||
| DVDD | 2.1 | ||||||
| PLL | AVDD | Additional power consumed when PLL is powered | 1.1 | mA | |||
| DVDD | 0.8 | ||||||
| Power down | AVDD | All supply voltages applied, all blocks programmed in lowest power state | 0.04 | μA | |||
| DVDD | 0.7 | ||||||
(1) Ratio of output level with 1-kHz full-scale sine-wave input, to the output level with the inputs short-circuited, measured A-weighted over a 20-Hz to 20-kHz bandwidth using an audio analyzer.
(2) All performance measurements done with 20-kHz lowpass filter and, where noted, A-weighted filter. Failure to use such a filter may result in higher THD+N and lower SNR and dynamic range readings than shown in the Electrical Characteristics. The lowpass filter removes out-of-band noise, which, although not audible, may affect dynamic specification values.
(3) When IOVDD < 1.6 V, minimum VIH is 1.1 V.
8.6 Dissipation Ratings(1)
| PACKAGE TYPE | TA = 25°C POWER RATING |
DERATING FACTOR | TA = 75°C POWER RATING |
TA = 85°C POWER RATING |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DSBGA | 1052.6 mW | 13.1 mW/°C | 394.7 mW | 263.2 mW |
8.7 I2S/LJF/RJF Timing in Master Mode
Specified at 25°C, DVDD = 1.8 V. All timing specifications are measured at characterization. See Figure 1 for timing diagram.| IOVDD = 1.8 V | IOVDD = 3.3 V | UNIT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIN | MAX | MIN | MAX | |||
| td(WS) | BCLK/WCLK delay time | 20 | 15 | ns | ||
| td(DO-WS) | BCLK/WCLK to DOUT delay time | 25 | 20 | ns | ||
| td(DO-BCLK) | BCLK to DOUT delay time | 20 | 15 | ns | ||
| tr | Rise time | 20 | 15 | ns | ||
| tf | Fall time | 20 | 15 | ns | ||
8.8 DSP Timing in Master Mode
Specified at 25°C, DVDD = 1.8 V. All timing specifications are measured at characterization. See Figure 2 for timing diagram.| IOVDD = 1.8 V | IOVDD = 3.3 V | UNIT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIN | MAX | MIN | MAX | |||
| td(WS) | BCLK/WCLK delay time | 25 | 15 | ns | ||
| td(DO-BCLK) | BCLK to DOUT delay time | 25 | 15 | ns | ||
| tr | Rise time | 20 | 15 | ns | ||
| tf | Fall time | 20 | 15 | ns | ||
8.9 I2S/LJF/RJF Timing in Slave Mode
Specified at 25°C, DVDD = 1.8 V. All timing specifications are measured at characterization. See Figure 3 for timing diagram.| IOVDD = 1.8 V | IOVDD = 3.3 V | UNIT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIN | MAX | MIN | MAX | |||
| tH(BCLK) | BCLK high period | 35 | 35 | ns | ||
| tL(BCLK) | BCLK low period | 35 | 35 | ns | ||
| ts(WS) | BCLK/WCLK setup time | 10 | 6 | ns | ||
| th(WS) | BCLK/WCLK hold time | 10 | 6 | ns | ||
| td(DO-WS) | BCLK/WCLK to DOUT delay time (for LJF Mode only) | 30 | 30 | ns | ||
| td(DO-BCLK) | BCLK to DOUT delay time | 25 | 20 | ns | ||
| tr | Rise time | 16 | 8 | ns | ||
| tf | Fall time | 16 | 8 | ns | ||
8.10 DSP Timing in Slave Mode
Specified at 25°C, DVDD = 1.8 V. All timing specifications are measured at characterization. See Figure 4 for timing diagram.| IOVDD = 1.8 V | IOVDD = 3.3 V | UNIT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIN | MAX | MIN | MAX | |||
| tH(BCLK) | BCLK high period | 35 | 35 | ns | ||
| tL(BCLK) | BCLK low period | 35 | 35 | ns | ||
| ts(WS) | BCLK/WCLK setup time | 10 | 8 | ns | ||
| th(WS) | BCLK/WCLK hold time | 10 | 8 | ns | ||
| td(DO-BCLK) | BCLK to DOUT delay time | 25 | 20 | ns | ||
| tr | Rise time | 15 | 8 | ns | ||
| tf | Fall time | 15 | 8 | ns | ||
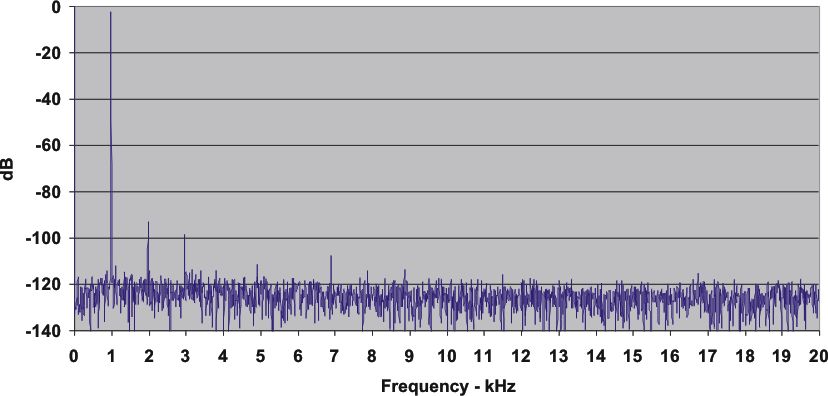
8.11 Typical Characteristics