SPRS945G January 2017 – January 2023 TMS320F280040-Q1 , TMS320F280040C-Q1 , TMS320F280041 , TMS320F280041-Q1 , TMS320F280041C , TMS320F280041C-Q1 , TMS320F280045 , TMS320F280048-Q1 , TMS320F280048C-Q1 , TMS320F280049 , TMS320F280049-Q1 , TMS320F280049C , TMS320F280049C-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings – Commercial
- 7.3 ESD Ratings – Automotive
- 7.4 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.5 Power Consumption Summary
- 7.6 Electrical Characteristics
- 7.7 Thermal Resistance Characteristics
- 7.8 Thermal Design Considerations
- 7.9
System
- 7.9.1
Power Management Module (PMM)
- 7.9.1.1 Introduction
- 7.9.1.2 Overview
- 7.9.1.3 External Components
- 7.9.1.4 Power Sequencing
- 7.9.1.5 Power Management Module Electrical Data and Timing
- 7.9.2 Reset Timing
- 7.9.3
Clock Specifications
- 7.9.3.1 Clock Sources
- 7.9.3.2 Clock Frequencies, Requirements, and Characteristics
- 7.9.3.3 Input Clocks and PLLs
- 7.9.3.4 Crystal (XTAL) Oscillator
- 7.9.3.5 Internal Oscillators
- 7.9.4 Flash Parameters
- 7.9.5 Emulation/JTAG
- 7.9.6 GPIO Electrical Data and Timing
- 7.9.7 Interrupts
- 7.9.8 Low-Power Modes
- 7.9.1
Power Management Module (PMM)
- 7.10 Analog Peripherals
- 7.11
Control Peripherals
- 7.11.1 Enhanced Capture (eCAP)
- 7.11.2 High-Resolution Capture Submodule (HRCAP6–HRCAP7)
- 7.11.3 Enhanced Pulse Width Modulator (ePWM)
- 7.11.4 High-Resolution Pulse Width Modulator (HRPWM)
- 7.11.5 Enhanced Quadrature Encoder Pulse (eQEP)
- 7.11.6 Sigma-Delta Filter Module (SDFM)
- 7.12
Communications Peripherals
- 7.12.1 Controller Area Network (CAN)
- 7.12.2 Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C)
- 7.12.3 Power Management Bus (PMBus) Interface
- 7.12.4 Serial Communications Interface (SCI)
- 7.12.5 Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI)
- 7.12.6 Local Interconnect Network (LIN)
- 7.12.7 Fast Serial Interface (FSI)
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3 Memory
- 8.4 Identification
- 8.5 Bus Architecture – Peripheral Connectivity
- 8.6 C28x Processor
- 8.7 Control Law Accelerator (CLA)
- 8.8 Direct Memory Access (DMA)
- 8.9 Boot ROM and Peripheral Booting
- 8.10 Dual Code Security Module
- 8.11 Watchdog
- 8.12 Configurable Logic Block (CLB)
- 8.13 Functional Safety
- 9 Applications, Implementation, and Layout
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.9.6.3 Sampling Window Width for Input Signals
The following section summarizes the sampling window width for input signals for various input qualifier configurations.
Sampling frequency denotes how often a signal is sampled with respect to SYSCLK.
Sampling frequency = SYSCLK/(2 × QUALPRD), if QUALPRD ≠ 0
Sampling frequency = SYSCLK, if QUALPRD = 0
Sampling period = SYSCLK cycle × 2 × QUALPRD, if QUALPRD ≠ 0
In the previous equations, SYSCLK cycle indicates the time period of SYSCLK.
Sampling period = SYSCLK cycle, if QUALPRD = 0
In a given sampling window, either 3 or 6 samples of the input signal are taken to determine the validity of the signal. This is determined by the value written to GPxQSELn register.
Case 1:
Qualification using 3 samples
Sampling window width = (SYSCLK cycle × 2 × QUALPRD) × 2, if QUALPRD ≠ 0
Sampling window width = (SYSCLK cycle) × 2, if QUALPRD = 0
Case 2:
Qualification using 6 samples
Sampling window width = (SYSCLK cycle × 2 × QUALPRD) × 5, if QUALPRD ≠ 0
Sampling window width = (SYSCLK cycle) × 5, if QUALPRD = 0
Figure 7-32 shows the general-purpose input timing.
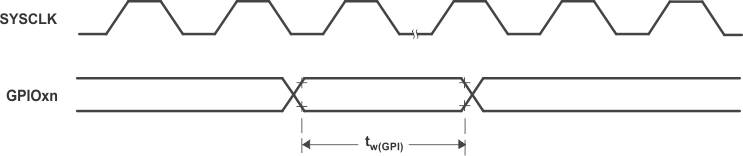 Figure 7-32 General-Purpose Input Timing
Figure 7-32 General-Purpose Input Timing