SBOS941D February 2019 – August 2021 TLV9301 , TLV9302 , TLV9304
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.3.1 Input Protection Circuitry
The TLV930x uses a patented input architecture to eliminate the requirement for input protection diodes but still provides robust input protection under transient conditions. Figure 7-1 shows conventional input diode protection schemes that are activated by fast transient step responses and introduce signal distortion and settling time delays because of alternate current paths, as shown in Figure 7-2. For low-gain circuits, these fast-ramping input signals forward-bias back-to-back diodes, causing an increase in input current and resulting in extended settling time.
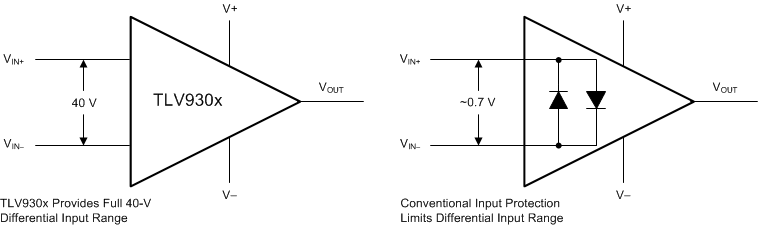 Figure 7-1 TLV930x Input Protection Does Not Limit Differential Input Capability
Figure 7-1 TLV930x Input Protection Does Not Limit Differential Input Capability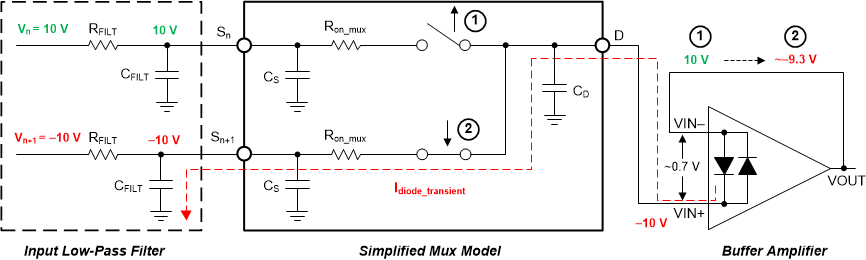 Figure 7-2 Back-to-Back Diodes Create Settling Issues
Figure 7-2 Back-to-Back Diodes Create Settling IssuesThe TLV930x family of operational amplifiers provides a true high-impedance differential input capability for high-voltage applications. This patented input protection architecture does not introduce additional signal distortion or delayed settling time, making the device an optimal op amp for multichannel, high-switched, input applications. The TLV930x tolerates a maximum differential swing (voltage between inverting and noninverting pins of the op amp) of up to 40 V, making the device suitable for use as a comparator or in applications with fast-ramping input signals.