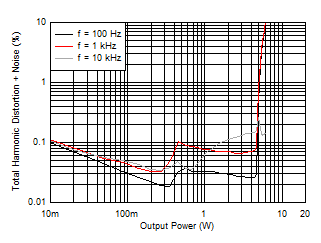
All measurements taken at audio frequency = 1 kHz, closed-loop gain = 26 dB, BD Modulation, 10 µH + 0.68 µF, TA = 25°C, AES17 measurement filter, unless otherwise noted.
All measurements taken at audio frequency = 1 kHz, closed-loop gain = 26 dB, BD Modulation, 10 µH + 0.68 µF, TA = 25°C, AES17 measurement filter, unless otherwise noted.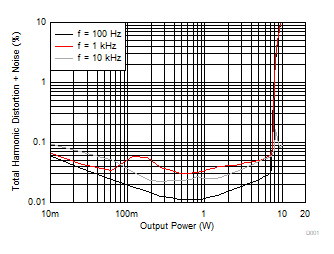
| AVCC = PVCC = 12 V, Load = 8 Ω, LC Filter |
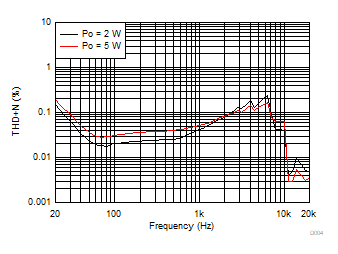
| AVCC = PVCC = 12 V, Load = 8 Ω, LC Filter |
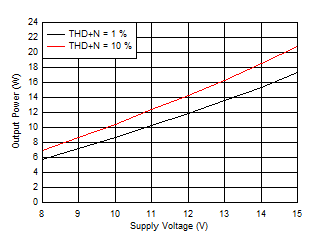 Figure 6-5 Output Power vs Supply Voltage (BTL)
Figure 6-5 Output Power vs Supply Voltage (BTL)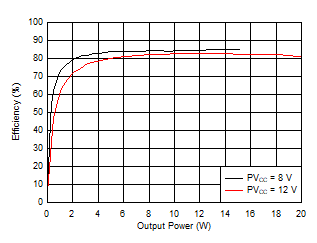 Figure 6-7 Efficiency vs Output Power (BTL)
Figure 6-7 Efficiency vs Output Power (BTL)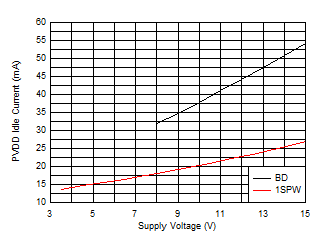 Figure 6-9 Idle Power vs Supply Voltage (BTL)
Figure 6-9 Idle Power vs Supply Voltage (BTL)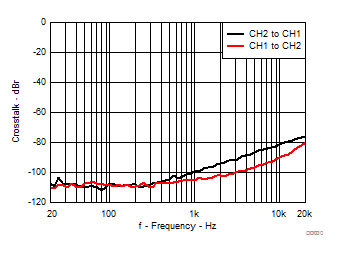
| AVCC=PVCC = 12 V, 1 W | Load = 6 Ω + 47 µH |
| Load = 8 Ω | Ferrite Bead Filter | |
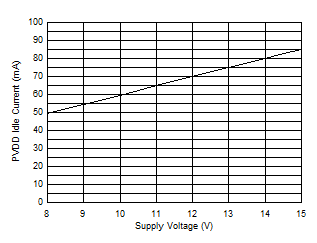
| AVCC=PVCC = 7.4 V | Load = 4 Ω | 1SPW |
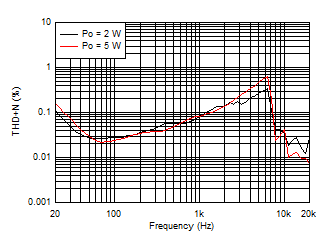
| AVCC=PVCC = 12 V | Load = 4 Ω | 1SPW |
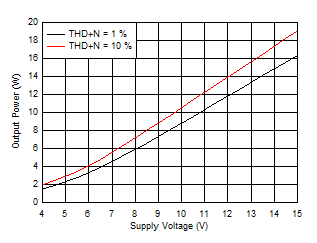 Figure 6-19 Output Power vs Supply Voltage, 4 Ω
Figure 6-19 Output Power vs Supply Voltage, 4 Ω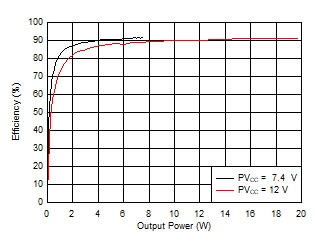 Figure 6-21 Efficiency vs Output Power, 8 Ω
Figure 6-21 Efficiency vs Output Power, 8 Ω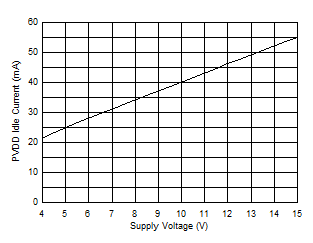
| Load = 8 Ω | Ferrite Bead Filter | 1SPW | |
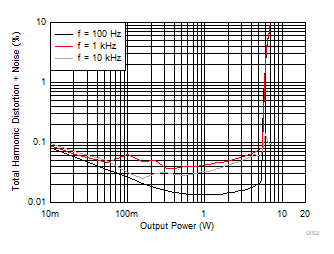
| AVCC=PVCC = 8 V, Load = 4 Ω, LC Filter |
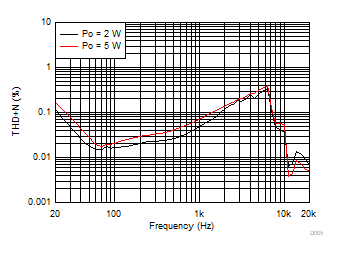
| AVCC=PVCC = 12 V, Load = 4 Ω |
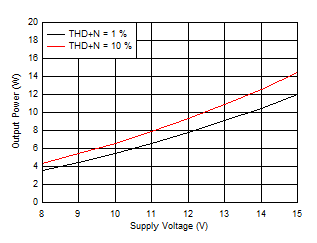 Figure 6-6 Output Power vs Supply Voltage (BTL)
Figure 6-6 Output Power vs Supply Voltage (BTL)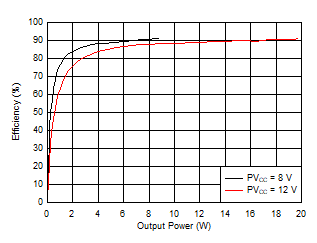 Figure 6-8 Efficiency vs Output Power (BTL)
Figure 6-8 Efficiency vs Output Power (BTL)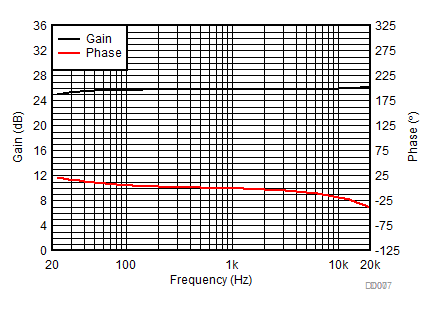
| AVCC= PVCC = 12 V | | Load = 6 Ω + 47 µH |
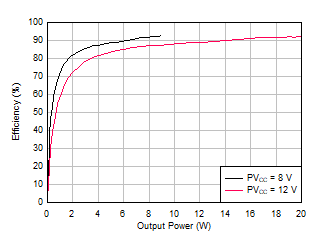
| Load = 8 Ω | Ferrite Bead Filter | |
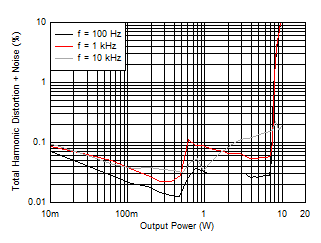
| AVCC=PVCC = 12 V, 1 W | Load = 8 Ω | 1SPW |
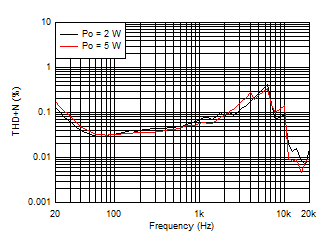
| AVCC=PVCC = 12 V | Load = 8 Ω | 1SPW |
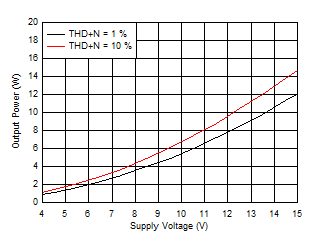 Figure 6-18 Output Power vs Supply Voltage, 8 Ω
Figure 6-18 Output Power vs Supply Voltage, 8 Ω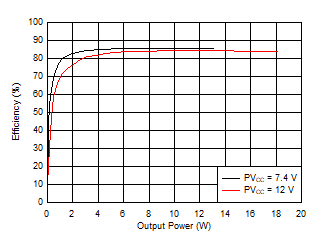 Figure 6-20 Efficiency vs Output Power, 4 Ω
Figure 6-20 Efficiency vs Output Power, 4 Ω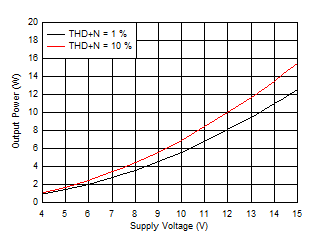
| Load = 8 Ω, | Ferrite Bead Filte | 1SPW |























