SNVSBU0 October 2020 TLV4062-Q1 , TLV4082-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DBV|6
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
6.8 Typical Characteristics
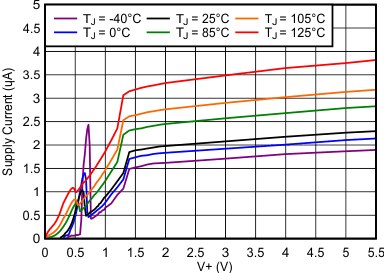
at TJ = 25°C with a 0.1-µF capacitor close to V+ (unless otherwise noted)
| IN1 = IN2 = 1.5 V |
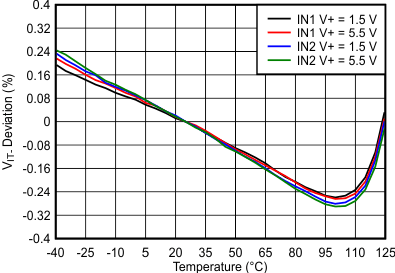 Figure 6-4 INx Threshold (VIT–) Deviation vs Temperature
Figure 6-4 INx Threshold (VIT–) Deviation vs Temperature
| V+ = 5.5 V |
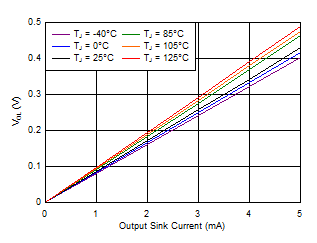 Figure 6-8 Output Voltage Low vs Output Current (V+ = 3.3 V)
Figure 6-8 Output Voltage Low vs Output Current (V+ = 3.3 V)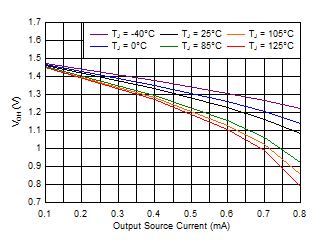 Figure 6-10 Output Voltage High vs Output Current (V+ = 1.5 V)
Figure 6-10 Output Voltage High vs Output Current (V+ = 1.5 V)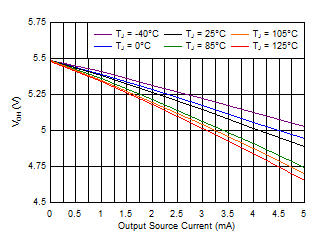 Figure 6-12 Output Voltage High vs Output Current (V+ = 5.5 V)
Figure 6-12 Output Voltage High vs Output Current (V+ = 5.5 V)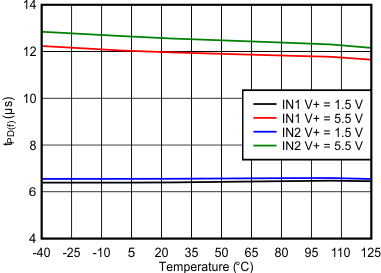
| IN1 = IN2 = 1.3 V to 0 V |
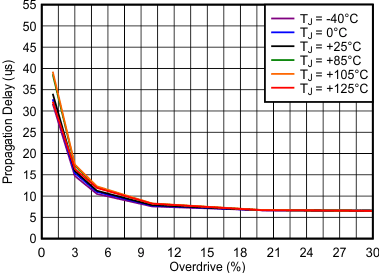
| High-to-low transition occurs above the curve |
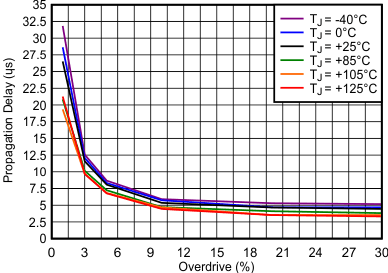
| Low-to-high transition occurs above the curve |
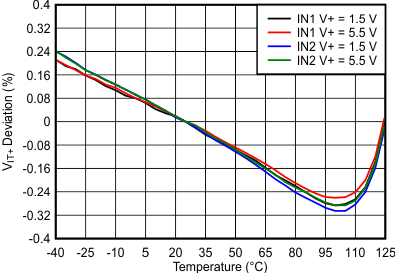 Figure 6-3 INx Threshold (VIT+) Deviation vs Temperature
Figure 6-3 INx Threshold (VIT+) Deviation vs Temperature
| V+ = 5.5 V |
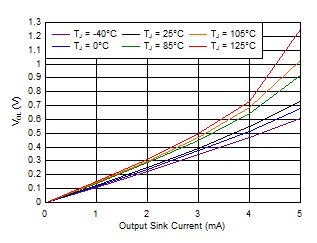 Figure 6-7 Output Voltage Low vs Output Current (V+ = 1.5 V)
Figure 6-7 Output Voltage Low vs Output Current (V+ = 1.5 V)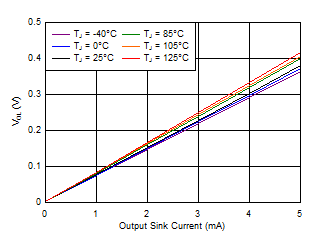 Figure 6-9 Output Voltage Low vs Output Current (V+ = 5.5 V)
Figure 6-9 Output Voltage Low vs Output Current (V+ = 5.5 V)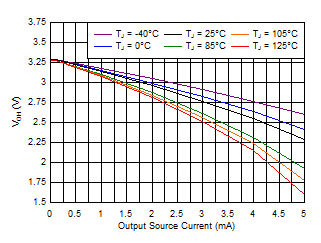 Figure 6-11 Output Voltage High vs Output Current (V+ = 3.3 V)
Figure 6-11 Output Voltage High vs Output Current (V+ = 3.3 V)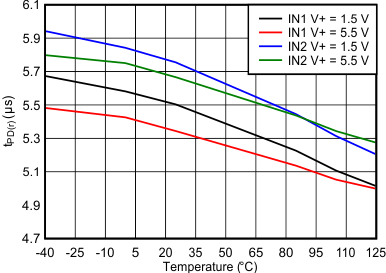
| IN1 = IN2 = 0 V to 1.3 V |
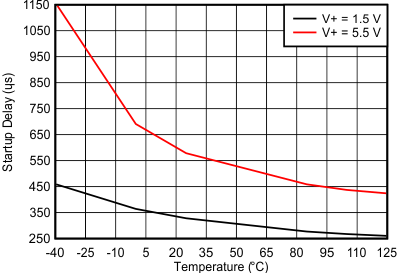 Figure 6-15 Startup Delay
Figure 6-15 Startup Delay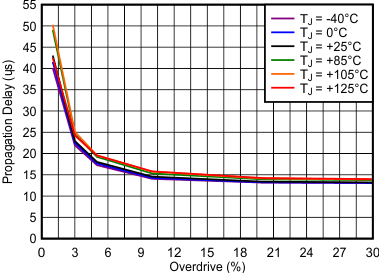
| High-to-low transition occurs above the curve |
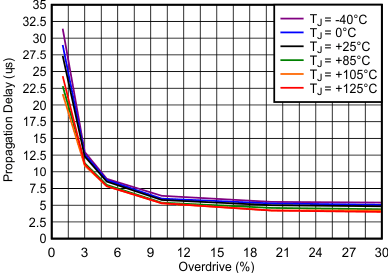
| Low-to-high transition occurs above the curve |