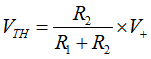SBOS941D February 2019 – August 2021 TLV9301 , TLV9302 , TLV9304
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8.2.1.2 Detailed Design Procedure
This noninverting comparator circuit applies the input voltage (VIN) to the noninverting terminal of the op amp. Two resistors (R1 and R2) divide the supply voltage (V+) to create a mid-supply threshold voltage (VTH) as calculated in Equation 1. The circuit is shown in Figure 8-1. When VIN is less then VTH, the output voltage transitions to the negative supply and equals the low-level output voltage. When VIN is greater than VTH, the output voltage transitions to the positive supply and equals the high-level output voltage.
In this example, resistor 1 and 2 have been selected to be 100 kΩ, which sets the reference threshold at 20 V. However, resistor 1 and 2 can be adjusted to modify the threshold using Equation 1. Resistor 1 and 2's values have also been selected to reduce power consumption, but these values can be further increased to reduce power consumption, or reduced to improve noise performance.