SLVS827D February 2009 – June 2015 TPS22904
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
- 9 Detailed Description
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- YFP|4
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
10 Application and Implementation
NOTE
Information in the following applications sections is not part of the TI component specification, and TI does not warrant its accuracy or completeness. TI’s customers are responsible for determining suitability of components for their purposes. Customers should validate and test their design implementation to confirm system functionality.
10.1 Application Information
10.1.1 Input Capacitor (Optional)
To limit the voltage drop on the input supply caused by transient in-rush currents when the switch turns on into a discharged load capacitor or short-circuit, a capacitor needs to be placed between VIN and GND. A 1-μF ceramic capacitor, CIN, placed close to the pins, is usually sufficient. Higher values of CIN can be used to further reduce the voltage drop during high-current application. When switching heavy loads, TI recommends to have an input capacitor about 10 times higher than the output capacitor to avoid excessive voltage drop.
10.1.2 Output Capacitor (Optional)
Due to the integral body diode in the PMOS switch, a CIN greater than CL is highly recommended. A CL greater than CIN can cause VOUT to exceed VIN when the system supply is removed. This could result in current flow through the body diode from VOUT to VIN.
10.2 Typical Application
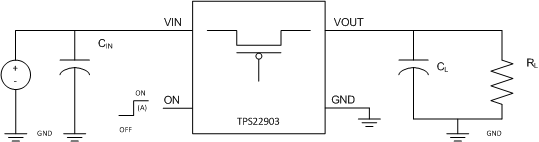 Figure 28. Typical Application Schematic
Figure 28. Typical Application Schematic
10.2.1 Design Requirements
Table 2 lists the design parameters for the TPS22903 device.
Table 2. Design Parameters
| DESIGN PARAMETER | EXAMPLE VALUE | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VIN | 1.8 V | |||
| Load Current | 0.3 A | |||
| Ambient Temperature | 25°C | |||
10.2.2 Detailed Design Procedure
10.2.2.1 VIN to VOUT Voltage Drop
The voltage drop from VIN to VOUT is determined by the ON-resistance of the device and the load current. RON can be found in Electrical Characteristics and is dependent on temperature. When the value of RON is found, Equation 1 can be used to calculate the voltage drop across the device:
where
- ΔV = Voltage drop across the device
- ILOAD = Load current
- RON = ON-resistance of the device
At VIN = 1.8 V, the TPS22903/4 has an RON value of 90 mΩ. Using this value and the defined load current, the above equation can be evaluated:
where
- ΔV = 27 mV
Therefore, the voltage drop across the device will be 27 mV.
10.2.3 Application Curve
Figure 29 shows the expected voltage drop across the device for different load currents and input voltages.
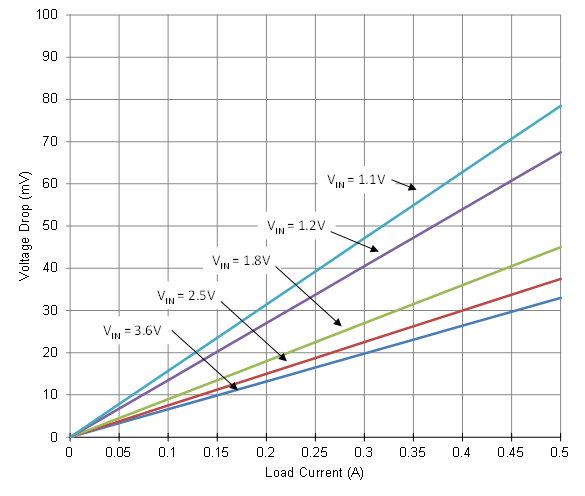 Figure 29. Voltage Drop vs Load Current
Figure 29. Voltage Drop vs Load Current