SLVSDW2B December 2018 – November 2020 TPS23755
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 CLS Classification
- 7.3.2 DEN Detection and Enable
- 7.3.3 Internal Pass MOSFET
- 7.3.4
DC-DC Controller Features
- 7.3.4.1 VCC, VB and Advanced PWM Startup
- 7.3.4.2 CS, Current Slope Compensation and Blanking
- 7.3.4.3 COMP, FB, CP and Opto-less Feedback
- 7.3.4.4 FRS Frequency Setting and Synchronization
- 7.3.4.5 Frequency Dithering for Spread Spectrum Applications
- 7.3.4.6 SST and Soft-Start of the Switcher
- 7.3.4.7 AUX_V, AUX_D and Secondary Adapter Or'ing
- 7.3.5 Internal Switching FET - DRAIN, RSNS, SRF and SRR
- 7.3.6 VPD Supply Voltage
- 7.3.7 VDD Supply Voltage
- 7.3.8 GND
- 7.3.9 VSS
- 7.3.10 Exposed Thermal PAD
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 Input Bridges and Schottky Diodes
- 8.2.2.2 Protection, D1
- 8.2.2.3 Capacitor, C1
- 8.2.2.4 Detection Resistor, RDEN
- 8.2.2.5 Classification Resistor, RCLS
- 8.2.2.6 Bulk Capacitance, CBULK
- 8.2.2.7 Output Voltage Feedback Divider, RAUX, R1,R2
- 8.2.2.8 Setting Frequency, RFRS
- 8.2.2.9 Frequency Dithering, RDTR and CDTR
- 8.2.2.10 Bias Voltage, CVB and DVB
- 8.2.2.11 Transformer design, T1
- 8.2.2.12 Current Sense Resistor, RCS
- 8.2.2.13 Current Slope Compensation, RS
- 8.2.2.14 Bias Supply Requirements, CCC, DCC
- 8.2.2.15 Switching Transformer Considerations, RVCC and CCC2
- 8.2.2.16 Primary FET Clamping, RCL, CCL, and DCL
- 8.2.2.17 Converter Output Capacitance, COUT
- 8.2.2.18 Secondary Output Diode Rectifier, DOUT
- 8.2.2.19 Slew rate control, RSRF and RSRR
- 8.2.2.20 Shutdown at Low Temperatures, DVDD and CVDD
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RJJ|23
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.3.4.4 FRS Frequency Setting and Synchronization
The FRS pin programs the (free-running) oscillator frequency, and may also be used to synchronize the TPS23755 converter to a higher frequency. The internal oscillator sets the maximum duty cycle and controls the current-compensation ramp circuit, making the ramp height independent of frequency. RFRS must be selected per Equation 2.
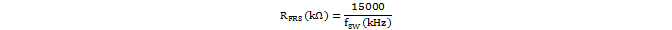
The TPS23755 may be synchronized to an external clock to eliminate beat frequencies from a sampled system, or to place emission spectrum away from an RF input frequency. Synchronization may be accomplished by applying a short pulse ( > 35 ns) of magnitude VSYNC to FRS as shown in Figure 7-3. RFRS must be chosen so that the maximum free-running frequency is just below the desired synchronization frequency. The synchronization pulse terminates the potential ON-time period, and the OFF-time period does not begin until the pulse terminates. A short pulse is preferred to avoid reducing the potential ON-time.
Figure 7-3 shows examples of nonisolated and transformer-coupled synchronization circuits. RT reduces noise susceptibility for the isolation transformer implementation. The FRS node must be protected from noise because it is high impedance.
 Figure 7-3 Synchronization
Figure 7-3 Synchronization