SLVSE18B June 2019 – February 2023 TPS1HB35-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3
Feature Description
- 9.3.1 Protection Mechanisms
- 9.3.2 Diagnostic Mechanisms
- 9.4 Device Functional Modes
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PWP|16
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- PWP|16
Orderable Information
9.3.2.1.2 Detection With Switch Disabled
While the switch is disabled, if DIA_EN is high, an internal comparator will detect the condition of VOUT. If the load is disconnected (open load condition) or there is a short to battery the VOUT voltage will be higher than the open load threshold (VOL,off) and a fault is indicated on the SNS pin. An internal pull-up of 1 MΩ is in series with an internal MOSFET switch, so no external component is required if a completely open load must be detected. However, if there is significant leakage or other current draw even when the load is disconnected, a lower value pull-up resistor and switch can be added externally to set the VOUT voltage above the VOL,off during open load conditions.
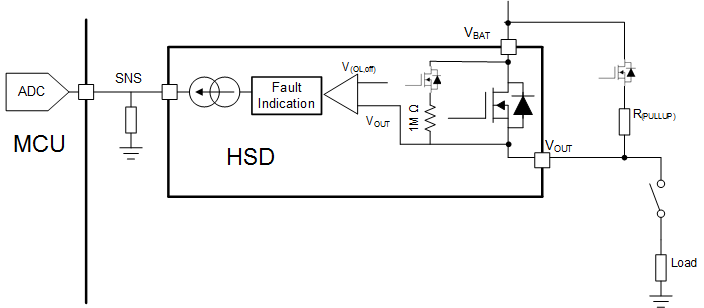
The detection circuitry is only enabled when DIA_EN = HIGH and EN = LOW. If VOUT > VOL, the SNS pin will go to the fault level, but if VOUT < VOL there will be no fault indication. The fault indication will only occur if the SEL1 pin is low.
While the switch is disabled and DIA_EN is high, the fault indication mechanisms will continuously represent the present status. For example, if VOUT decreases from greater than VOL to less than VOL, the fault indication is reset. Additionally, the fault indication is reset upon the falling edge of DIA_EN or the rising edge of EN.
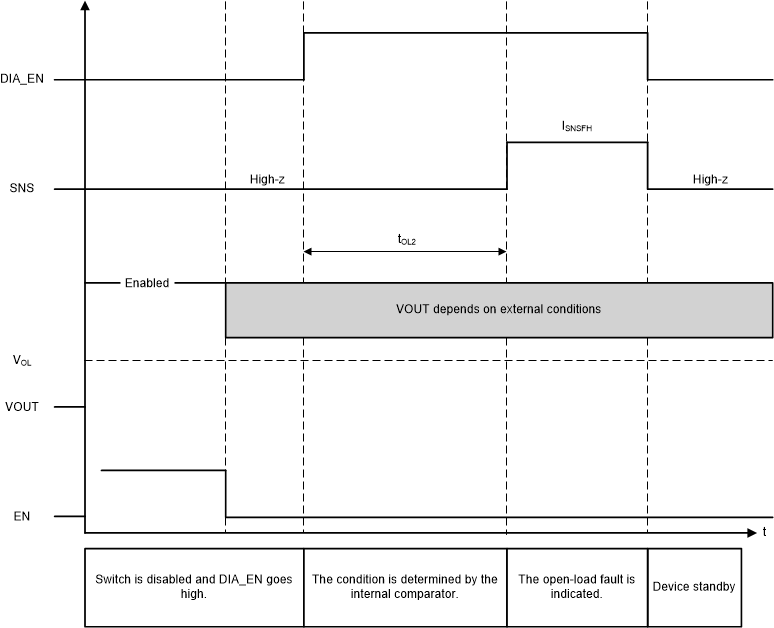 Figure 9-12 Open Load
Figure 9-12 Open Load