SLOS490C July 2006 – November 2015
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
- 9 Detailed Description
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7 Specifications
7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)(1)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VDD | Supply voltage | –0.3 | 6 | V | |
| VI | Input voltage | INx and SHUTDOWN pins | –0.3 | 0.3 | V |
| Continuous total power dissipation | See Dissipation Ratings | ||||
| TA | Operating free-air temperature | –40 | 85 | ºC | |
| TJ | Junction temperature | –40 | 125 | ºC | |
| Lead temperature 1.6 mm (1/16 inch) from case for 10 seconds | ZQV, DRB, DGN | 260 | ºC | ||
| Tstg | Storage temperature | –65 | 150 | °C | |
(1) Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, which do not imply functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under Recommended Operating Conditions. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
7.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human-body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001(1) | ±4000 | V |
| Charged-device model (CDM), per JEDEC specification JESD22-C101(2) | ±1500 | |||
(1) JEDEC document JEP155 states that 500-V HBM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
(2) JEDEC document JEP157 states that 250-V CDM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VDD | Supply voltage | 2.5 | 5.5 | V | ||
| VIH | High-level input voltage | SHUTDOWN | 1.15 | V | ||
| VIL | Low-level input voltage | SHUTDOWN | 0.5 | V | ||
| VIC | Common-mode input voltage | VDD = 2.5 V, 5.5 V, CMRR ≤ –60 dB | 0.5 | VDD–0.8 | V | |
| TA | Operating free-air temperature | –40 | 85 | °C | ||
| ZL | Load impedance | 6.4 | 8 | Ω | ||
7.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | TPA6205A1 | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BGA MICROSTAR JUNIOR | SON | MSOP PowerPAD | |||
| 8 PINS | 8 PINS | 8 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 134.4 | 57.3 | 109.5 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 79.8 | 84.0 | 67.8 | °C/W |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 71.1 | 32.2 | 47.6 | °C/W |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 5.3 | 3.7 | 4.7 | °C/W |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 71.0 | 32.2 | 47.2 | °C/W |
| RθJC(bot) | Junction-to-case (bottom) thermal resistance | — | 11.8 | 15.9 | °C/W |
(1) For more information about traditional and new thermal metrics, see the Semiconductor and IC Package Thermal Metrics application report, SPRA953.
7.5 Electrical Characteristics
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [VOO] | Output offset voltage (measured differentially) | VI = 0 V, VDD = 2.5 V to 5.5 V | 9 | mV | |||
| PSRR | Power supply rejection ratio | VDD = 2.5 V to 5.5 V | –90 | –70 | dB | ||
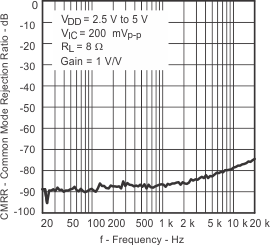
| CMRR | Common-mode rejection ratio | VDD = 3.6 V to 5.5 V, VIC = 0.5 V to VDD – 0.8 | –70 | –65 | dB | ||
| VDD = 2.5 V, VIC = 0.5 V to 1.7 V | –62 | –55 | |||||
| VOL | Low-level output voltage | RL = 8 Ω, VIN+ = VDD, VIN– = 0 V or VIN+ = 0 V, VIN– = VDD | VDD = 5.5 V | 0.3 | 0.46 | V | |
| VDD = 3.6 V | 0.22 | ||||||
| VDD = 2.5 V | 0.19 | 0.26 | |||||
| VOH | High-level output voltage | RL = 8 Ω, VIN+ = VDD, VIN– = 0 V or VIN+ = 0 V, VIN– = VDD | VDD = 5.5 V | 4.8 | 5.12 | V | |
| VDD = 3.6 V | 3.28 | ||||||
| VDD = 2.5 V | 2.1 | 2.24 | |||||
| [IIH] | High-level input current | VDD = 5.5 V, VI = 5.8 V | 1.2 | µA | |||
| [IIL] | Low-level input current | VDD = 5.5 V, VI = –0.3 V | 1.2 | µA | |||
| IDD | Supply current | VDD = 2.5 V to 5.5 V, No load, SHUTDOWN = VIH | 1.7 | 2 | mA | ||
| IDD(SD) | Supply current in shutdown mode | SHUTDOWN = VIL , VDD = 2.5 V to 5.5 V, No load | 0.01 | 0.9 | µA | ||
7.6 Operating Characteristics
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
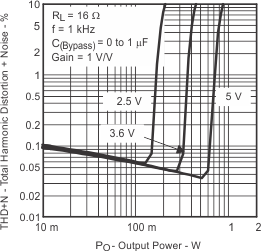
| PO | Output power | THD + N = 1%, f = 1 kHz | VDD = 5 V | 1.25 | W | ||
| VDD = 3.6 V | 0.63 | ||||||
| VDD = 2.5 V | 0.3 | ||||||
| THD+N | Total harmonic distortion plus noise | VDD = 5 V, PO = 1 W, f = 1 kHz | 0.06% | ||||
| VDD = 3.6 V, PO = 0.5 W, f = 1 kHz | 0.07% | ||||||
| VDD = 2.5 V, PO = 200 mW, f = 1 kHz | 0.08% | ||||||
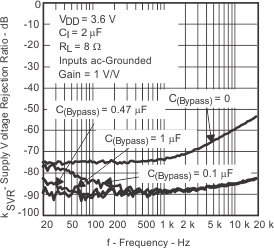
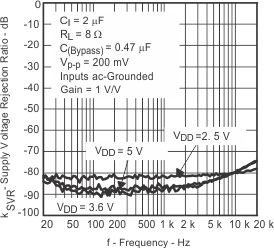
| kSVR | Supply ripple rejection ratio | C(BYPASS) = 0.47°F, VDD = 3.6 V to 5.5 V, Inputs AC-grounded with CI = 2 F | f = 217 Hz to 2 kHz, VRIPPLE = 200 mVPP | –87 | dB | ||
| C(BYPASS) = 0.47 F, VDD = 2.5 V to 3.6 V, Inputs AC-grounded with CI = 2 F | f = 217 Hz to 2 kHz, VRIPPLE = 200 mVPP | –82 | |||||
| C(BYPASS) = 0.47 F, VDD = 2.5 V to 5.5 V, Inputs AC-grounded with CI = 2 F | f = 40 Hz to 20 kHz, VRIPPLE = 200 mVPP | ≤ –74 | |||||
| SNR | Signal-to-noise ratio | VDD = 5 V, PO= 1 W | 104 | dB | |||
| Vn | Output voltage noise | f = 20 Hz to 20 kHz | No weighting | 17 | VRMS | ||
| A weighting | 13 | ||||||
| CMRR | Common-mode rejection ratio | VDD= 2.5 V to 5.5 V, Resistor tolerance = 0.1%, Gain = 4V/V, VICM = 200 mVPP | f = 20 Hz to 1 kHz | ≤ –85 | dB | ||
| f = 20 Hz to 20 kHz | ≤ –74 | ||||||
| ZI | Input impedance | 2 | MΩ | ||||
| ZO | Output impedance | Shutdown mode | >10 | kΩ | |||
| Shutdown attenuation | f = 20 Hz to 20 kHz, RF = RI = 20 kΩ | –80 | dB | ||||
7.7 Dissipation Ratings
| PACKAGE | TA ≤ 25°C POWER RATING | DERATING FACTOR | TA ≤ 70°C POWER RATING | TA ≤ 85°C POWER RATING |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZQV | 885 mW | 8.8 mW/°C | 486 mW | 354 mW |
| DGN | 2.13 W | 17.1 mW/°C | 1.36 W | 1.11 W |
| DRB | 2.7 W | 21.8 mW/°C | 1.7 W | 1.4 W |
7.8 Typical Characteristics
Table 1. Table of Graphs
| FIGURE | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
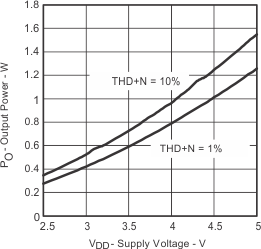
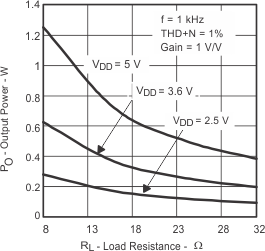
| PO | Output power | vs Supply voltage | Figure 1 | |
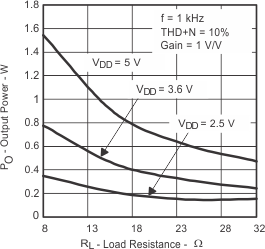
| vs Load resistance | Figure 2, Figure 3 | |||
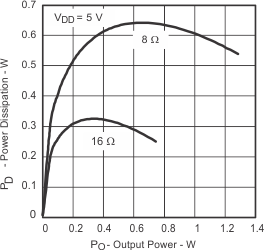
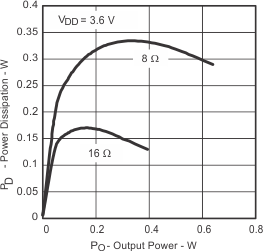
| PD | Power dissipation | vs Output power | Figure 4, Figure 5 | |
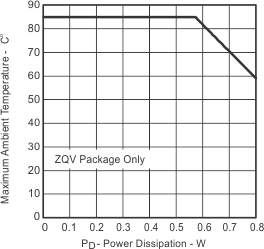
| Maximum ambient temperature | vs Power dissipation | Figure 6 | ||
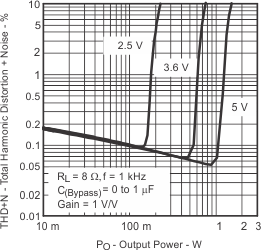
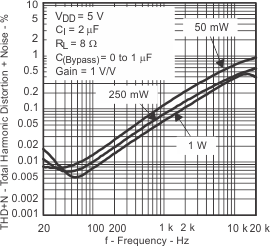
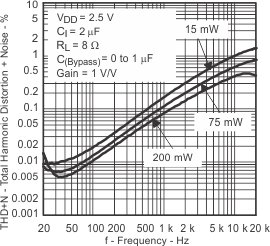
| Total harmonic distortion + noise | vs Output power | Figure 7, Figure 8 | ||
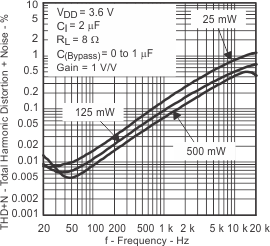
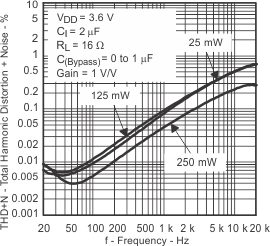
| vs Frequency | Figure 9, Figure 10, Figure 11, Figure 12 | |||
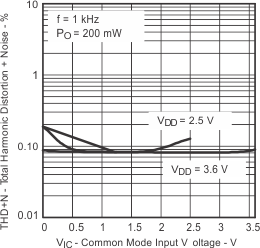
| vs Common-mode input voltage | Figure 13 | |||
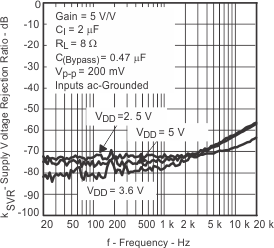
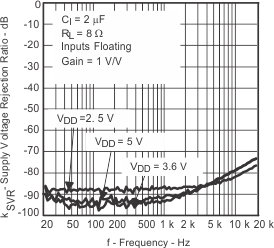
| Supply voltage rejection ratio | vs Frequency | Figure 14, Figure 15, Figure 16, Figure 17 | ||
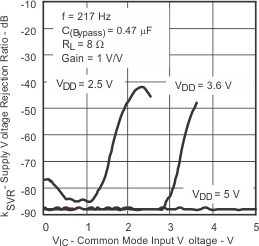
| Supply voltage rejection ratio | vs Common-mode input voltage | Figure 18 | ||
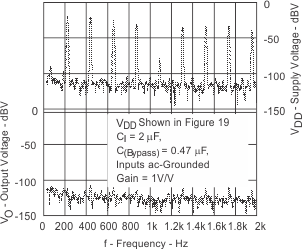
| GSM Power supply rejection | vs Time | Figure 19 | ||
| GSM Power supply rejection | vs Frequency | Figure 20 | ||
| CMRR | Common-mode rejection ratio | vs Frequency | Figure 21 | |
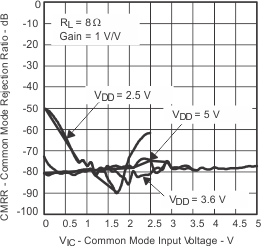
| vs Common-mode input voltage | Figure 22 | |||
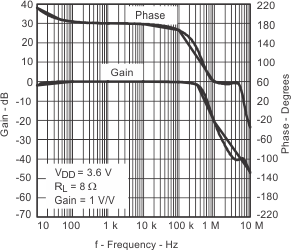
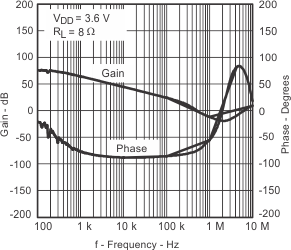
| Closed loop gain/phase | vs Frequency | Figure 23 | ||
| Open loop gain/phase | vs Frequency | Figure 24 | ||
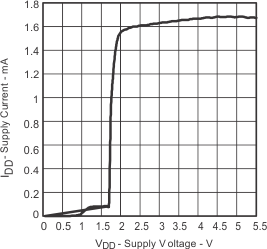
| IDD | Supply current | vs Supply voltage | Figure 25 | |
| Start-up time | vs Bypass capacitor | Figure 26 | ||
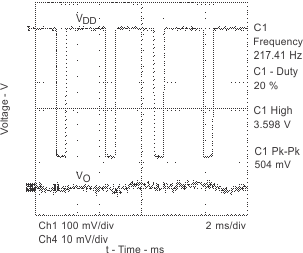
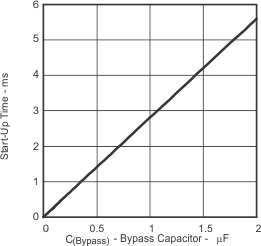
| Start-Up time is the time it takes (from a low-to-high transition on SHUTDOWN) for the gain of the amplifier to reach –3 dB of the final gain |