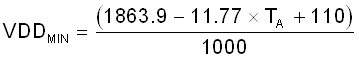SBOSA26A December 2020 – February 2021 TMP9A00-EP
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Introduction to Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DCK|5
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8.2.1 Design Requirements
ADCs that are found in microcontrollers have leakage current during the sampling phase to charge the sampling capacitor. A high sampling frequency can have higher average input leakage that sags the output voltage of the TMP9A00-EP, which results in a reading that is hotter than normal. To mitigate this, place a capacitor (CF) between the TMP9A00-EP and the ADC. The capacitor functions as a charge reservoir to smooth out the output voltage and remove the voltage sag.
The TMP9A00-EP output voltage has a negative slope and can not output a voltage higher than the VDD voltage. For this reason the effective operating temperature range of the device is restricted by supply. At 2.7 V, the device will output accurate temperature results from –55 °C to 150 °C. Using a supply voltage of 1.8 V will rail the output unless the temperature range is between 15 °C to 150 °C. Equation 7 can be used to find the minimum operating temperature of the device in this region. The minimum VDD must also satisfy the Section 6.3 1.8 V regardless of ambient temperature.