SLAS509G April 2006 – July 2021 TLV320AIC3106
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description (continued)
- 6 Device Comparison Table
- 7 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 8 Specifications
- 9 Parameter Measurement Information
-
10Detailed Description
- 10.1 Overview
- 10.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 10.3
Feature Description
- 10.3.1 Hardware Reset
- 10.3.2 Digital Audio Data Serial Interface
- 10.3.3 Audio Data Converters
- 10.3.4 Audio Analog Inputs
- 10.3.5 Analog Fully Differential Line Output Drivers
- 10.3.6 Analog High Power Output Drivers
- 10.3.7 Input Impedance and VCM Control
- 10.3.8 General-Purpose I/O
- 10.3.9 Digital Microphone Connectivity
- 10.3.10 Micbias Generation
- 10.3.11 Short Circuit Output Protection
- 10.3.12 Jack/Headset Detection
- 10.4 Device Functional Modes
- 10.5 Programming
- 10.6 Register Maps
- 11Application and Implementation
- 12Power Supply Recommendations
- 13Layout
- 14Device and Documentation Support
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RGZ|48
Orderable Information
10.3.3.1 Audio Clock Generation
The audio converters in the TLV320AIC3106 need an internal audio master clock at a frequency of 256 × fS(ref), which can be obtained in a variety of manners from an external clock signal applied to the device.
A more detailed diagram of the audio clock section of the TLV320AIC3106 is shown in Figure 10-8.
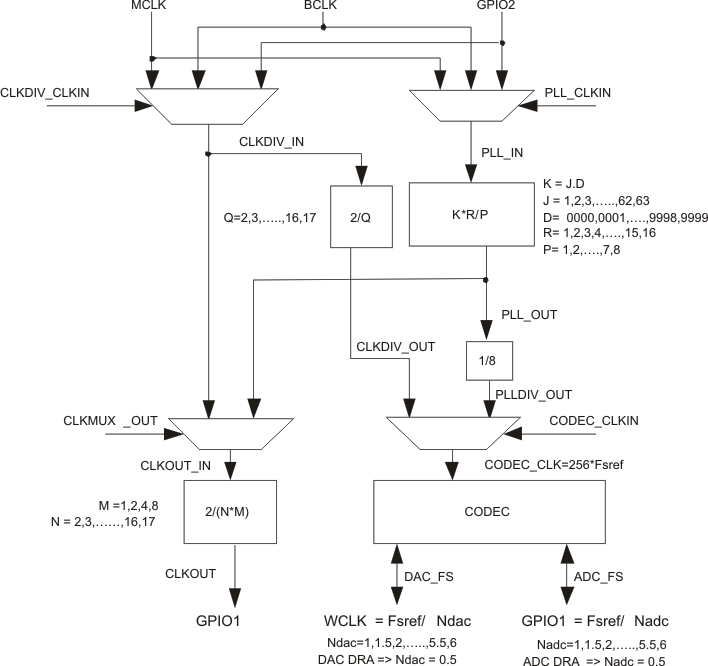 Figure 10-8 Audio Clock Generation Processing
Figure 10-8 Audio Clock Generation ProcessingThe part can accept an MCLK input from 512 kHz to 50 MHz, which can then be passed through either a programmable divider or a PLL, to get the proper internal audio master clock needed by the part. The BCLK or GPIO2 inputs can also be used to generate the internal audio master clock.
This design also allows the PLL to be used for an entirely separate purpose in a system, if the audio codec is not powered up. The user can supply a separate clock to GPIO2, route this through the PLL, with the resulting output clock driven out GPIO1, for use by other devices in the system
A primary concern is proper operation of the codec at various sample rates with the limited MCLK frequencies available in the system. This device includes a highly programmable PLL to accommodate such situations easily. The integrated PLL can generate audio clocks from a wide variety of possible MCLK inputs, with particular focus paid to the standard MCLK rates already widely used.
When the PLL is disabled:
where:
- Q = 2, 3, …, 17
CLKDIV_IN can be MCLK, BCLK, or GPIO2, selected by register 102, bits D7-D6.
When the PLL is enabled:
where
- P = 1, 2, 3,…, 8
- R = 1, 2, …, 16
- K = J.D
- J = 1, 2, 3, …, 63
- D = 0000, 0001, 0002, 0003, …, 9998, 9999
- PLLCLK_IN can be MCLK or BCLK, selected by Page 0, register 102, bits D5-D4
P, R, J, and D are register programmable. J is the integer portion of K (the numbers to the left of the decimal point), while D is the fractional portion of K (the numbers to the right of the decimal point, assuming four digits of precision).
Examples:
If K = 8.5, then J = 8, D = 5000
If K = 7.12, then J =
7, D = 1200
If K = 14.03, then J = 14, D = 0300
If K = 6.0004, then J = 6, D = 0004
When the PLL is enabled and D = 0000, the following conditions must be satisfied to meet specified performance:
2 MHz ≤ ( PLLCLK_IN / P ) ≤ 20 MHz
80 MHz ≤ (PLLCLK _IN × K × R / P ) ≤ 110 MHz
4 ≤ J ≤ 55
When the PLL is enabled and D≠0000, the following conditions must be satisfied to meet specified performance:
10 MHz ≤ PLLCLK _IN / P ≤ 20 MHz
80 MHz ≤ PLLCLK _IN × K × R / P ≤ 110 MHz
4 ≤ J ≤ 11
R = 1
Example:
MCLK = 12 MHz and fS(ref) = 44.1 kHz
Select P = 1, R = 1, K = 7.5264, which results in J = 7, D = 5264
Example:
MCLK = 12 MHz and fS(ref) = 48 kHz
Select P = 1, R = 1, K = 8.192, which results in J = 8, D = 1920
Table 10-1 lists several example cases of typical MCLK rates and how to program the PLL to achieve fS(ref) = 44.1 kHz or 48 kHz.
| fS(ref) = 44.1 kHz | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MCLK (MHz) | P | R | J | D | ACHIEVED fS(ref) | % ERROR |
| 2.8224 | 1 | 1 | 32 | 0 | 44100.00 | 0.0000 |
| 5.6448 | 1 | 1 | 16 | 0 | 44100.00 | 0.0000 |
| 12.0 | 1 | 1 | 7 | 5264 | 44100.00 | 0.0000 |
| 13.0 | 1 | 1 | 6 | 9474 | 44099.71 | –0.0007 |
| 16.0 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 6448 | 44100.00 | 0.0000 |
| 19.2 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 7040 | 44100.00 | 0.0000 |
| 19.68 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 5893 | 44100.30 | 0.0007 |
| 48.0 | 4 | 1 | 7 | 5264 | 44100.00 | 0.0000 |
| fS(ref) = 48 kHz | ||||||
| MCLK (MHz) | P | R | J | D | ACHIEVED fS(ref) | % ERROR |
| 2.048 | 1 | 1 | 48 | 0 | 48000.00 | 0.0000 |
| 3.072 | 1 | 1 | 32 | 0 | 48000.00 | 0.0000 |
| 4.096 | 1 | 1 | 24 | 0 | 48000.00 | 0.0000 |
| 6.144 | 1 | 1 | 16 | 0 | 48000.00 | 0.0000 |
| 8.192 | 1 | 1 | 12 | 0 | 48000.00 | 0.0000 |
| 12.0 | 1 | 1 | 8 | 1920 | 48000.00 | 0.0000 |
| 13.0 | 1 | 1 | 7 | 5618 | 47999.71 | –0.0006 |
| 16.0 | 1 | 1 | 6 | 1440 | 48000.00 | 0.0000 |
| 19.2 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 1200 | 48000.00 | 0.0000 |
| 19.68 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 9951 | 47999.79 | –0.0004 |
| 48.0 | 4 | 1 | 8 | 1920 | 48000.00 | 0.0000 |
The TLV320AIC3106 can also output a separate clock on the GPIO1 pin. If the PLL is being used for the audio data converter clock, the M and N settings can be used to provide a divided version of the PLL output. If the PLL is not being used for the audio data converter clock, the PLL can still be enabled to provide a completely independent clock output on GPIO1. The formula for the GPIO1 clock output when PLL is enabled and CLKMUX_OUT is 0 is:
When CLKMUX_OUT is 1, regardless of whether PLL is enabled or disabled, the input to the clock output divider can be selected as MCLK, BCLK, or GPIO2. Is this case, the formula for the GPIO1 clock is:
where:
- M = 1, 2, 4, 8
- N = 2, 3, …, 17
- CLKDIV_IN can be BCLK, MCLK, or GPIO2, selected by page 0, register 102, bits D7-D6