SPRS439Q June 2007 – August 2022 TMS320F28232 , TMS320F28232-Q1 , TMS320F28234 , TMS320F28234-Q1 , TMS320F28235 , TMS320F28235-Q1 , TMS320F28332 , TMS320F28333 , TMS320F28334 , TMS320F28335 , TMS320F28335-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison
- 6 Terminal Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings – Automotive
- 7.3 ESD Ratings – Commercial
- 7.4 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.5 Power Consumption Summary
- 7.6 Electrical Characteristics
- 7.7 Thermal Resistance Characteristics
- 7.8 Thermal Design Considerations
- 7.9
Timing and Switching Characteristics
- 7.9.1 Timing Parameter Symbology
- 7.9.2 Power Sequencing
- 7.9.3 Clock Requirements and Characteristics
- 7.9.4
Peripherals
- 7.9.4.1
General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO)
- 7.9.4.1.1 GPIO - Output Timing
- 7.9.4.1.2 GPIO - Input Timing
- 7.9.4.1.3 Sampling Window Width for Input Signals
- 7.9.4.1.4
Low-Power Mode Wakeup Timing
- 7.9.4.1.4.1 IDLE Mode Timing Requirements
- 7.9.4.1.4.2 IDLE Mode Switching Characteristics
- 7.9.4.1.4.3 IDLE Mode Timing Diagram
- 7.9.4.1.4.4 STANDBY Mode Timing Requirements
- 7.9.4.1.4.5 STANDBY Mode Switching Characteristics
- 7.9.4.1.4.6 STANDBY Mode Timing Diagram
- 7.9.4.1.4.7 HALT Mode Timing Requirements
- 7.9.4.1.4.8 HALT Mode Switching Characteristics
- 7.9.4.1.4.9 HALT Mode Timing Diagram
- 7.9.4.2 Enhanced Control Peripherals
- 7.9.4.3 External Interrupt Timing
- 7.9.4.4 I2C Electrical Specification and Timing
- 7.9.4.5 Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) Timing
- 7.9.4.6
Multichannel Buffered Serial Port (McBSP) Timing
- 7.9.4.6.1 McBSP Transmit and Receive Timing
- 7.9.4.6.2
McBSP as SPI Master or Slave Timing
- 7.9.4.6.2.1 McBSP as SPI Master or Slave Timing Requirements (CLKSTP = 10b, CLKXP = 0)
- 7.9.4.6.2.2 McBSP as SPI Master or Slave Switching Characteristics (CLKSTP = 10b, CLKXP = 0)
- 7.9.4.6.2.3 McBSP as SPI Master or Slave Timing Requirements (CLKSTP = 11b, CLKXP = 0)
- 7.9.4.6.2.4 McBSP as SPI Master or Slave Switching Characteristics (CLKSTP = 11b, CLKXP = 0)
- 7.9.4.6.2.5 McBSP as SPI Master or Slave Timing Requirements (CLKSTP = 10b, CLKXP = 1)
- 7.9.4.6.2.6 McBSP as SPI Master or Slave Switching Characteristics (CLKSTP = 10b, CLKXP = 1)
- 7.9.4.6.2.7 McBSP as SPI Master or Slave Timing Requirements (CLKSTP = 11b, CLKXP = 1)
- 7.9.4.6.2.8 McBSP as SPI Master or Slave Switching Characteristics (CLKSTP = 11b, CLKXP = 1)
- 7.9.4.1
General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO)
- 7.9.5 JTAG Debug Probe Connection Without Signal Buffering for the MCU
- 7.9.6
External Interface (XINTF) Timing
- 7.9.6.1 USEREADY = 0
- 7.9.6.2 Synchronous Mode (USEREADY = 1, READYMODE = 0)
- 7.9.6.3 Asynchronous Mode (USEREADY = 1, READYMODE = 1)
- 7.9.6.4 XINTF Signal Alignment to XCLKOUT
- 7.9.6.5 External Interface Read Timing
- 7.9.6.6 External Interface Write Timing
- 7.9.6.7
External Interface Ready-on-Read Timing With One External Wait State
- 7.9.6.7.1 External Interface Read Switching Characteristics (Ready-on-Read, One Wait State)
- 7.9.6.7.2 External Interface Read Timing Requirements (Ready-on-Read, One Wait State)
- 7.9.6.7.3 Synchronous XREADY Timing Requirements (Ready-on-Read, One Wait State)
- 7.9.6.7.4 Asynchronous XREADY Timing Requirements (Ready-on-Read, One Wait State)
- 7.9.6.8 External Interface Ready-on-Write Timing With One External Wait State
- 7.9.6.9 XHOLD and XHOLDA Timing
- 7.9.7 Flash Timing
- 7.10 On-Chip Analog-to-Digital Converter
- 7.11 Migrating Between F2833x Devices and F2823x Devices
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1
Brief Descriptions
- 8.1.1 C28x CPU
- 8.1.2 Memory Bus (Harvard Bus Architecture)
- 8.1.3 Peripheral Bus
- 8.1.4 Real-Time JTAG and Analysis
- 8.1.5 External Interface (XINTF)
- 8.1.6 Flash
- 8.1.7 M0, M1 SARAMs
- 8.1.8 L0, L1, L2, L3, L4, L5, L6, L7 SARAMs
- 8.1.9 Boot ROM
- 8.1.10 Security
- 8.1.11 Peripheral Interrupt Expansion (PIE) Block
- 8.1.12 External Interrupts (XINT1–XINT7, XNMI)
- 8.1.13 Oscillator and PLL
- 8.1.14 Watchdog
- 8.1.15 Peripheral Clocking
- 8.1.16 Low-Power Modes
- 8.1.17 Peripheral Frames 0, 1, 2, 3 (PFn)
- 8.1.18 General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO) Multiplexer
- 8.1.19 32-Bit CPU-Timers (0, 1, 2)
- 8.1.20 Control Peripherals
- 8.1.21 Serial Port Peripherals
- 8.2
Peripherals
- 8.2.1 DMA Overview
- 8.2.2 32-Bit CPU-Timer 0, CPU-Timer 1, CPU-Timer 2
- 8.2.3 Enhanced PWM Modules
- 8.2.4 High-Resolution PWM (HRPWM)
- 8.2.5 Enhanced CAP Modules
- 8.2.6 Enhanced QEP Modules
- 8.2.7 Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) Module
- 8.2.8 Multichannel Buffered Serial Port (McBSP) Module
- 8.2.9 Enhanced Controller Area Network (eCAN) Modules (eCAN-A and eCAN-B)
- 8.2.10 Serial Communications Interface (SCI) Modules (SCI-A, SCI-B, SCI-C)
- 8.2.11 Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) Module (SPI-A)
- 8.2.12 Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C)
- 8.2.13 GPIO MUX
- 8.2.14 External Interface (XINTF)
- 8.3 Memory Maps
- 8.4 Register Map
- 8.5 Interrupts
- 8.6 System Control
- 8.7 Low-Power Modes Block
- 8.1
Brief Descriptions
- 9 Applications, Implementation, and Layout
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- ZJZ|176
- PTP|176
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- PTP|176
Orderable Information
7.9.2.2 Reset (XRS) Timing Requirements
| MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tw(RSL1) (1) | Pulse duration, stable input clock to XRS high | 32tc(OSCCLK) | cycles | ||||
| tw(RSL2) | Pulse duration, XRS low | Warm reset | 32tc(OSCCLK) | cycles | |||
| tw(WDRS) | Pulse duration, reset pulse generated by watchdog | 512tc(OSCCLK) | cycles | ||||
| td(EX) | Delay time, address/data valid after XRS high | 32tc(OSCCLK) | cycles | ||||
| tOSCST (2) | Oscillator start-up time | 1 | 10 | ms | |||
| th(boot-mode) | Hold time for boot-mode pins | 200tc(OSCCLK) | cycles | ||||
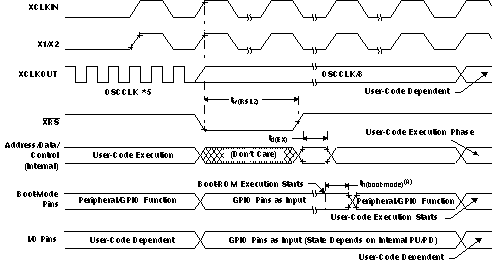
Figure 7-6 shows an example for the effect of writing into PLLCR register. In the first phase, PLLCR = 0x0004 and SYSCLKOUT = OSCCLK × 2. The PLLCR is then written with 0x0008. Right after the PLLCR register is written, the PLL lock-up phase begins. During this phase, SYSCLKOUT = OSCCLK/2. After the PLL lock-up is complete (which takes 131072 OSCCLK cycles), SYSCLKOUT reflects the new operating frequency, OSCCLK × 4.
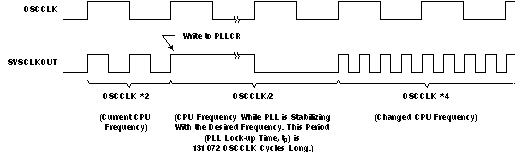 Figure 7-6 Example of Effect of Writing Into PLLCR Register
Figure 7-6 Example of Effect of Writing Into PLLCR Register