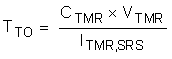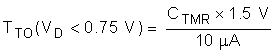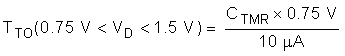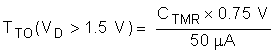SLVSDF9A December 2017 – January 2019 TPS23523
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2
Typical Application
- 9.2.1 Design Requirements
- 9.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.2.2.1 Selecting RSNS
- 9.2.2.2 Selecting Soft Start Setting: CSS and CSS,VEE
- 9.2.2.3 Selecting VDS Switch Over Threshold
- 9.2.2.4 Timer Selection
- 9.2.2.5 MOSFET Selection and SOA Checks
- 9.2.2.6 Input Cap, Input TVS, and OR-ing FET selection
- 9.2.2.7 EMI Filter Consideration
- 9.2.2.8 Undervoltage and Overvoltage Settings
- 9.2.2.9 Choosing RVCC and CVCC
- 9.2.2.10 Power Good Interface to Downstream DC/DC
- 9.2.3 Application Curves
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PW|16
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8.3.3 Timer
Timer is a critical feature in the hot swap, which manages the stress level in the MOSFET. The timer will source and sink current into the timer capacitor as follows:
- Not in current limit: sink 2 µA
- If the part is in current limit and VGATE < VGATE,TH, the timer sources current as follows:
- VD < VD,CL_SW: source 10 µA
- VD > VD,CL_SW: source 50 µA
The TPS23523 times out and shuts down the hot swap as follows.
- If VD < VD,TMR_SW then the hot swap times out when VTMR reaches 1.5 V.
- If VD > VD,TMR_SW then the hot swap times out when VTMR reaches 0.75 V.
The above behavior maximizes the ability of the hot swap to ride out voltage steps, while ensuring that the FET remains safe even if the part can not ride out a voltage step.
A cool down period follows after the part times out. During this time the timer performs the following:
- Discharge CTMR with a 2-µA current source until 0.5 V
- Charge CTMR with a 10-µA current source until it is back to 1.5 V.
- Repeat the above 64 times
- Discharge timer to 0 V.
The part attempts to restart after finishing the above. If the UVEN signal is toggled while the 64 cycles are in progress the part restarts immediately after the 64 cycles are completed.
The timer operates as follows when recovering from POR:
- If VTMR < 0.5 V:
- Proceed to regular startup
- Do not discharge VTMR
- If VTMR > 0.5 V:
- Go through 64 charge/discharge cycles
- Discharge VTMR
- Proceed to startup
The Time Out (TTO) can be computed using the equations below. Note that the time out depends on the VDS of the MOSFET.