SPRS867A February 2013 – August 2016 TMS320DM369
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1TMS320DM369 Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC)
- 2Revision History
-
3Device Overview
- 3.1 Device Comparison
- 3.2 Device Characteristics
- 3.3 Device Compatibility
- 3.4
ARM Subsystem Overview
- 3.4.1 Components of the ARM Subsystem
- 3.4.2 ARM926EJ-S RISC CPU
- 3.4.3 CP15
- 3.4.4 MMU
- 3.4.5 Caches and Write Buffer
- 3.4.6 Tightly Coupled Memory (TCM)
- 3.4.7 Advanced High-performance Bus (AHB)
- 3.4.8 Embedded Trace Macrocell (ETM) and Embedded Trace Buffer (ETB)
- 3.4.9 ARM Memory Mapping
- 3.4.10 Peripherals
- 3.4.11 ARM Interrupt Controller (AINTC)
- 3.5 System Control Module
- 3.6 Power Management
- 3.7 Memory Map Summary
- 3.8 Pin Assignments
- 3.9 Terminal Functions
- 4Device Configurations
- 5System Interconnect
- 6Device Operating Conditions
-
7Peripheral Information and Electrical Specifications
- 7.1 Parameter Information Device-Specific Information
- 7.2 Recommended Clock and Control Signal Transition Behavior
- 7.3 Power Supplies
- 7.4 Power-Supply Sequencing
- 7.5 Reset
- 7.6 Oscillators and Clocks
- 7.7 Power Management and Real Time Clock Subsystem (PRTCSS)
- 7.8 General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO)
- 7.9 EDMA Controller
- 7.10
External Memory Interface (EMIF)
- 7.10.1 Asynchronous EMIF (AEMIF)
- 7.10.2 DDR2/mDDR Memory Controller
- 7.10.3
DDR2/mDDR Memory Controller Electrical Data/Timing
- 7.10.3.1
DDR2/mDDR Routing Specifications
- 7.10.3.1.1 DDR2/mDDR Interface
- 7.10.3.1.2 DDR2/mDDR Interface Schematic
- 7.10.3.1.3 Compatible JEDEC DDR2/mDDR Devices
- 7.10.3.1.4 PCB Stack Up
- 7.10.3.1.5 Placement
- 7.10.3.1.6 DDR2/mDDR Keep Out Region
- 7.10.3.1.7 Bulk Bypass Capacitors
- 7.10.3.1.8 High-Speed Bypass Capacitors
- 7.10.3.1.9 Net Classes
- 7.10.3.1.10 DDR2/mDDR Signal Termination
- 7.10.3.1.11 VREF Routing
- 7.10.3.1.12 DDR2/mDDR CK and ADDR_CTRL Routing
- 7.10.3.1
DDR2/mDDR Routing Specifications
- 7.11 MMC/SD
- 7.12 Video Processing Subsystem (VPSS) Overview
- 7.13 USB2.0
- 7.14 Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter (UART)
- 7.15 Serial Port Interface (SPI)
- 7.16 Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C)
- 7.17 Multichannel Buffered Serial Port (McBSP)
- 7.18 Timer
- 7.19 Pulse Width Modulator (PWM)
- 7.20 Real Time Out (RTO)
- 7.21 Ethernet Media Access Controller (EMAC)
- 7.22 Management Data Input/Output (MDIO)
- 7.23 Host-Port Interface (HPI) Peripheral
- 7.24 Key Scan
- 7.25 Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC)
- 7.26 Voice Codec
- 7.27 IEEE 1149.1 JTAG
- 8Device and Documentation Support
- 9Mechanical Packaging and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- ZCE|338
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8 Device and Documentation Support
8.1 Development Tools
TI offers an extensive line of development tools for device systems, including tools to evaluate the performance of the processors, generate code, develop algorithm implementations, and fully integrate and debug software and hardware modules. The tools support documentation is electronically available within the Code Composer Studio™ Integrated Development Environment (IDE).
The following products support development of device based applications:
Software Development Tools:
Code Composer Studio™ Integrated Development Environment (IDE): including Editor
C/C++/Assembly Code Generation, and Debug plus additional development tools
Hardware Development Tools:Extended Development System (XDS™) Emulator (supports TMS320DM369 DMSoC multiprocessor system debug) EVM (Evaluation Module)
For a complete listing of development-support tools for the TMS320DM369 DMSoC platform, visit the Texas Instruments web site on the Worldwide Web at www.ti.com. For information on pricing and availability, contact the nearest TI field sales office or authorized distributor.
8.2 Device Nomenclature
To designate the stages in the product development cycle, TI assigns prefixes to the part numbers of all DSP devices and support tools. Each DSP commercial family member has one of three prefixes: TMX, TMP, or TMS (for example, TMS320DM369ZCEDF). Texas Instruments recommends two of three possible prefix designators for its support tools: TMDX and TMDS. These prefixes represent evolutionary stages of product development from engineering prototypes (TMX/TMDX) through fully qualified production devices/tools (TMS/TMDS).
Device development evolutionary flow:
-
TMX Experimental device that is not necessarily representative of the final device's electrical specifications.
-
TMP Final silicon die that conforms to the device's electrical specifications but has not completed quality and reliability verification.
-
TMS Fully-qualified production device.
Support tool development evolutionary flow:
-
TMDX Development-support product that has not yet completed Texas Instruments internal qualification testing.
-
TMDS Fully qualified development-support product.
TMX and TMP devices and TMDX development-support tools are shipped against the following disclaimer:
"Developmental product is intended for internal evaluation purposes."
TMS devices and TMDS development-support tools have been characterized fully, and the quality and reliability of the device have been demonstrated fully. TI's standard warranty applies.
Predictions show that prototype devices (TMX or TMP) have a greater failure rate than the standard production devices. Texas Instruments recommends that these devices not be used in any production system because their expected end-use failure rate is undefined. Only qualified production devices are to be used in production.
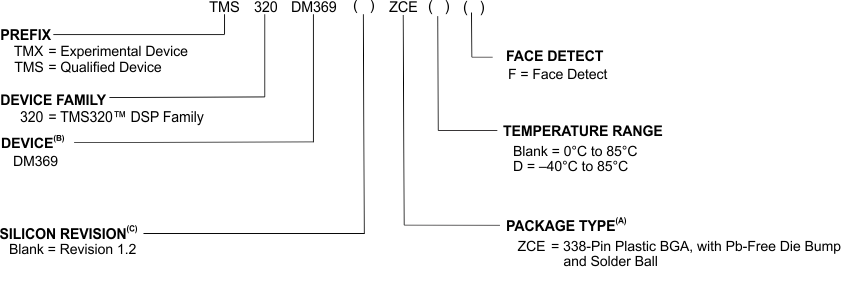
TI device nomenclature also includes a suffix with the device family name. This suffix indicates the package type (for example, ZCE), the temperature range (for example, "Blank" is the commercial temperature range). The following figure provides a legend for reading the complete device name for any TMS320DM369 DMSoC platform member.
For device part numbers and further ordering information of TMS320DM36x devices in the ZCE package type, see the TI website (www.ti.com) or contact your TI sales representative.
For additional description of the device nomenclature markings on the die, see the TMS320DM369 Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC), Silicon Revision 1.2, Silicon Errata (SPRZ441).
8.3 Documentation Support
To receive notification of documentation updates, navigate to the device product folder on www.ti.com. In the upper right corner, click on Alert me to register and receive a weekly digest of any product information that has changed. For change details, review the revision history included in any revised document.
The following documents describe the TMS320DM36x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC). Copies of these documents are available on the internet at www.ti.com.
Errata
-
SPRZ441 TMS320DM369 Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC), Silicon Revision 1.2, Silicon Errata. This document describes the known exceptions to the functional specifications for the TMS320DM369 DMSoC.
User's Guides
-
SPRUFG5 TMS320DM36x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC) ARM Subsystem User's Guide. This document describes the ARM Subsystem in the TMS320DM36x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC). The ARM subsystem is designed to give the ARM926EJ-S (ARM9) master control of the device. In general, the ARM is responsible for configuration and control of the device; including the components of the ARM Subsystem, the peripherals, and the external memories.
-
SPRUFG8 TMS320DM36x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC) Video Processing Front End (VPFE) User's Guide. This document describes the Video Processing Front End (VPFE) in the TMS320DM36x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC).
-
SPRUFG9 TMS320DM36x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC) Video Processing Back End (VPBE) User's Guide. This document describes the Video Processing Back End (VPBE) in the TMS320DM36x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC).
-
SPRUFH0 TMS320DM36x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC) 64-bit Timer/Watchdog Timer User's Guide. This document describes the operation of the software-programmable 64-bit timers in the TMS320DM36x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC).
-
SPRUFH1 TMS320DM36x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC) Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) User's Guide. This document describes the serial peripheral interface (SPI) in the TMS320DM36x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC). The SPI is a high-speed synchronous serial input/output port that allows a serial bit stream of programmed length (1 to 16 bits) to be shifted into and out of the device at a programmed bit-transfer rate. The SPI is normally used for communication between the DMSoC and external peripherals. Typical applications include an interface to external I/O or peripheral expansion via devices such as shift registers, display drivers, SPI EPROMs and analog-to-digital converters.
-
SPRUFH2 TMS320DM36x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC) Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter (UART) User's Guide. This document describes the universal asynchronous receiver/transmitter (UART) peripheral in the TMS320DM36x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC). The UART peripheral performs serial-to-parallel conversion on data received from a peripheral device, and parallel-to-serial conversion on data received from the CPU.
-
SPRUFH3 TMS320DM36x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC) Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C) Peripheral User's Guide. This document describes the inter-integrated circuit (I2C) peripheral in the TMS320DM36x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC). The I2C peripheral provides an interface between the DMSoC and other devices compliant with the I2C-bus specification and connected by way of an I2C-bus.
-
SPRUFH5 TMS320DM36x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC) Multimedia Card (MMC)/Secure Digital (SD) Card Controller User's Guide. This document describes the multimedia card (MMC)/secure digital (SD) card controller in the TMS320DM36x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC).
-
SPRUFH6 TMS320DM36x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC) Pulse-Width Modulator (PWM) User's Guide. This document describes the pulse-width modulator (PWM) peripheral in the TMS320DM36x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC).
-
SPRUFH7 TMS320DM36x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC) Real-Time Out (RTO) Controller User's Guide. This document describes the Real Time Out (RTO) controller in the TMS320DM36x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC).
-
SPRUFH8 TMS320DM36x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC) General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO) User's Guide. This document describes the general-purpose input/output (GPIO) peripheral in the TMS320DM36x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC). The GPIO peripheral provides dedicated general-purpose pins that can be configured as either inputs or outputs.
-
SPRUFH9 TMS320DM36x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC) Universal Serial Bus (USB) Controller User's Guide. This document describes the universal serial bus (USB) controller in the TMS320DM36x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC). The USB controller supports data throughput rates up to 480 Mbps. It provides a mechanism for data transfer between USB devices and also supports host negotiation.
-
SPRUFI0 TMS320DM36x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC) Enhanced Direct Memory Access (EDMA) Controller User's Guide. This document describes the operation of the enhanced direct memory access (EDMA3) controller in the TMS320DM36x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC). The EDMA controller's primary purpose is to service user-programmed data transfers between two memory-mapped slave endpoints on the DMSoC.
-
SPRUFI1 TMS320DM36x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC) Asynchronous External Memory Interface (EMIF) User's Guide. This document describes the asynchronous external memory interface (EMIF) in the TMS320DM36x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC). The EMIF supports a glueless interface to a variety of external devices.
-
SPRUFI2 TMS320DM36x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC) DDR2/Mobile DDR (DDR2/mDDR) Memory Controller User's Guide. This document describes the DDR2/mDDR memory controller in the TMS320DM36x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC). The DDR2/mDDR memory controller is used to interface with JESD79D-2A standard compliant DDR2 SDRAM and mobile DDR devices.
-
SPRUFI3 TMS320DM36x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC) Multibuffered Serial Port Interface (McBSP) User's Guide. This document describes the operation of the multibuffered serial host port interface in the TMS320DM36x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC). The primary audio modes that are supported by the McBSP are the AC97 and IIS modes. In addition to the primary audio modes, the McBSP supports general serial port receive and transmit operation.
-
SPRUFI4 TMS320DM36x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC) Universal Host Port Interface (UHPI) User's Guide. This document describes the operation of the universal host port interface in the TMS320DM36x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC).
-
SPRUFI5 TMS320DM36x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC) Ethernet Media Access Controller (EMAC) User's Guide. This document describes the operation of the ethernet media access controller interface in the TMS320DM36x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC).
-
SPRUFI7 TMS320DM36x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC) Analog to Digital Converter (ADC) User's Guide. This document describes the operation of the analog to digital conversion in the TMS320DM36x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC).
-
SPRUFI8 TMS320DM36x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC) Key Scan User's Guide. This document describes the key scan peripheral in the TMS320DM36x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC).
-
SPRUFI9 TMS320DM36x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC) Voice Codec User's Guide. This document describes the voice codec peripheral in the TMS320DM36x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC). This module can access ADC/DAC data with internal FIFO (Read FIFO/Write FIFO). The CPU communicates to the voice codec module using 32-bit-wide control registers accessible via the internal peripheral bus.
-
SPRUFJ0 TMS320DM36x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC) Power Management and Real-Time Clock Subsystem (PRTCSS) User's Guide. This document provides a functional description of the Power Management and Real-Time Clock Subsystem (PRTCSS) in the TMS320DM36x Digital Media System-on-Chip (DMSoC) and PRTC interface (PRTCIF).
Reference Guides
-
SPRU811 Flip Chip Ball Grid Array Package Reference Guide. This document provides application guidelines for effective flip chip BGA device handling and management, including board design rules, board assembly parameters, rework process, thermal management, troubleshooting, and other critical factors.
Application Reports
-
SPRA839 Using IBIS Models for Timing Analysis Application Report. This application report discusses how to properly use IBIS models to attain accurate timing analysis for a given system.
-
SPRAAV0 Understanding TI’s PCB Routing Rule-Based DDR Timing Specification. This application report provides additional guidelines when using the DDR2/mDDR Routing Specifications specified in the data manual.
8.4 Community Resources
The following links connect to TI community resources. Linked contents are provided "AS IS" by the respective contributors. They do not constitute TI specifications and do not necessarily reflect TI's views; see TI's Terms of Use.
-
TI E2E™ Online Community The TI engineer-ro-engineer (E2E) community was created to foster collaboration among engineers. At e2e.ti.com, you can ask questions, share knowledge, explore ideas and help solve problems with fellow engineers.
-
TI Embedded Processors Wiki Established to help developers get started with Embedded Processors from Texas Instruments and to foster innovation and growth of general knowledge about the hardware and software surrounding these devices.
8.5 Trademarks
E2E is a trademark of Texas Instruments.
ARM926EJ-S, ARM9 are registered trademarks of ARM Limited (or its subsidiaries) in the EU and.
ARM, Thumb, Jazelle are registered trademarks of ARM Limited (or its subsidiaries) in the EU and.
All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
8.6 Electrostatic Discharge Caution

This integrated circuit can be damaged by ESD. Texas Instruments recommends that all integrated circuits be handled with appropriate precautions. Failure to observe proper handling and installation procedures can cause damage.
ESD damage can range from subtle performance degradation to complete device failure. Precision integrated circuits may be more susceptible to damage because very small parametric changes could cause the device not to meet its published specifications.
8.7 Glossary
-
TI Glossary This glossary lists and explains terms, acronyms, and definitions.