SLVSET9F September 2018 – February 2023 TPS1663
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3
Feature Description
- 9.3.1 Hot Plug-In and In-Rush Current Control
- 9.3.2 Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO)
- 9.3.3 Overvoltage Protection (OVP)
- 9.3.4 Overload and Short Circuit Protection
- 9.3.5 Output Power Limiting, PLIM (TPS16632 Only)
- 9.3.6 Current Monitoring Output (IMON)
- 9.3.7 FAULT Response (FLT)
- 9.3.8 Power Good Output (PGOOD)
- 9.3.9 IN, P_IN, OUT and GND Pins
- 9.3.10 Thermal Shutdown
- 9.3.11 Low Current Shutdown Control (SHDN)
- 9.4 Device Functional Modes
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RGE|24
- PWP|20
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
9.3.6 Current Monitoring Output (IMON)
The TPS1663x devices feature an accurate analog current monitoring output. A current source at IMON terminal is internally configured to be proportional to the current flowing from IN to OUT. This current can be converted into a voltage using a resistor R(IMON) from IMON terminal to GND terminal. The IMON voltage can be used as a means of monitoring current flow through the system. The maximum voltage (V(IMONmax) for monitoring the current is limited to 4 V. This limitation puts a limitation on maximum value of R(IMON) resistor and is determined by #SLVSDG25212.
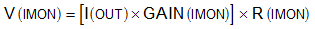
Where,
- GAIN(IMON) is the gain factor I(IMON):I(OUT) = 27.9μA/A (typical)
- I(OUT) is the load current
Refer to GUID-11039971-F80E-4560-8527-B1E4A4C9D168.html#SLVSDG27559 for IMON output versus load current plot. #T4331977-50 illustrates IMON performance.
 Figure 9-12 IMON Response During a Load Step
Figure 9-12 IMON Response During a Load StepThe IMON pin must not have a bypass capacitor to avoid delay in the current monitoring information.