SPRS357D August 2006 – June 2020 TMS320F28044
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1Device Overview
- 2Revision History
- 3Device Comparison
- 4Terminal Configuration and Functions
-
5Specifications
- 5.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 5.2 ESD Ratings – Commercial
- 5.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 5.4 Power Consumption Summary
- 5.5 Electrical Characteristics
- 5.6 Thermal Resistance Characteristics for F28044 100-Ball GGM Package
- 5.7 Thermal Resistance Characteristics for F28044 100-Pin PZ Package
- 5.8 Thermal Design Considerations
- 5.9
Timing and Switching Characteristics
- 5.9.1 Timing Parameter Symbology
- 5.9.2 Power Sequencing
- 5.9.3 Clock Requirements and Characteristics
- 5.9.4
Peripherals
- 5.9.4.1 General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO)
- 5.9.4.2 Enhanced Control Peripherals
- 5.9.4.3 External Interrupt Timing
- 5.9.4.4 I2C Electrical Specification and Timing
- 5.9.4.5 Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) Master Mode Timing
- 5.9.4.6 SPI Slave Mode Timing
- 5.9.5 JTAG Debug Probe Connection Without Signal Buffering for the DSP
- 5.9.6 Flash Timing
- 5.10 On-Chip Analog-to-Digital Converter
-
6Detailed Description
- 6.1
Brief Descriptions
- 6.1.1 C28x CPU
- 6.1.2 Memory Bus (Harvard Bus Architecture)
- 6.1.3 Peripheral Bus
- 6.1.4 Real-Time JTAG and Analysis
- 6.1.5 Flash
- 6.1.6 M0, M1 SARAMs
- 6.1.7 L0, L1 SARAMs
- 6.1.8 Boot ROM
- 6.1.9 Security
- 6.1.10 Peripheral Interrupt Expansion (PIE) Block
- 6.1.11 External Interrupts (XINT1, XINT2, XNMI)
- 6.1.12 Oscillator and PLL
- 6.1.13 Watchdog
- 6.1.14 Peripheral Clocking
- 6.1.15 Low-Power Modes
- 6.1.16 Peripheral Frames 0, 1, 2 (PFn)
- 6.1.17 General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO) Multiplexer
- 6.1.18 32-Bit CPU-Timers (0, 1, 2)
- 6.1.19 Control Peripherals
- 6.1.20 Serial Port Peripherals
- 6.2
Peripherals
- 6.2.1 32-Bit CPU-Timers 0/1/2
- 6.2.2 Enhanced PWM Modules (ePWM1–16)
- 6.2.3 Hi-Resolution PWM (HRPWM)
- 6.2.4 Enhanced Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) Module
- 6.2.5 Serial Communications Interface (SCI) Module (SCI-A)
- 6.2.6 Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) Module (SPI-A)
- 6.2.7 Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C)
- 6.2.8 GPIO MUX
- 6.3 Memory Map
- 6.4 Register Map
- 6.5 Interrupts
- 6.6 System Control
- 6.7 Low-Power Modes Block
- 6.1
Brief Descriptions
- 7Applications, Implementation, and Layout
- 8Device and Documentation Support
- 9Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PZ|100
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- PZ|100
Orderable Information
6.2.6 Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) Module (SPI-A)
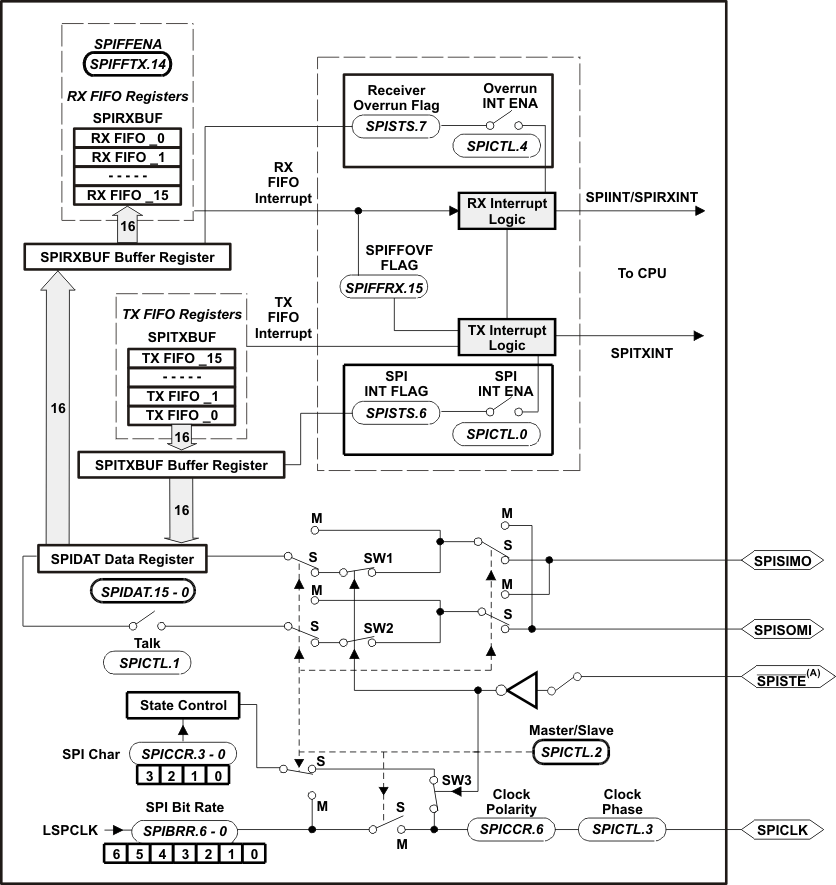
The F28044 device includes the four-pin serial peripheral interface (SPI) module. The SPI is a high-speed, synchronous serial I/O port that allows a serial bit stream of programmed length (one to sixteen bits) to be shifted into and out of the device at a programmable bit-transfer rate. Normally, the SPI is used for communications between the DSP controller and external peripherals or another processor. Typical applications include external I/O or peripheral expansion through devices such as shift registers, display drivers, and ADCs. Multidevice communications are supported by the master/slave operation of the SPI.
The SPI module features include:
- Four external pins:
- SPISOMI: SPI slave-output/master-input pin
- SPISIMO: SPI slave-input/master-output pin
- SPISTE: SPI slave transmit-enable pin
- SPICLK: SPI serial-clock pin
NOTE: All four pins can be used as GPIO, if the SPI module is not used.
- Two operational modes: master and slave
- Data word length: one to sixteen data bits
- Four clocking schemes (controlled by clock polarity and clock phase bits) include:
- Falling edge without phase delay: SPICLK active-high. SPI transmits data on the falling edge of the SPICLK signal and receives data on the rising edge of the SPICLK signal.
- Falling edge with phase delay: SPICLK active-high. SPI transmits data one half-cycle ahead of the falling edge of the SPICLK signal and receives data on the falling edge of the SPICLK signal.
- Rising edge without phase delay: SPICLK inactive-low. SPI transmits data on the rising edge of the SPICLK signal and receives data on the falling edge of the SPICLK signal.
- Rising edge with phase delay: SPICLK inactive-low. SPI transmits data one half-cycle ahead of the rising edge of the SPICLK signal and receives data on the rising edge of the SPICLK signal.
- Simultaneous receive and transmit operation (transmit function can be disabled in software)
- Transmitter and receiver operations are accomplished through either interrupt-driven or polled algorithms.
- Nine SPI module control registers: Located in control register frame beginning at address 7040h.
Baud rate: 125 different programmable rates.
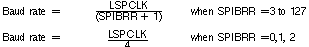
NOTE
All registers in this module are 16-bit registers that are connected to Peripheral Frame 2. When a register is accessed, the register data is in the lower byte (7–0), and the upper byte (15–8) is read as zeros. Writing to the upper byte has no effect.
Enhanced feature:
- 16-level transmit/receive FIFO
- Delayed transmit control
The SPI port operation is configured and controlled by the registers listed in Table 6-9.
Table 6-9 SPI-A Registers
| NAME | ADDRESS | SIZE (x16) | DESCRIPTION(1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SPICCR | 0x7040 | 1 | SPI-A Configuration Control Register |
| SPICTL | 0x7041 | 1 | SPI-A Operation Control Register |
| SPISTS | 0x7042 | 1 | SPI-A Status Register |
| SPIBRR | 0x7044 | 1 | SPI-A Baud Rate Register |
| SPIRXEMU | 0x7046 | 1 | SPI-A Receive Emulation Buffer Register |
| SPIRXBUF | 0x7047 | 1 | SPI-A Serial Input Buffer Register |
| SPITXBUF | 0x7048 | 1 | SPI-A Serial Output Buffer Register |
| SPIDAT | 0x7049 | 1 | SPI-A Serial Data Register |
| SPIFFTX | 0x704A | 1 | SPI-A FIFO Transmit Register |
| SPIFFRX | 0x704B | 1 | SPI-A FIFO Receive Register |
| SPIFFCT | 0x704C | 1 | SPI-A FIFO Control Register |
| SPIPRI | 0x704F | 1 | SPI-A Priority Control Register |
Figure 6-9 is a block diagram of the SPI in slave mode.