SPRS945G January 2017 – January 2023 TMS320F280040-Q1 , TMS320F280040C-Q1 , TMS320F280041 , TMS320F280041-Q1 , TMS320F280041C , TMS320F280041C-Q1 , TMS320F280045 , TMS320F280048-Q1 , TMS320F280048C-Q1 , TMS320F280049 , TMS320F280049-Q1 , TMS320F280049C , TMS320F280049C-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings – Commercial
- 7.3 ESD Ratings – Automotive
- 7.4 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.5 Power Consumption Summary
- 7.6 Electrical Characteristics
- 7.7 Thermal Resistance Characteristics
- 7.8 Thermal Design Considerations
- 7.9
System
- 7.9.1
Power Management Module (PMM)
- 7.9.1.1 Introduction
- 7.9.1.2 Overview
- 7.9.1.3 External Components
- 7.9.1.4 Power Sequencing
- 7.9.1.5 Power Management Module Electrical Data and Timing
- 7.9.2 Reset Timing
- 7.9.3
Clock Specifications
- 7.9.3.1 Clock Sources
- 7.9.3.2 Clock Frequencies, Requirements, and Characteristics
- 7.9.3.3 Input Clocks and PLLs
- 7.9.3.4 Crystal (XTAL) Oscillator
- 7.9.3.5 Internal Oscillators
- 7.9.4 Flash Parameters
- 7.9.5 Emulation/JTAG
- 7.9.6 GPIO Electrical Data and Timing
- 7.9.7 Interrupts
- 7.9.8 Low-Power Modes
- 7.9.1
Power Management Module (PMM)
- 7.10 Analog Peripherals
- 7.11
Control Peripherals
- 7.11.1 Enhanced Capture (eCAP)
- 7.11.2 High-Resolution Capture Submodule (HRCAP6–HRCAP7)
- 7.11.3 Enhanced Pulse Width Modulator (ePWM)
- 7.11.4 High-Resolution Pulse Width Modulator (HRPWM)
- 7.11.5 Enhanced Quadrature Encoder Pulse (eQEP)
- 7.11.6 Sigma-Delta Filter Module (SDFM)
- 7.12
Communications Peripherals
- 7.12.1 Controller Area Network (CAN)
- 7.12.2 Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C)
- 7.12.3 Power Management Bus (PMBus) Interface
- 7.12.4 Serial Communications Interface (SCI)
- 7.12.5 Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI)
- 7.12.6 Local Interconnect Network (LIN)
- 7.12.7 Fast Serial Interface (FSI)
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3 Memory
- 8.4 Identification
- 8.5 Bus Architecture – Peripheral Connectivity
- 8.6 C28x Processor
- 8.7 Control Law Accelerator (CLA)
- 8.8 Direct Memory Access (DMA)
- 8.9 Boot ROM and Peripheral Booting
- 8.10 Dual Code Security Module
- 8.11 Watchdog
- 8.12 Configurable Logic Block (CLB)
- 8.13 Functional Safety
- 9 Applications, Implementation, and Layout
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PZ|100
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- PZ|100
Orderable Information
7.10 Analog Peripherals
The analog subsystem module is described in this section.
The analog modules on this device include the ADC, PGA, temperature sensor, buffered DAC, and CMPSS.
The analog subsystem has the following features:
- Flexible voltage references
- The ADCs are
referenced to VREFHIx and VREFLOx pins.
- VREFHIx pin voltage can be driven in externally or can be generated by an internal bandgap voltage reference.
- The internal voltage reference range can be selected to be 0 V to 3.3 V or 0 V to 2.5 V.
- The ADCs are
referenced to VREFHIx and VREFLOx pins.
- The buffered DACs are
referenced to VREFHIx and VREFLOx.
- Alternately, these DACs can be referenced to the VDAC pin and VSSA.
- The comparator DACs are
referenced to VDDA and VSSA.
- Alternately, these DACs can be referenced to the VDAC pin and VSSA.
- Flexible pin usage
- Buffered DAC outputs, comparator subsystem inputs, PGA functions, and digital inputs are multiplexed with ADC inputs
- Internal connection to VREFLO on all ADCs for offset self-calibration
Figure 7-37 shows the Analog Subsystem Block Diagram for the 100-pin PZ LQFP.
Figure 7-38 shows the Analog Subsystem Block Diagram for the 64-pin PM LQFP.
Figure 7-39 shows the Analog Subsystem Block Diagram for the 56-pin RSH VQFN.
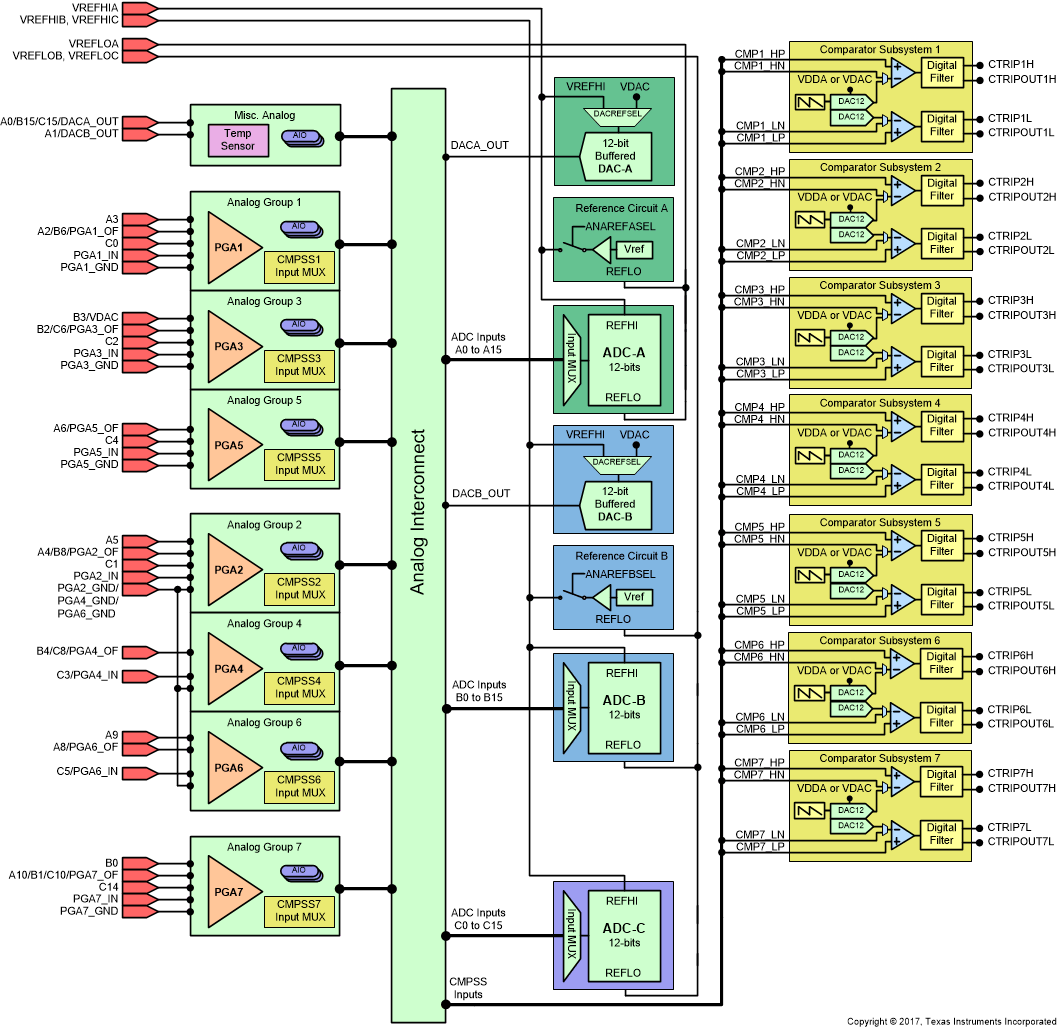 Figure 7-37 Analog
Subsystem Block Diagram (100-Pin PZ LQFP)
Figure 7-37 Analog
Subsystem Block Diagram (100-Pin PZ LQFP)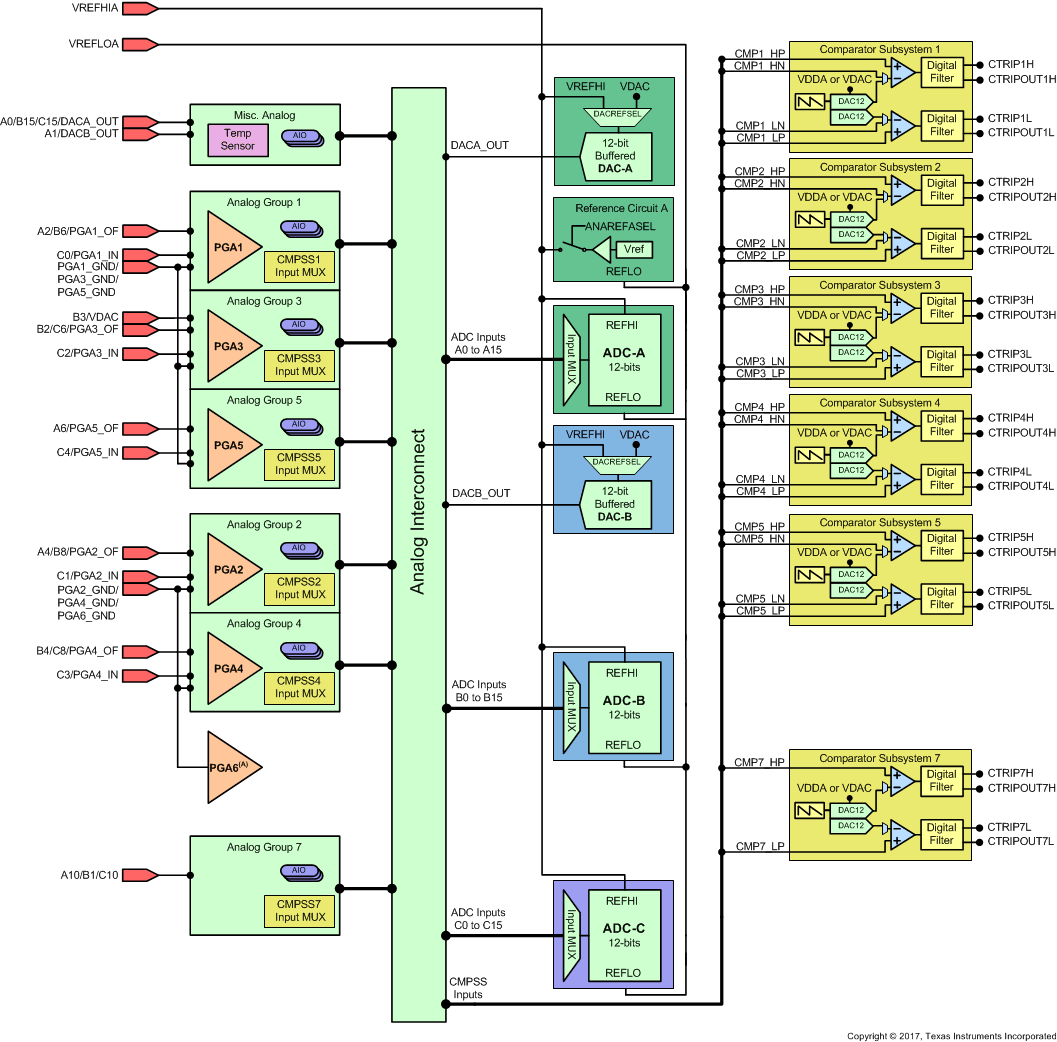
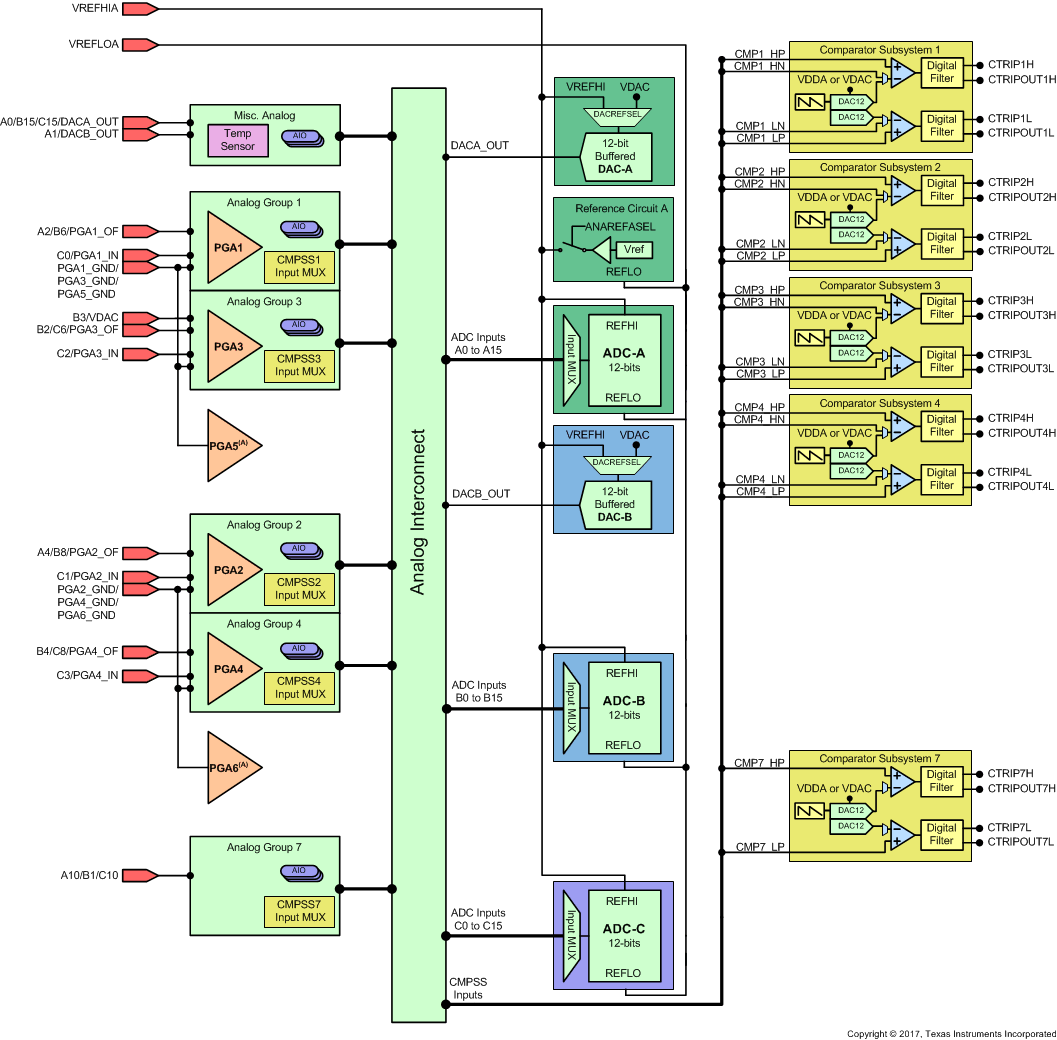
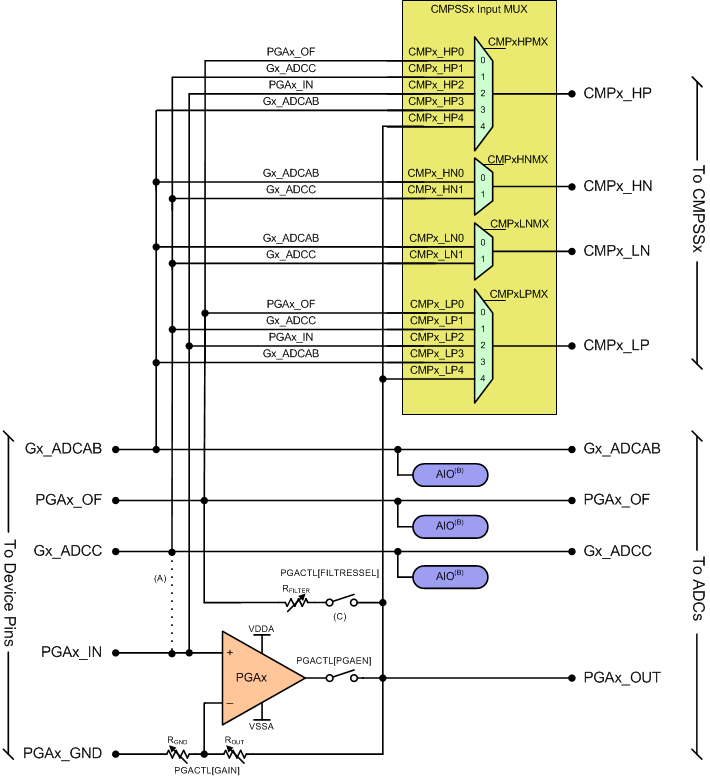
Figure 7-40 shows the analog group connections. See the Analog Pins and Internal Connections table for the specific connections for each group for each package. The Analog Signal Descriptions table provides descriptions of the analog signals.
| PIN NAME | GROUP NAME | PACKAGE | ALWAYS CONNECTED (NO MUX) | COMPARATOR SUBSYSTEM (MUX) | AIO INPUT | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 PZ | 64 PM | 56 RSH | ADCA | ADCB | ADCC | PGA | DAC | HIGH POSITIVE | HIGH NEGATIVE | LOW POSITIVE | LOW NEGATIVE | |||
| VREFHIA | - | 25 | 16 | 14 | ||||||||||
| VREFHIB | - | 24 | ||||||||||||
| VREFHIC | - | |||||||||||||
| VREFLOA | - | 27 | 17 | 15 | A13 | |||||||||
| VREFLOB | - | 26 | B13 | |||||||||||
| VREFLOC | - | C13 | ||||||||||||
| Analog Group 1 | CMP1 | |||||||||||||
| A3 | G1_ADCAB | 10 | A3 | HPMXSEL = 3 | HNMXSEL = 0 | LPMXSEL = 3 | LNMXSEL = 0 | AIO233 | ||||||
| A2/B6/PGA1_OF | PGA1_OF | 9 | 9 | 8 | A2 | B6 | PGA1_OF | HPMXSEL = 0 | LPMXSEL = 0 | AIO224 | ||||
| C0 | G1_ADCC | 19 | 12 | 10 | C0 | HPMXSEL = 1 | HNMXSEL = 1 | LPMXSEL = 1 | LNMXSEL = 1 | AIO237 | ||||
| PGA1_IN | PGA1_IN | 18 | PGA1_IN | HPMXSEL = 2 | LPMXSEL = 2 | |||||||||
| PGA1_GND | PGA1_GND | 14 | 10 | 9 | PGA1_GND | |||||||||
| - | PGA1_OUT(1) | A11 | B7 | PGA1_OUT | HPMXSEL = 4 | LPMXSEL = 4 | ||||||||
| Analog Group 2 | CMP2 | |||||||||||||
| A5 | G2_ADCAB | 35 | A5 | HPMXSEL = 3 | HNMXSEL = 0 | LPMXSEL = 3 | LNMXSEL = 0 | AIO234 | ||||||
| A4/B8/PGA2_OF | PGA2_OF | 36 | 23 | 21 | A4 | B8 | PGA2_OF | HPMXSEL = 0 | LPMXSEL = 0 | AIO225 | ||||
| C1 | G2_ADCC | 29 | 18 | 16 | C1 | HPMXSEL = 1 | HNMXSEL = 1 | LPMXSEL = 1 | LNMXSEL = 1 | AIO238 | ||||
| PGA2_IN | PGA2_IN | 30 | PGA2_IN | HPMXSEL = 2 | LPMXSEL = 2 | |||||||||
| PGA2_GND | PGA2_GND | 32 | 20 | 18 | PGA2_GND | |||||||||
| - | PGA2_OUT(1) | A12 | B9 | PGA2_OUT | HPMXSEL = 4 | LPMXSEL = 4 | ||||||||
| Analog Group 3 | CMP3 | |||||||||||||
| B3/VDAC | G3_ADCAB | 8 | 8 | 7 | B3 | VDAC | HPMXSEL = 3 | HNMXSEL = 0 | LPMXSEL = 3 | LNMXSEL = 0 | AIO242 | |||
| B2/C6/PGA3_OF | PGA3_OF | 7 | 7 | 6 | B2 | C6 | PGA3_OF | HPMXSEL = 0 | LPMXSEL = 0 | AIO226 | ||||
| C2 | G3_ADCC | 21 | 13 | 11 | C2 | HPMXSEL = 1 | HNMXSEL = 1 | LPMXSEL = 1 | LNMXSEL = 1 | AIO244 | ||||
| PGA3_IN | PGA3_IN | 20 | PGA3_IN | HPMXSEL = 2 | LPMXSEL = 2 | |||||||||
| PGA3_GND | PGA3_GND | 15 | 10 | 9 | PGA3_GND | |||||||||
| - | PGA3_OUT(1) | B10 | C7 | PGA3_OUT | HPMXSEL = 4 | LPMXSEL = 4 | ||||||||
| Analog Group 4 | CMP4 | |||||||||||||
| B5 | G4_ADCAB | B5 | HPMXSEL = 3 | HNMXSEL = 0 | LPMXSEL = 3 | LNMXSEL = 0 | AIO243 | |||||||
| B4/C8/PGA4_OF | PGA4_OF | 39 | 24 | 22 | B4 | C8 | PGA4_OF | HPMXSEL = 0 | LPMXSEL = 0 | AIO227 | ||||
| C3 | G4_ADCC | 31 | 19 | 17 | C3 | HPMXSEL = 1 | HNMXSEL = 1 | LPMXSEL = 1 | LNMXSEL = 1 | AIO245 | ||||
| PGA4_IN | PGA4_IN | PGA4_IN | HPMXSEL = 2 | LPMXSEL = 2 | ||||||||||
| PGA4_GND | PGA4_GND | 32 | 20 | 18 | PGA4_GND | |||||||||
| - | PGA4_OUT(1) | B11 | C9 | PGA4_OUT | HPMXSEL = 4 | LPMXSEL = 4 | ||||||||
| Analog Group 5 | CMP5 | |||||||||||||
| A7 | G5_ADCAB | A7 | HPMXSEL = 3 | HNMXSEL = 0 | LPMXSEL = 3 | LNMXSEL = 0 | AIO235 | |||||||
| A6/PGA5_OF | PGA5_OF | 6 | 6 | A6 | PGA5_OF | HPMXSEL = 0 | LPMXSEL = 0 | AIO228 | ||||||
| C4 | G5_ADCC | 17 | 11 | C4 | HPMXSEL = 1 | HNMXSEL = 1 | LPMXSEL = 1 | LNMXSEL = 1 | AIO239 | |||||
| PGA5_IN | PGA5_IN | 16 | PGA5_IN | HPMXSEL = 2 | LPMXSEL = 2 | |||||||||
| PGA5_GND | PGA5_GND | 13 | 10 | 9 | PGA5_GND | |||||||||
| - | PGA5_OUT(1) | A14 | PGA5_OUT | HPMXSEL = 4 | LPMXSEL = 4 | |||||||||
| Analog Group 6 | CMP6 | |||||||||||||
| A9 | G6_ADCAB | 38 | A9 | HPMXSEL = 3 | HNMXSEL = 0 | LPMXSEL = 3 | LNMXSEL = 0 | AIO236 | ||||||
| A8/PGA6_OF | PGA6_OF | 37 | A8 | PGA6_OF | HPMXSEL = 0 | LPMXSEL = 0 | AIO229 | |||||||
| C5 | G6_ADCC | 28 | C5 | HPMXSEL = 1 | HNMXSEL = 1 | LPMXSEL = 1 | LNMXSEL = 1 | AIO240 | ||||||
| PGA6_IN | PGA6_IN | PGA6_IN | HPMXSEL = 2 | LPMXSEL = 2 | ||||||||||
| PGA6_GND | PGA6_GND | 32 | 20 | 18 | PGA6_GND | |||||||||
| - | PGA6_OUT(1) | A15 | PGA6_OUT | HPMXSEL = 4 | LPMXSEL = 4 | |||||||||
| Analog Group 7 | CMP7 | |||||||||||||
| B0 | G7_ADCAB | 41 | B0 | HPMXSEL = 3 | HNMXSEL = 0 | LPMXSEL = 3 | LNMXSEL = 0 | AIO241 | ||||||
| A10/B1/C10/PGA7_OF | PGA7_OF(2) | 40 | 25 | 23 | A10 | B1 | C10 | PGA7_OF | HPMXSEL = 0 | LPMXSEL = 0 | AIO230 | |||
| C14 | G7_ADCC | 44 | C14 | HPMXSEL = 1 | HNMXSEL = 1 | LPMXSEL = 1 | LNMXSEL = 1 | AIO246 | ||||||
| PGA7_IN | PGA7_IN | 43 | PGA7_IN | HPMXSEL = 2 | LPMXSEL = 2 | |||||||||
| PGA7_GND | PGA7_GND | 42 | PGA7_GND | |||||||||||
| - | PGA7_OUT(1) | B12 | C11 | PGA7_OUT | HPMXSEL = 4 | LPMXSEL = 4 | ||||||||
| Other Analog | ||||||||||||||
| A0/B15/C15/DACA_OUT | 23 | 15 | 13 | A0 | B15 | C15 | DACA_OUT | AIO231 | ||||||
| A1/DACB_OUT | 22 | 14 | 12 | A1 | DACB_OUT | AIO232 | ||||||||
| C12 | C12 | AIO247 | ||||||||||||
| - | TempSensor(1) | B14 | ||||||||||||
| SIGNAL NAME | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| AIOx | Digital input on ADC pin |
| Ax | ADC A Input |
| Bx | ADC B Input |
| Cx | ADC C Input |
| CMPx_DACH | Comparator subsystem high DAC output |
| CMPx_DACL | Comparator subsystem low DAC output |
| CMPx_HNy | Comparator subsystem high comparator negative input |
| CMPx_HPy | Comparator subsystem high comparator positive input |
| CMPx_LNy | Comparator subsystem low comparator negative input |
| CMPx_LPy | Comparator subsystem low comparator positive input |
| DACx_OUT | Buffered DAC Output |
| PGAx_GND | PGA Ground |
| PGAx_IN | PGA Input |
| PGAx_OF | PGA Output for filter |
| PGAx_OUT | PGA Output to internal ADC |
| TempSensor | Internal temperature sensor |
| VDAC | Optional external reference voltage for on-chip DACs. There is a 100-pF capacitor to VSSA on this pin whether used for ADC input or DAC reference which cannot be disabled. If this pin is used as a reference for the on-chip DACs, place at least a 1-µF capacitor on this pin. |