SLVSC97B March 2014 – September 2020 TPS2556-Q1 , TPS2557-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Application
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Terminal Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Applications and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DRB|8
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DRB|8
Orderable Information
9.2.2.4 Selecting Current-Limit Resistor 2
Some applications require that current limiting must occur below a certain threshold. For this example, assume that the desired upper current-limit threshold must be below 5,000 mA to protect an upstream power supply. Use the IOS equations and Figure 9-2 to select R(ILIM).
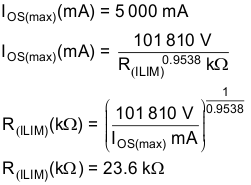
Select the closest 1% resistor greater than the calculated value: R(ILIM) = 23.7 kΩ. This sets the maximum current-limit threshold at 5 000 mA . Use the IOS equations, Figure 10-2, and the previously calculated value for RILIM to calculate the minimum resulting current-limit threshold.

The resulting minimum current-limit threshold is 4 406 mA with a 23.7-kΩ resistor.