-
TLV854x 500-nA, RRIO, Nanopower Operational Amplifiers for Cost-Optimized Systems
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description (continued)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
- IMPORTANT NOTICE
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
TLV854x 500-nA, RRIO, Nanopower Operational Amplifiers for Cost-Optimized Systems
1 Features
- For Cost-Optimized Systems
- Nanopower Supply Current: 500 nA per Channel
- Offset Voltage: 3.1 mV (maximum)
- TcVos: 0.8 µV/°C
- Gain Bandwidth: 8 kHz
- Unity-Gain Stable
- Low Input-Bias Current: 100 fA
- Wide Supply Range: 1.7 V to 3.6 V
- Rail-to-Rail Input and Output (RRIO)
- Temperature Range –40°C to +125°C
- Industry Standard Package
- Leadless Package
- Dual in 8-Pin X2QFN
2 Applications
- Motion Detectors Using PIR Sensors SNAA301
- Motion Detectors Using Microwave Sensors
- Gas Detectors
- Ionization Smoke Alarms
- Thermostats
- Remote Sensors, IoT (Internet of Things)
- Active RFID Readers and Tags
- Portable Medical Equipment
- Glucose Monitoring
3 Description
The TLV854x ultra-low-power operational amplifiers (op amps) are intended for cost-optimized sensing applications in wireless and low-power wired equipment. The TLV854x family of op amps minimize power consumption in equipment such as motion detecting security systems (like microwave and PIR motion sensing) where operational battery life is critical. They also have a carefully designed CMOS input stage, enabling very low, femto-ampere bias currents, thereby reducing IBIAS and IOS errors that would otherwise impact sensitive applications. Examples of these include transimpedance amplifier (TIA) configurations with megaohm feedback resistors, and high source impedance sensing applications. Additionally, built-in EMI protection reduces sensitivity to unwanted RF signals from sources such as mobile phones, WiFi, radio transmitters and tab readers.
Device Information(1)
| PART NUMBER | PACKAGE | BODY SIZE |
|---|---|---|
| TLV8544 | TSSOP (14) | 5.00 mm × 4.40 mm |
| SOIC (14) | 8.65 mm × 3.91 mm | |
| TLV8542 | SOIC (8) | 4.9 mm × 3.90 mm |
| X2QFN (8) | 1.50 mm × 1.50 mm | |
| TLV8541 | SOT-23 (5) | 2.90 mm x 1.60 mm |
- For all available packages, see the orderable addendum at the end of the data sheet.
Device Images
Low Power PIR Motion Detector

4 Revision History
Changes from D Revision (November 2017) to E Revision
- Released TLV8542 X2QFN package as production dataGo
- Released TLV8544 SOIC package as production data Go
Changes from C Revision (October 2017) to D Revision
Changes from B Revision (June 2017) to C Revision
- Changed TLV8542 dual datasheet to production dataGo
Changes from A Revision (March 2017) to B Revision
- Added Advance Information TLV8542 to the TLV8544 Data Sheet Go
Changes from * Revision (December 2016) to A Revision
- Changed Product Preview to Production Data release. Go
5 Description (continued)
The TLV854x op amps operates with a single supply voltage down to 1.7 V supply, providing continuous performance in low battery situations over the extended temperature range of –40°C to +125°C. All versions are specified for operation from –40°C to 125°C. The TLV8541 (single version) is available in the 5-pin SOT-23 while the TLV8542 (dual version) is available in the 8-pin SOIC package. The 4-channel TLV8544 (quad version) is available in the industry standard 14-pin TSSOP package.
6 Pin Configuration and Functions
Pin Functions: TLV8541 DBV
| PIN | I/O | DESCRIPTION | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NUMBER | NAME | |||
| 1 | OUT | O | Output | |
| 2 | V– | P | Negative (lowest) power supply | |
| 3 | +IN | I | Non-Inverting Input | |
| 4 | –IN | I | Inverting Input | |
| 5 | V+ | P | Positive (highest) power supply | |

Pin Functions: TLV8542 D & RUG
| PIN | I/O | DESCRIPTION | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NUMBER | NAME | |||
| 1 | OUT A | O | Channel A Output | |
| 2 | –IN A | I | Channel A Inverting Input | |
| 3 | +IN A | I | Channel A Non-Inverting Input | |
| 4 | V– | P | Negative (lowest) power supply | |
| 5 | +IN B | I | Channel B Non-Inverting Input | |
| 6 | –IN B | I | Channel B Inverting Input | |
| 7 | OUT B | O | Channel B Output | |
| 8 | V+ | P | Positive (highest) power supply | |
Pin Functions: TLV8544 PW & D
| PIN | I/O | DESCRIPTION | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NUMBER | NAME | |||
| 1 | OUTA | O | Channel A output | |
| 2 | –INA | I | Channel A inverting input | |
| 3 | +INA | I | Channel A non-inverting input | |
| 4 | V+ | P | Positive (highest) power supply | |
| 5 | +INB | I | Channel B non-inverting input | |
| 6 | –INB | I | Channel B inverting input | |
| 7 | OUTB | O | Channel B output | |
| 8 | OUTC | O | Channel C output | |
| 9 | –INC | I | Channel C inverting input | |
| 10 | +INC | I | Channel C non-inverting input | |
| 11 | V– | P | Negative (lowest) power supply | |
| 12 | +IND | I | Channel D non-inverting input | |
| 13 | –IND | I | Channel D inverting input | |
| 14 | OUTD | O | Channel D output | |
7 Specifications
7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
Over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted) (1)(2)(3)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supply voltage, Vs = (V+) – (V–) | –0.3 | 4 | V | ||
| Input pins | Voltage | Common mode | (V–) – 0.3 | (V+) + 0.3 | V |
| Differential | (V–) – 0.3 | (V+) + 0.3 | V | ||
| Input pins | Current | –10 | 10 | mA | |
| Output short current(4) | Continuous | Continuous | |||
| Operating ambient temperature | –40 | 125 | °C | ||
| Storage temperature, Tstg | –65 | 150 | °C | ||
| Junction temperature | 150 | °C | |||
7.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human-body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001(1) | ±1000 | V |
| Charged-device model (CDM), per JEDEC specification JESD22-C101(2) | ±250 | |||
7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supply voltage (V+ – V–) | 1.7 | 3.6 | V | ||
| Specified ambient temperature | –40 | 125 | °C | ||
7.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | TLV8544 | TLV8542 | TLV8541 | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PW (TSSOP) | D
(SOIC) |
D
(SOIC) |
RUG (X2QFN) | DBV (SOT-23) | |||
| 14 PINS | 14 PINS | 8 PINS | 8 PINS | 5 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 124.5 | 104.1 | 141.6 | 188.3 | 244.6 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 52.7 | 61.5 | 85.7 | 88.9 | 127.3 | °C/W |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 66.2 | 59.9 | 84.7 | 100.2 | 79.4 | °C/W |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 7.3 | 22.9 | 36.3 | 3.9 | 44.1 | °C/W |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 65.7 | 59.5 | 84.0 | 100.3 | 78.8 | °C/W |
| RθJC(bot) | Junction-to-case (bottom) thermal resistance | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | °C/W |
7.5 Electrical Characteristics
TA = 25°C, VS = 1.8 V to 3.3 V, VCM = VOUT = VS / 2, and RL≥ 10 MΩ to VS / 2, unless otherwise noted.| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OFFSET VOLTAGE | ||||||
| VOS | Input offset voltage | VCM = V– , VS = 1.8 V and 3.3 V | –3.1 | See Plots | 3.1 | mV |
| VCM = V+, VS = 1.8 V and 3.3 V | –3.4 | See Plots | 3.4 | |||
| dVOS/dT | Input offset drift | VCM = V–, TA = –40°C to 125°C | 0.8 | µV/°C | ||
| PSRR | Power-supply rejection ratio | VCM = V– , VS =1.8 V and 3.3 V | 66 | 90 | dB | |
| INPUT VOLTAGE RANGE | ||||||
| VCM | Common-mode voltage range | VS = 3.3 V | 0 | 3.3 | V | |
| CMRR | Common-mode rejection ratio | (V–) ≤ VCM ≤ (V+), Vs = 3.3 V | 60 | 80 | dB | |
| (V–) ≤ VCM ≤ (V+) – 1.2 V | 90 | |||||
| INPUT BIAS CURRENT | ||||||
| IB | Input bias current | 100 | fA | |||
| IOS | Input offset current | 100 | fA | |||
| INPUT IMPEDANCE | ||||||
| Differential | 2 | pF | ||||
| Common mode | 4 | pF | ||||
| NOISE | ||||||
| En | Input voltage noise | ƒ = 0.1 Hz to 10 Hz | 8.6 | µVp–p | ||
| en | Input voltage noise density | ƒ = 1 kHz | 264 | nV/√Hz | ||
| OPEN-LOOP GAIN | ||||||
| AOL | Open-loop voltage gain | (V–) + 0.3 V ≤ VO ≤ (V+) – 0.3 V, RL = 100 kΩ to V+/2 | 120 | dB | ||
| OUTPUT | ||||||
| VOH | Voltage output swing from positive rail | RL = 100 kΩ to V+/2, VS = 3.3 V | 12 | mV | ||
| VOL | Voltage output swing from negative rail | RL = 100 kΩ to V+/2, VS = 3.3 V | 12 | mV | ||
| ISC | Short-circuit current | Sourcing, VO to V–, VIN(diff) = 100 mV, VS = 3.3 V | 15 | mA | ||
| Sinking, VO to V+, VIN(diff) = –100 mV, VS = 3.3 V | 30 | |||||
| ZO | Open loop output impedance | ƒ = 1 kHz, IO = 0 mA | 8 | kΩ | ||
| FREQUENCY RESPONSE | ||||||
| GBP | Gain-bandwidth product | CL = 20 pF, RL = 10 MΩ | 8 | kHz | ||
| SR | Slew rate (10% to 90%) | G = 1, rising edge, CL = 20 pF | 3.5 | V/ms | ||
| G = 1, falling edge, CL = 20 pF | 4.5 | |||||
| POWER SUPPLY | ||||||
| IQ–TLV8541 | Quiescent Current | VCM = V–, IO = 0 mA, VS = 3.3 V | 550 | 640 | nA | |
| IQ–TLV8542 | Quiescent Current, per channel | VCM = V–, IO = 0 mA, VS = 3.3 V | 550 | 640 | nA | |
| IQ–TLV8544 | Quiescent current, per channel | VCM = V–, IO = 0 mA, VS = 3.3 V | 500 | 640 | nA | |
7.6 Typical Characteristics
TA = 25°C, RL = 10 MΩ to VS/2 ,CL = 20 pF, VCM = VS / 2 V unless otherwise specified.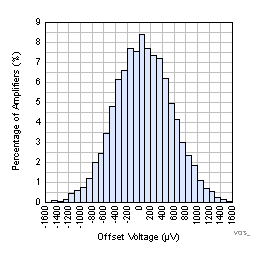
| VS = 1.8 V | VCM = V+ | Data from 1500 4-channel devices |

| VS = 3.3 V | VCM = V+ | Data from 1500 4-channel devices |

| VS = 1.8 V | TA = –40, 25, 125°C | Per Channel |

| VS = 1.8 V | TA = –40, 25, 125°C | |

| VS = 1.6 to 3.6V | TA = –40, 25, 125°C | VCM = V- |

| VS= 3.3V | TA = 25°C | VCM = V– |

| VS = 3.3 V | TA = –40, 25, 125°C | |

| VS = 3.3 V | TA = –40, 25, 125°C | |

| VS = 3.3 V | TA = –40°C | |

| VS = 3.3 V | TA = 25°C | |

| VS = 3.3 V | TA = 125°C | |

| VS = 3.3 V | TA = 25°C | |

| VS = 3.3 V | TA = 25°C | |
| AV = 1 |

| VS = 3.3 V | TA = 25 °C | CL = 50 pF |
| VIN = 1.65 ± 0.1 V | AV = 1 |

| VS = 3.3 V | TA = 25°C | CL = 50 pF |
| VIN = 1.65 ± 1 V | AV = 1 |

| VS = 1.8 V | VCM = V– | Data from 1500 4-channel devices |

| VS = 3.3 V | VCM = V– | Data from 1500 4-channel devices |

| VS = 3.3 V | TA = –40, 25, 125°C | Per Channel |

| VS = 3.3 V | TA = –40, 25, 125°C | |

| VS= 3.3V | TA = 25°C | |

| VS = 1.8 V | TA = –40, 25, 125°C | |

| VS = 1.8 V | TA = –40, 25, 125°C | |

| VS = 1.8 V | TA = –40°C | |

| VS = 1.8 V | TA = 25°C | |

| VS= 1.8V | TA = 125°C | |

| VS = 3.3 V | TA = –40, 25, 125°C | CL = 50 pF |

| VS = 3.3 V | TA = 25°C | |

| VS = 1.8 V | TA = 25°C | CL = 50 pF |
| VIN = 0.9 ± 0.1 V | AV = 1 |

| VS = 1.8 V | TA = 25°C | CL = 50 pF |
| VIN = 0.9 ± 0.5 V | AV = 1 |
8 Detailed Description
8.1 Overview
The TLV854x amplifiers are unity-gain stable and can operate on a single supply, making them highly versatile and easy to use.
Parameters that vary significantly with operating voltages or temperature are shown in the Typical Characteristics curves.
8.2 Functional Block Diagram

8.3 Feature Description
The differential inputs of the TLV854x device consist of a non-inverting input (+IN) and an inverting input (–IN). The device amplifies only the difference in voltage between the two inputs, which is called the differential input voltage. The output voltage of the op-amps VOUT are given by Equation 1:
where
- AOL is the open-loop gain of the amplifier, typically around 100 dB.
8.4 Device Functional Modes
8.4.1 Rail-To-Rail Input
The input common-mode voltage range of the TLV854x extends to the supply rails. This is achieved with a complementary input stage — an N-channel input differential pair in parallel with a P-channel differential pair. The N-channel pair is active for input voltages close to the positive rail, typically (V+) – 800 mV to 200 mV above the positive supply, while the P-channel pair is on for inputs from 300 mV below the negative supply to approximately (V+) – 800 mV. There is a small transition region, typically (V+) – 1.2 V to (V+) – 0.8 V, in which both pairs are on. This 400-mV transition region can vary 200 mV with process variation. Within the 400-mV transition region PSRR, CMRR, offset voltage, offset drift, and THD may be degraded compared to operation outside this region.
8.4.2 Supply Current Changes Over Common Mode
Because of the ultra-low supply current, changes in common mode voltages cause a noticeable change in the supply current as the input stages transition through the transition region, as shown in Figure 30.
 Figure 30. Supply Current Change Over Common Mode at 1.8 V
Figure 30. Supply Current Change Over Common Mode at 1.8 V
For the lowest supply current operation, keep the input common mode range between V– and 1 V below V+.
8.4.3 Design Optimization With Rail-To-Rail Input
In most applications, operation is within the range of only one differential pair. However, some applications can subject the amplifier to a common-mode signal in the transition region. Under this condition, the inherent mismatch between the two differential pairs may lead to degradation of the CMRR and THD. The unity-gain buffer configuration is the most problematic as it traverses through the transition region if a sufficiently wide input swing is required.