SLVSGP9 October 2023 TPS25730
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Device Comparison Table
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Recommended Capacitance
- 6.5 Thermal Information
- 6.6 Power Supply Characteristics
- 6.7 Power Consumption
- 6.8 PPHV Power Switch Characteristics - TPS25730D
- 6.9 PP_EXT Power Switch Characteristics - TPS25730S
- 6.10 Power Path Supervisory
- 6.11 CC Cable Detection Parameters
- 6.12 CC PHY Parameters
- 6.13 Thermal Shutdown Characteristics
- 6.14 ADC Characteristics
- 6.15 Input/Output (I/O) Characteristics
- 6.16 I2C Requirements and Characteristics
- 6.17 Typical Characteristics
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 USB-PD Physical Layer
- 8.3.2 Power Management
- 8.3.3 Power Paths
- 8.3.4 Cable Plug and Orientation Detection
- 8.3.5 Overvoltage Protection (CC1, CC2)
- 8.3.6 Default Behavior Configuration (ADCIN1, ADCIN2)
- 8.3.7 ADC
- 8.3.8 Digital Interfaces
- 8.3.9 Digital Core
- 8.3.10 I2C Interface
- 8.3.11 Minimum Voltage Configuration
- 8.3.12 Maximum Voltage Configuration
- 8.3.13 Sink Current Configuration
- 8.3.14 Autonegotiate Sink Minimum Power
- 8.3.15 Extended Sink Capabilities Power Delivery Power
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5 Schottky for Current Surge Protection
- 8.6 Thermal Shutdown
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Revision History
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RSM|32
Orderable Information
8.3.10.1.2 Unique Address Interface
The Unique Address Interface allows for complex interaction between an I2C controller and a single TPS25730. The I2C target sub-address is used to receive or respond to Host Interface protocol commands. Figure 8-23 and Figure 8-24 show the write and read protocol for the I2C target interface, and a key is included in Figure 8-25 to explain the terminology used. The key to the protocol diagrams is in the SMBus Specification and is repeated here in part.
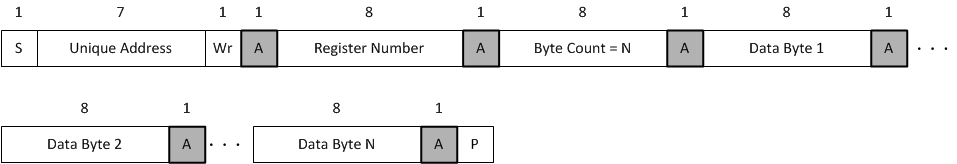 Figure 8-23 I2C Unique Address Write Register Protocol
Figure 8-23 I2C Unique Address Write Register Protocol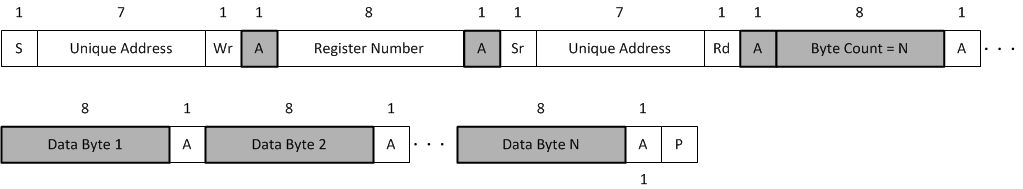 Figure 8-24 I2C Unique Address Read Register Protocol
Figure 8-24 I2C Unique Address Read Register Protocol Figure 8-25 I2C Read/Write Protocol Key
Figure 8-25 I2C Read/Write Protocol Key