SLVSCJ0E March 2014 – June 2021 TPS25200
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DRV|6
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DRV|6
Orderable Information
9.2.2.4 Design Above a Minimum Current Limit
Some applications require that current limiting cannot occur below a certain threshold. For this example, assume that 2.1 A must be delivered to the load so that the minimum desired current-limit threshold is 2100 mA. Use the IOS equations (Equation 1) and Figure 9-4 to select RILIM as shown in Equation 2.
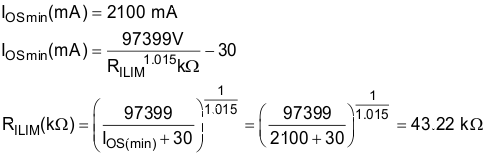
Select the closest 1% resistor less than the calculated value: RILIM = 42.2 kΩ. This sets the minimum current-limit threshold at 2130 mA as shown in Equation 3.
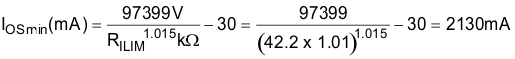
Use the IOS equations (Equation 1), Figure 9-4, and the previously calculated value for RILIM to calculate the maximum resulting current-limit threshold as shown in Equation 4.
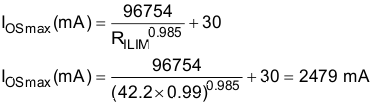
The resulting current-limit threshold minimum is 2130 mA and maximum is 2479 mA with RILIM = 42.2kΩ ± 1%.