SLVSGF4B june 2022 – may 2023 TPS1641
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Enable and Shutdown Input (EN/SHDN)
- 8.3.2 Overvoltage Protection (OVP)
- 8.3.3 Output Slew Rate and Inrush Current Control (dVdt)
- 8.3.4 Active Current Limiting (ILIM) With the TPS16412, TPS16413, TPS16416, and TPS16417
- 8.3.5 Active Power Limiting (PLIM) With the TPS16410, TPS16411, TPS16414, and TPS16415
- 8.3.6 Overcurrent Protection (IOCP) and Blanking Time (IDLY or PDLY) for Transient Loads
- 8.3.7 Fast-Trip and Short-Circuit Protection
- 8.3.8 Analog Load Current Monitor (IMON) on the IOCP Pin
- 8.3.9 IN to OUT Short Detection (TPS16410, TPS16411, TPS16412, and TPS16413)
- 8.3.10 Thermal Shutdown and Overtemperature Protection
- 8.3.11 Fault Response and Indication (FLT)
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DRC|10
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DRC|10
Orderable Information
8.3.4 Active Current Limiting (ILIM) With the TPS16412, TPS16413, TPS16416, and TPS16417
The TPS16412, TPS16413, TPS16416, and TPS16417 devices respond to output overcurrent or overload conditions by actively limiting the current. The devices first provide a blanking time configured by capacitance on the IDLY pin. During this blanking time, the device can provide a current up to IOCP value. After the end of this blanking time, the devices limit current to ILIM value. ILIM can be set by connecting resistor on ILIM pin. RILIM can be calculated by Equation 3.
If the output current exceeds IOCP, the device goes into current limiting. During current limiting, if the output current goes below ILIM (IOUT < ILIM), the device resets the IDLY timer and restarts IDLY timer when IOUT > ILIM. Figure 8-10 illustrates the current limiting behavior for IOUT < IOCP and for IOCP ≤ IOUT < Ifast-trip. During current limiting, if the output current goes below ILIM (IOUT < ILIM), the device resets the IDLY timer and restarts the IDLY timer when IOUT > ILIM.
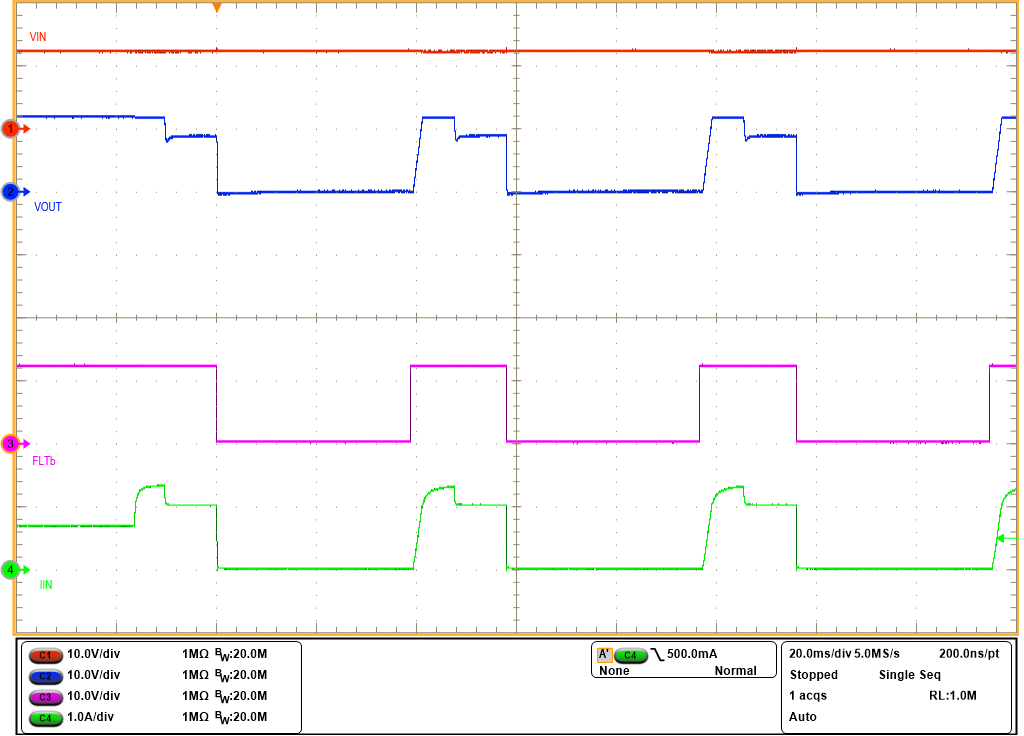 Figure 8-10 Current Limiting for
IOUT < IOCP
Figure 8-10 Current Limiting for
IOUT < IOCP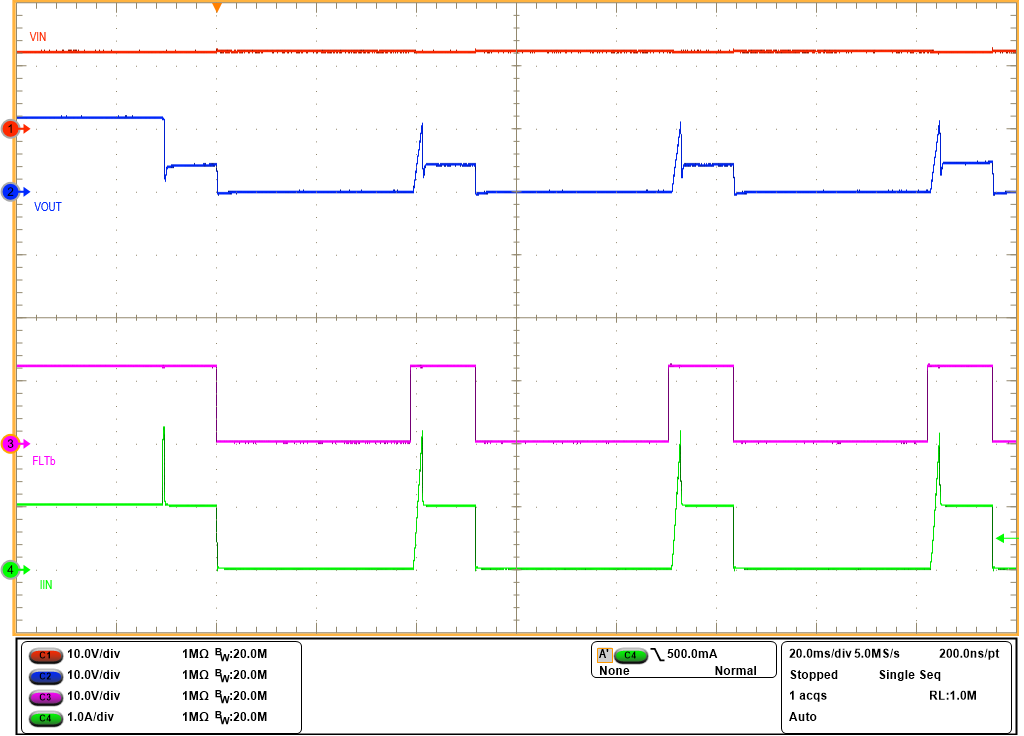 Figure 8-11 IOCP ≤
IOUT < Ifast-trip
Figure 8-11 IOCP ≤
IOUT < Ifast-tripDuring the current limiting, the device dissipates a power of (VIN – VOUT) × IOUT and the device gets heated up. If the junction temperature of device reaches thermal shutdown temperature (TTSD), the device turns off the internal FET. If the device does not go into thermal shutdown, the internal FET is turned off after a duration of tILIM-DUR. After the internal FET is turned off, the TPS16412 and TPS16416 auto-retry while the TPS16413 and TPS16417 latch off. If ILIM pin is connected to GND or left open, the device turns-off the internal FET. If the IDLY pin is left open or connected to GND, device provides tILIM-DUR = 155 ms unless the device enters thermal shutdown. Table 8-1 summarizes the device behavior for different output currents.
| Output Current (IOUT) | Device Response |
|---|---|
| IOUT < ILIM | The device provides current up to ILIM. |
| ILIM ≤ IOUT < IOCP | The device provides current up to IOCP for a duration of IDLY and then limits current to ILIM for a maximum duration of tILIM-DUR. |
| IOCP ≤ IOUT < Ifast-trip | The device limits current to ILIM for a maximum duration of tILIM-DUR. |
| Ifast-trip ≤ IOUT < ISCP | The device turns off the internal FET after a delay of tfast-trip. |
| ISCP ≤ IOUT | The device turns off the internal FET after a delay of tSCP_dly. |