SPRSP25A June 2018 – July 2018 TMS320F28035-EP
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1Device Overview
- 2Revision History
- 3Terminal Configuration and Functions
-
4Specifications
- 4.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 4.2 ESD Ratings
- 4.3 Power-On Hours (POH) Limits
- 4.4 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 4.5 Power Consumption Summary
- 4.6 Electrical Characteristics
- 4.7 Thermal Resistance Characteristics
- 4.8 Thermal Design Considerations
- 4.9 Emulator Connection Without Signal Buffering for the MCU
- 4.10 Parameter Information
- 4.11 Test Load Circuit
- 4.12 Power Sequencing
- 4.13 Clock Specifications
- 4.14 Flash Timing
-
5Detailed Description
- 5.1
Overview
- 5.1.1 CPU
- 5.1.2 Control Law Accelerator (CLA)
- 5.1.3 Memory Bus (Harvard Bus Architecture)
- 5.1.4 Peripheral Bus
- 5.1.5 Real-Time JTAG and Analysis
- 5.1.6 Flash
- 5.1.7 M0, M1 SARAMs
- 5.1.8 L0 SARAM, and L1, L2, and L3 DPSARAMs
- 5.1.9 Boot ROM
- 5.1.10 Security
- 5.1.11 Peripheral Interrupt Expansion (PIE) Block
- 5.1.12 External Interrupts (XINT1–XINT3)
- 5.1.13 Internal Zero Pin Oscillators, Oscillator, and PLL
- 5.1.14 Watchdog
- 5.1.15 Peripheral Clocking
- 5.1.16 Low-power Modes
- 5.1.17 Peripheral Frames 0, 1, 2, 3 (PFn)
- 5.1.18 General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO) Multiplexer
- 5.1.19 32-Bit CPU-Timers (0, 1, 2)
- 5.1.20 Control Peripherals
- 5.1.21 Serial Port Peripherals
- 5.2 Memory Maps
- 5.3 Register Maps
- 5.4 Device Emulation Registers
- 5.5 VREG/BOR/POR
- 5.6 System Control
- 5.7 Low-Power Modes Block
- 5.8 Interrupts
- 5.9
Peripherals
- 5.9.1 Control Law Accelerator (CLA) Overview
- 5.9.2 Analog Block
- 5.9.3 Detailed Descriptions
- 5.9.4 Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) Module
- 5.9.5 Serial Communications Interface (SCI) Module
- 5.9.6 Local Interconnect Network (LIN)
- 5.9.7 Enhanced Controller Area Network (eCAN) Module
- 5.9.8 Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C)
- 5.9.9 Enhanced PWM Modules (ePWM1/2/3/4/5/6/7)
- 5.9.10 High-Resolution PWM (HRPWM)
- 5.9.11 Enhanced Capture Module (eCAP1)
- 5.9.12 High-Resolution Capture (HRCAP) Module
- 5.9.13 Enhanced Quadrature Encoder Pulse (eQEP)
- 5.9.14 JTAG Port
- 5.9.15 General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO) MUX
- 5.1
Overview
- 6Applications, Implementation, and Layout
- 7Device and Documentation Support
- 8Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PN|80
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
Table 5-70 HALT Mode Switching Characteristics
over recommended operating conditions (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | MIN | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| td(IDLE-XCOL) | Delay time, IDLE instruction executed to XCLKOUT low | 32tc(SCO) | 45tc(SCO) | cycles |
| tp | PLL lock-up time | 1 | ms | |
| td(WAKE-HALT) | Delay time, PLL lock to program execution resume
|
1125tc(SCO) | cycles | |
|
35tc(SCO) | cycles | ||
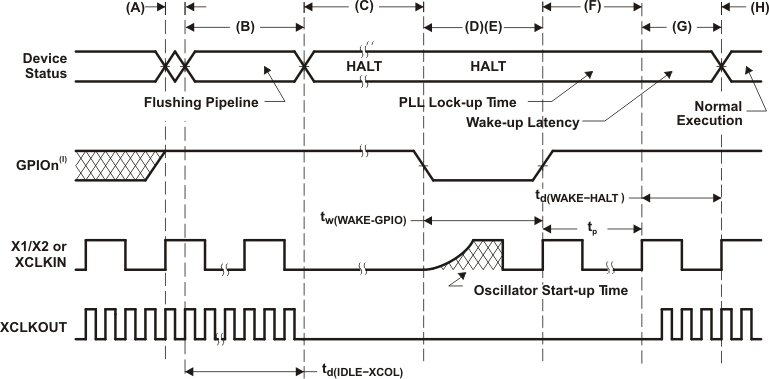
A. IDLE instruction is executed to put the device into HALT mode.
B. The PLL block responds to the HALT signal. SYSCLKOUT is held for the number of cycles indicated below before oscillator is turned off and the CLKIN to the core is stopped:
- 16 cycles, when DIVSEL = 00 or 01
- 32 cycles, when DIVSEL = 10
- 64 cycles, when DIVSEL = 11
C. Clocks to the peripherals are turned off and the PLL is shut down. If a quartz crystal or ceramic resonator is used as the clock source, the internal oscillator is shut down as well. The device is now in HALT mode and consumes absolute minimum power. It is possible to keep the zero-pin internal oscillators (INTOSC1 and INTOSC2) and the watchdog alive in HALT mode. This is done by writing to the appropriate bits in the CLKCTL register. After the IDLE instruction is executed, a delay of 5 OSCCLK cycles (minimum) is needed before the wake-up signal could be asserted.
D. When the GPIOn pin (used to bring the device out of HALT) is driven low, the oscillator is turned on and the oscillator wake-up sequence is initiated. The GPIO pin should be driven high only after the oscillator has stabilized. This enables the provision of a clean clock signal during the PLL lock sequence. Because the falling edge of the GPIO pin asynchronously begins the wake-up procedure, care should be taken to maintain a low noise environment prior to entering and during HALT mode.
E. The wake-up signal fed to a GPIO pin to wake up the device must meet the minimum pulse width requirement. Furthermore, this signal must be free of glitches. If a noisy signal is fed to a GPIO pin, the wake-up behavior of the device will not be deterministic and the device may not exit low-power mode for subsequent wake-up pulses.
F. Once the oscillator has stabilized, the PLL lock sequence is initiated, which takes 1 ms.
G. When CLKIN to the core is enabled, the device will respond to the interrupt (if enabled), after a latency. The HALT mode is now exited.
H. Normal operation resumes.
I. From the time the IDLE instruction is executed to place the device into low-power mode (LPM), wakeup should not be initiated until at least 4 OSCCLK cycles have elapsed.
Figure 5-49 HALT Mode Wakeup Using GPIOn