SPRS945G January 2017 – January 2023 TMS320F280040-Q1 , TMS320F280040C-Q1 , TMS320F280041 , TMS320F280041-Q1 , TMS320F280041C , TMS320F280041C-Q1 , TMS320F280045 , TMS320F280048-Q1 , TMS320F280048C-Q1 , TMS320F280049 , TMS320F280049-Q1 , TMS320F280049C , TMS320F280049C-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings – Commercial
- 7.3 ESD Ratings – Automotive
- 7.4 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.5 Power Consumption Summary
- 7.6 Electrical Characteristics
- 7.7 Thermal Resistance Characteristics
- 7.8 Thermal Design Considerations
- 7.9
System
- 7.9.1
Power Management Module (PMM)
- 7.9.1.1 Introduction
- 7.9.1.2 Overview
- 7.9.1.3 External Components
- 7.9.1.4 Power Sequencing
- 7.9.1.5 Power Management Module Electrical Data and Timing
- 7.9.2 Reset Timing
- 7.9.3
Clock Specifications
- 7.9.3.1 Clock Sources
- 7.9.3.2 Clock Frequencies, Requirements, and Characteristics
- 7.9.3.3 Input Clocks and PLLs
- 7.9.3.4 Crystal (XTAL) Oscillator
- 7.9.3.5 Internal Oscillators
- 7.9.4 Flash Parameters
- 7.9.5 Emulation/JTAG
- 7.9.6 GPIO Electrical Data and Timing
- 7.9.7 Interrupts
- 7.9.8 Low-Power Modes
- 7.9.1
Power Management Module (PMM)
- 7.10 Analog Peripherals
- 7.11
Control Peripherals
- 7.11.1 Enhanced Capture (eCAP)
- 7.11.2 High-Resolution Capture Submodule (HRCAP6–HRCAP7)
- 7.11.3 Enhanced Pulse Width Modulator (ePWM)
- 7.11.4 High-Resolution Pulse Width Modulator (HRPWM)
- 7.11.5 Enhanced Quadrature Encoder Pulse (eQEP)
- 7.11.6 Sigma-Delta Filter Module (SDFM)
- 7.12
Communications Peripherals
- 7.12.1 Controller Area Network (CAN)
- 7.12.2 Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C)
- 7.12.3 Power Management Bus (PMBus) Interface
- 7.12.4 Serial Communications Interface (SCI)
- 7.12.5 Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI)
- 7.12.6 Local Interconnect Network (LIN)
- 7.12.7 Fast Serial Interface (FSI)
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3 Memory
- 8.4 Identification
- 8.5 Bus Architecture – Peripheral Connectivity
- 8.6 C28x Processor
- 8.7 Control Law Accelerator (CLA)
- 8.8 Direct Memory Access (DMA)
- 8.9 Boot ROM and Peripheral Booting
- 8.10 Dual Code Security Module
- 8.11 Watchdog
- 8.12 Configurable Logic Block (CLB)
- 8.13 Functional Safety
- 9 Applications, Implementation, and Layout
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PM|64
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
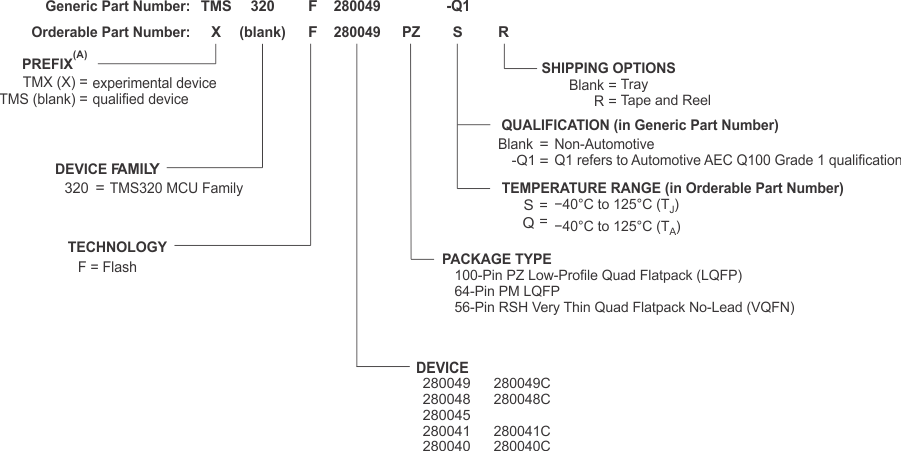
10.1 Device and Development Support Tool Nomenclature
To designate the stages in the product development cycle, TI assigns prefixes to the part numbers of all TMS320 MCU devices and support tools. Each TMS320™ MCU commercial family member has one of three prefixes: TMX, TMP, or TMS (for example, TMS320F280049). Texas Instruments recommends two of three possible prefix designators for its support tools: TMDX and TMDS. These prefixes represent evolutionary stages of product development from engineering prototypes (with TMX for devices and TMDX for tools) through fully qualified production devices and tools (with TMS for devices and TMDS for tools).
Device development evolutionary flow:
-
TMX
Experimental device that is not necessarily representative of the final
device's electrical specifications and may not use production assembly
flow.
-
TMP
Prototype device that is not necessarily the final silicon die and may not
necessarily meet final electrical specifications.
-
TMS
Production version of the silicon die that is fully qualified.
Support tool development evolutionary flow:
-
TMDX
Development-support product that has not yet completed Texas Instruments
internal qualification testing.
-
TMDS
Fully-qualified development-support product.
TMX and TMP devices and TMDX development-support tools are shipped against the following disclaimer:
"Developmental product is intended for internal evaluation purposes."
Production devices and TMDS development-support tools have been characterized fully, and the quality and reliability of the device have been demonstrated fully. TI's standard warranty applies.
Predictions show that prototype devices (X or P) have a greater failure rate than the standard production devices. Texas Instruments recommends that these devices not be used in any production system because their expected end-use failure rate still is undefined. Only qualified production devices are to be used.
TI device nomenclature also includes a suffix with the device family name. This suffix indicates the package type (for example, PZ) and temperature range (for example, S).
For device part numbers and further ordering information, see the TI website (www.ti.com) or contact your TI sales representative.
For additional description of the device nomenclature markings on the die, see the TMS320F28004x Real-Time MCUs Silicon Errata.