SLVSFX8A March 2021 – March 2022 TPS2521
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Input Reverse Polarity Protection
- 8.3.2 Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO and UVP)
- 8.3.3 Overvoltage Clamp (OVC)
- 8.3.4 Inrush Current, Overcurrent, and Short Circuit Protection
- 8.3.5 Analog Load Current Monitor
- 8.3.6 Reverse Current Protection
- 8.3.7 Overtemperature Protection (OTP)
- 8.3.8 Fault Response
- 8.3.9 Power Good Indication (PG)
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RPW|10
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
9.3.3.3 Setting Output Voltage Rise Time (tR)
The slew rate (SR) needed to meet the target specification is:
Equation 8. 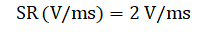
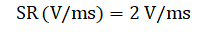
The CdVdt needed to achieve this slew rate can be calculated as:
Equation 9. 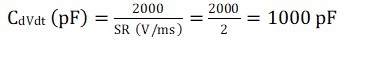
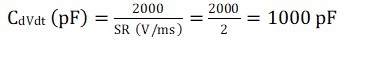
Choose the nearest standard capacitor value as 1 nF.
For this slew rate, the inrush current can be calculated as:
Equation 10. 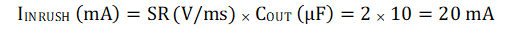
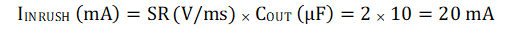
The average power dissipation inside the part during inrush can be calculated as:
Equation 11. 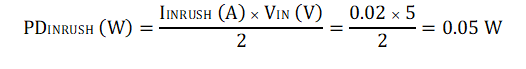
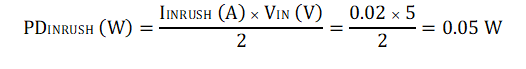
The power dissipation is below the allowed limit for a successful start-up without hitting thermal shut-down within the target rise time as shown in Figure 9-4.
Figure 9-4 Thermal Shut-Down Plot
During Inrush