SNIS216 November 2019 TMP392
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DRL|6
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8.2.2 TMP392 With 10°C Hysteresis
Figure 11 shows an example circuit for dual overtemperature protection using the TMP392. In this example, the trip points are set at +60°C and +90°C with 10°C hysteresis. This circuit is useful in cases where a lower overtemperature detection may be used to warn the application of rising system temperature and take software corrective actions such as lowering the performance, while the higher overtemperature detection may be used to start a fan to cool the system to a lower temperature.
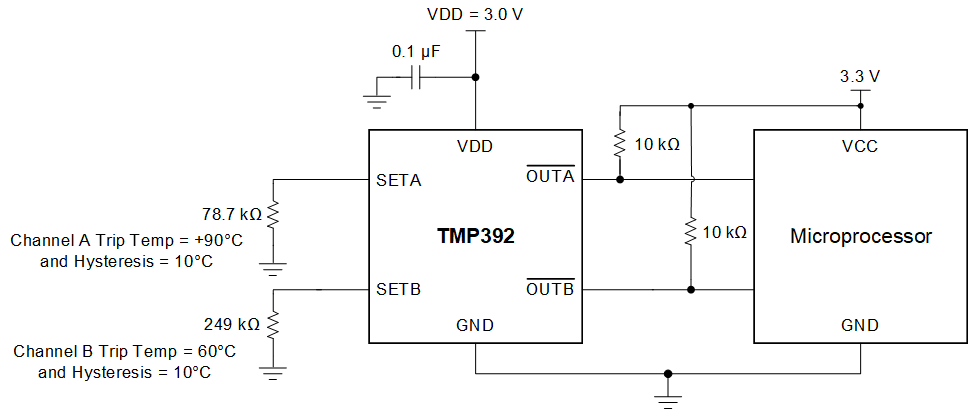 Figure 11. TMP392 Example Circuit at +90°C and +60°C Thresholds With 10°C Hysteresis
Figure 11. TMP392 Example Circuit at +90°C and +60°C Thresholds With 10°C Hysteresis