SPRSP25A June 2018 – July 2018 TMS320F28035-EP
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1Device Overview
- 2Revision History
- 3Terminal Configuration and Functions
-
4Specifications
- 4.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 4.2 ESD Ratings
- 4.3 Power-On Hours (POH) Limits
- 4.4 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 4.5 Power Consumption Summary
- 4.6 Electrical Characteristics
- 4.7 Thermal Resistance Characteristics
- 4.8 Thermal Design Considerations
- 4.9 Emulator Connection Without Signal Buffering for the MCU
- 4.10 Parameter Information
- 4.11 Test Load Circuit
- 4.12 Power Sequencing
- 4.13 Clock Specifications
- 4.14 Flash Timing
-
5Detailed Description
- 5.1
Overview
- 5.1.1 CPU
- 5.1.2 Control Law Accelerator (CLA)
- 5.1.3 Memory Bus (Harvard Bus Architecture)
- 5.1.4 Peripheral Bus
- 5.1.5 Real-Time JTAG and Analysis
- 5.1.6 Flash
- 5.1.7 M0, M1 SARAMs
- 5.1.8 L0 SARAM, and L1, L2, and L3 DPSARAMs
- 5.1.9 Boot ROM
- 5.1.10 Security
- 5.1.11 Peripheral Interrupt Expansion (PIE) Block
- 5.1.12 External Interrupts (XINT1–XINT3)
- 5.1.13 Internal Zero Pin Oscillators, Oscillator, and PLL
- 5.1.14 Watchdog
- 5.1.15 Peripheral Clocking
- 5.1.16 Low-power Modes
- 5.1.17 Peripheral Frames 0, 1, 2, 3 (PFn)
- 5.1.18 General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO) Multiplexer
- 5.1.19 32-Bit CPU-Timers (0, 1, 2)
- 5.1.20 Control Peripherals
- 5.1.21 Serial Port Peripherals
- 5.2 Memory Maps
- 5.3 Register Maps
- 5.4 Device Emulation Registers
- 5.5 VREG/BOR/POR
- 5.6 System Control
- 5.7 Low-Power Modes Block
- 5.8 Interrupts
- 5.9
Peripherals
- 5.9.1 Control Law Accelerator (CLA) Overview
- 5.9.2 Analog Block
- 5.9.3 Detailed Descriptions
- 5.9.4 Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) Module
- 5.9.5 Serial Communications Interface (SCI) Module
- 5.9.6 Local Interconnect Network (LIN)
- 5.9.7 Enhanced Controller Area Network (eCAN) Module
- 5.9.8 Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C)
- 5.9.9 Enhanced PWM Modules (ePWM1/2/3/4/5/6/7)
- 5.9.10 High-Resolution PWM (HRPWM)
- 5.9.11 Enhanced Capture Module (eCAP1)
- 5.9.12 High-Resolution Capture (HRCAP) Module
- 5.9.13 Enhanced Quadrature Encoder Pulse (eQEP)
- 5.9.14 JTAG Port
- 5.9.15 General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO) MUX
- 5.1
Overview
- 6Applications, Implementation, and Layout
- 7Device and Documentation Support
- 8Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PN|80
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
5.9.1 Control Law Accelerator (CLA) Overview
The control law accelerator extends the capabilities of the C28x CPU by adding parallel processing. Time-critical control loops serviced by the CLA can achieve low ADC sample to output delay. Thus, the CLA enables faster system response and higher frequency control loops. Utilizing the CLA for time-critical tasks frees up the main CPU to perform other system and communication functions concurently. The following is a list of major features of the CLA.
- Clocked at the same rate as the main CPU (SYSCLKOUT).
- An independent architecture allowing CLA algorithm execution independent of the main C28x CPU.
- Complete bus architecture:
- Program address bus and program data bus
- Data address bus, data read bus, and data write bus
- Independent eight-stage pipeline.
- 12-bit program counter (MPC)
- Four 32-bit result registers (MR0–MR3)
- Two 16-bit auxillary registers (MAR0, MAR1)
- Status register (MSTF)
- Complete bus architecture:
- Instruction set includes:
- IEEE single-precision (32-bit) floating-point math operations
- Floating-point math with parallel load or store
- Floating-point multiply with parallel add or subtract
- 1/X and 1/sqrt(X) estimations
- Data type conversions.
- Conditional branch and call
- Data load/store operations
- The CLA program code can consist of up to eight tasks or interrupt service routines.
- The start address of each task is specified by the MVECT registers.
- No limit on task size as long as the tasks fit within the CLA program memory space.
- One task is serviced at a time through to completion. There is no nesting of tasks.
- Upon task completion, a task-specific interrupt is flagged within the PIE.
- When a task finishes, the next highest-priority pending task is automatically started.
- Task trigger mechanisms:
- C28x CPU through the IACK instruction
- Task1 to Task7: the corresponding ADC or ePWM module interrupt. For example:
- Task1: ADCINT1 or EPWM1_INT
- Task2: ADCINT2 or EPWM2_INT
- Task7: ADCINT7 or EPWM7_INT
- Task8: ADCINT8 or by CPU Timer 0.
- Memory and Shared Peripherals:
- Two dedicated message RAMs for communication between the CLA and the main CPU.
- The C28x CPU can map CLA program and data memory to the main CPU space or CLA space.
- The CLA has direct access to the ADC Result registers, comparator registers, and the ePWM+HRPWM registers.
For more information on the CLA, see the TMS320x2803x Piccolo Control Law Accelerator (CLA) Reference Guide.
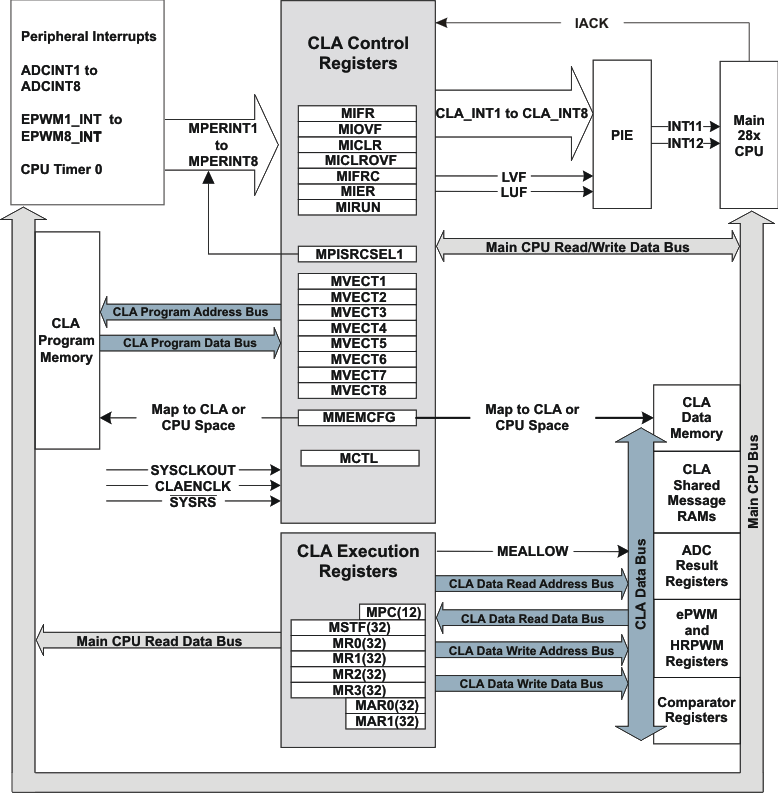 Figure 5-12 CLA Block Diagram
Figure 5-12 CLA Block Diagram Table 5-22 CLA Control Registers
| REGISTER NAME | CLA1
ADDRESS |
SIZE (x16) | EALLOW
PROTECTED |
DESCRIPTION(1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MVECT1 | 0x1400 | 1 | Yes | CLA Interrupt/Task 1 Start Address |
| MVECT2 | 0x1401 | 1 | Yes | CLA Interrupt/Task 2 Start Address |
| MVECT3 | 0x1402 | 1 | Yes | CLA Interrupt/Task 3 Start Address |
| MVECT4 | 0x1403 | 1 | Yes | CLA Interrupt/Task 4 Start Address |
| MVECT5 | 0x1404 | 1 | Yes | CLA Interrupt/Task 5 Start Address |
| MVECT6 | 0x1405 | 1 | Yes | CLA Interrupt/Task 6 Start Address |
| MVECT7 | 0x1406 | 1 | Yes | CLA Interrupt/Task 7 Start Address |
| MVECT8 | 0x1407 | 1 | Yes | CLA Interrupt/Task 8 Start Address |
| MCTL | 0x1410 | 1 | Yes | CLA Control Register |
| MMEMCFG | 0x1411 | 1 | Yes | CLA Memory Configure Register |
| MPISRCSEL1 | 0x1414 | 2 | Yes | Peripheral Interrupt Source Select Register 1 |
| MIFR | 0x1420 | 1 | Yes | Interrupt Flag Register |
| MIOVF | 0x1421 | 1 | Yes | Interrupt Overflow Register |
| MIFRC | 0x1422 | 1 | Yes | Interrupt Force Register |
| MICLR | 0x1423 | 1 | Yes | Interrupt Clear Register |
| MICLROVF | 0x1424 | 1 | Yes | Interrupt Overflow Clear Register |
| MIER | 0x1425 | 1 | Yes | Interrupt Enable Register |
| MIRUN | 0x1426 | 1 | Yes | Interrupt RUN Register |
| MIPCTL | 0x1427 | 1 | Yes | Interrupt Priority Control Register |
| MPC(2) | 0x1428 | 1 | – | CLA Program Counter |
| MAR0(2) | 0x142A | 1 | – | CLA Aux Register 0 |
| MAR1(2) | 0x142B | 1 | – | CLA Aux Register 1 |
| MSTF(2) | 0x142E | 2 | – | CLA STF Register |
| MR0(2) | 0x1430 | 2 | – | CLA R0H Register |
| MR1(2) | 0x1434 | 2 | – | CLA R1H Register |
| MR2(2) | 0x1438 | 2 | – | CLA R2H Register |
| MR3(2) | 0x143C | 2 | – | CLA R3H Register |
(1) All registers in this table are CSM protected
(2) The main C28x CPU has read only access to this register for debug purposes. The main CPU cannot perform CPU or debugger writes to this register.
Table 5-23 CLA Message RAM
| ADDRESS RANGE | SIZE (x16) | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|
| 0x1480 – 0x14FF | 128 | CLA to CPU Message RAM |
| 0x1500 – 0x157F | 128 | CPU to CLA Message RAM |