SPRSP25A June 2018 – July 2018 TMS320F28035-EP
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1Device Overview
- 2Revision History
- 3Terminal Configuration and Functions
-
4Specifications
- 4.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 4.2 ESD Ratings
- 4.3 Power-On Hours (POH) Limits
- 4.4 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 4.5 Power Consumption Summary
- 4.6 Electrical Characteristics
- 4.7 Thermal Resistance Characteristics
- 4.8 Thermal Design Considerations
- 4.9 Emulator Connection Without Signal Buffering for the MCU
- 4.10 Parameter Information
- 4.11 Test Load Circuit
- 4.12 Power Sequencing
- 4.13 Clock Specifications
- 4.14 Flash Timing
-
5Detailed Description
- 5.1
Overview
- 5.1.1 CPU
- 5.1.2 Control Law Accelerator (CLA)
- 5.1.3 Memory Bus (Harvard Bus Architecture)
- 5.1.4 Peripheral Bus
- 5.1.5 Real-Time JTAG and Analysis
- 5.1.6 Flash
- 5.1.7 M0, M1 SARAMs
- 5.1.8 L0 SARAM, and L1, L2, and L3 DPSARAMs
- 5.1.9 Boot ROM
- 5.1.10 Security
- 5.1.11 Peripheral Interrupt Expansion (PIE) Block
- 5.1.12 External Interrupts (XINT1–XINT3)
- 5.1.13 Internal Zero Pin Oscillators, Oscillator, and PLL
- 5.1.14 Watchdog
- 5.1.15 Peripheral Clocking
- 5.1.16 Low-power Modes
- 5.1.17 Peripheral Frames 0, 1, 2, 3 (PFn)
- 5.1.18 General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO) Multiplexer
- 5.1.19 32-Bit CPU-Timers (0, 1, 2)
- 5.1.20 Control Peripherals
- 5.1.21 Serial Port Peripherals
- 5.2 Memory Maps
- 5.3 Register Maps
- 5.4 Device Emulation Registers
- 5.5 VREG/BOR/POR
- 5.6 System Control
- 5.7 Low-Power Modes Block
- 5.8 Interrupts
- 5.9
Peripherals
- 5.9.1 Control Law Accelerator (CLA) Overview
- 5.9.2 Analog Block
- 5.9.3 Detailed Descriptions
- 5.9.4 Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) Module
- 5.9.5 Serial Communications Interface (SCI) Module
- 5.9.6 Local Interconnect Network (LIN)
- 5.9.7 Enhanced Controller Area Network (eCAN) Module
- 5.9.8 Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C)
- 5.9.9 Enhanced PWM Modules (ePWM1/2/3/4/5/6/7)
- 5.9.10 High-Resolution PWM (HRPWM)
- 5.9.11 Enhanced Capture Module (eCAP1)
- 5.9.12 High-Resolution Capture (HRCAP) Module
- 5.9.13 Enhanced Quadrature Encoder Pulse (eQEP)
- 5.9.14 JTAG Port
- 5.9.15 General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO) MUX
- 5.1
Overview
- 6Applications, Implementation, and Layout
- 7Device and Documentation Support
- 8Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PN|80
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
5.9.8 Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C)
The device contains one I2C Serial Port. Figure 5-34 shows how the I2C peripheral module interfaces within the device.
The I2C module has the following features:
- Compliance with the Philips Semiconductors I2C-bus specification (version 2.1):
- Support for 1-bit to 8-bit format transfers
- 7-bit and 10-bit addressing modes
- General call
- START byte mode
- Support for multiple master-transmitters and slave-receivers
- Support for multiple slave-transmitters and master-receivers
- Combined master transmit/receive and receive/transmit mode
- Data transfer rate of from 10 kbps up to 400 kbps (I2C Fast-mode rate)
- One 4-word receive FIFO and one 4-word transmit FIFO
- One interrupt that can be used by the CPU. This interrupt can be generated as a result of one of the following conditions:
- Transmit-data ready
- Receive-data ready
- Register-access ready
- No-acknowledgment received
- Arbitration lost
- Stop condition detected
- Addressed as slave
- An additional interrupt that can be used by the CPU when in FIFO mode
- Module enable/disable capability
- Free data format mode
For more information on the I2C, see the TMS320x2802x, 2803x Piccolo Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C) Module Reference Guide.
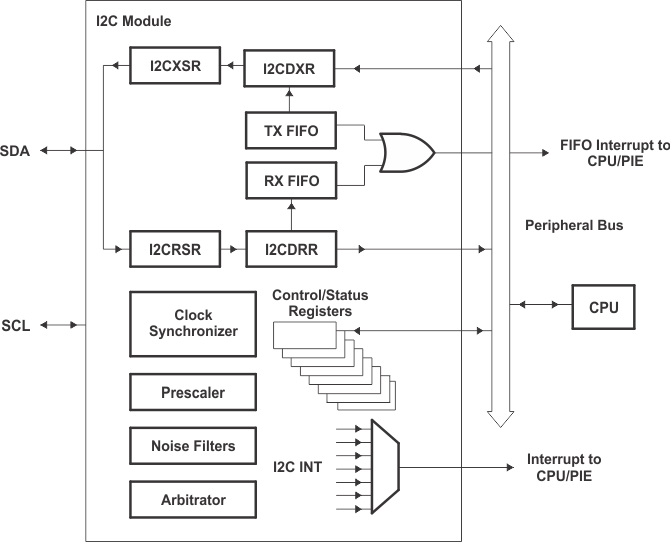
A. The I2C registers are accessed at the SYSCLKOUT rate. The internal timing and signal waveforms of the I2C port are also at the SYSCLKOUT rate.
B. The clock enable bit (I2CAENCLK) in the PCLKCRO register turns off the clock to the I2C port for low-power operation. Upon reset, I2CAENCLK is clear, which indicates the peripheral internal clocks are off.
Figure 5-34 I2C Peripheral Module Interfaces The registers in Table 5-43 configure and control the I2C port operation.
Table 5-43 I2C-A Registers
| NAME | ADDRESS | EALLOW PROTECTED | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|---|
| I2COAR | 0x7900 | No | I2C own address register |
| I2CIER | 0x7901 | No | I2C interrupt enable register |
| I2CSTR | 0x7902 | No | I2C status register |
| I2CCLKL | 0x7903 | No | I2C clock low-time divider register |
| I2CCLKH | 0x7904 | No | I2C clock high-time divider register |
| I2CCNT | 0x7905 | No | I2C data count register |
| I2CDRR | 0x7906 | No | I2C data receive register |
| I2CSAR | 0x7907 | No | I2C slave address register |
| I2CDXR | 0x7908 | No | I2C data transmit register |
| I2CMDR | 0x7909 | No | I2C mode register |
| I2CISRC | 0x790A | No | I2C interrupt source register |
| I2CPSC | 0x790C | No | I2C prescaler register |
| I2CFFTX | 0x7920 | No | I2C FIFO transmit register |
| I2CFFRX | 0x7921 | No | I2C FIFO receive register |
| I2CRSR | – | No | I2C receive shift register (not accessible to the CPU) |
| I2CXSR | – | No | I2C transmit shift register (not accessible to the CPU) |