SLVSH93A October 2023 – March 2024 TPS25751
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Device Comparison Table
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Recommended Capacitance
- 6.5 Thermal Information
- 6.6 Power Supply Characteristics
- 6.7 Power Consumption
- 6.8 PP_5V Power Switch Characteristics
- 6.9 PPHV Power Switch Characteristics - TPS25751D
- 6.10 PP_EXT Power Switch Characteristics - TPS25751S
- 6.11 Power Path Supervisory
- 6.12 CC Cable Detection Parameters
- 6.13 CC VCONN Parameters
- 6.14 CC PHY Parameters
- 6.15 Thermal Shutdown Characteristics
- 6.16 ADC Characteristics
- 6.17 Input/Output (I/O) Characteristics
- 6.18 BC1.2 Characteristics
- 6.19 I2C Requirements and Characteristics
- 6.20 Typical Characteristics
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 USB-PD Physical Layer
- 8.3.2 Power Management
- 8.3.3 Power Paths
- 8.3.4 Cable Plug and Orientation Detection
- 8.3.5 Overvoltage Protection (CC1, CC2)
- 8.3.6 Default Behavior Configuration (ADCIN1, ADCIN2)
- 8.3.7 ADC
- 8.3.8 BC 1.2 (USB_P, USB_N)
- 8.3.9 Digital Interfaces
- 8.3.10 Digital Core
- 8.3.11 I2C Interface
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5 Thermal Shutdown
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2 Typical Application
- 9.3 Power Supply Recommendations
- 9.4
Layout
- 9.4.1 TPS25751D - Layout
- 9.4.2 TPS25751S - Layout
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Revision History
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RSM|32
Orderable Information
8.3.3.3.1 Overvoltage Protection (OVP)
The application firmware enables the OVP and configures it based on the expected VBUS voltage. If the voltage on VBUS surpasses the configured threshold VOVP4VSYS = VOVP4RCP/rOVP, then GATE_VSYS is automatically disabled within tPPHV_FSD to protect the system. If the voltage on VBUS surpasses the configured threshold VOVP4RCP, then GATE_VBUS is automatically disabled within tPPHV_OVP. When VVBUS falls below VOVP4RCP - VOVP4RCPH, GATE_VBUS is automatically re-enabled within tPPHV_ON because the OVP condition has cleared. This action allows two sinking power paths to be enabled simultaneously and GATE_VBUS disables when necessary to ensure that VVBUS remains below VOVP4RCP.
While the TPS25751D is in BOOT mode in a dead-battery scenario (that is VIN_3V3 is low), it handles an OVP condition slightly differently. As long as the OVP condition is present, GATE_VBUS and GATE_VSYS are disabled. Once the OVP condition clears, both GATE_VBUS and GATE_VSYS are re-enabled. Because this is a dead-battery condition, the TPS25751D draws approximately IVIN_3V3, ActSnk from VBUS during this time to help discharge it.
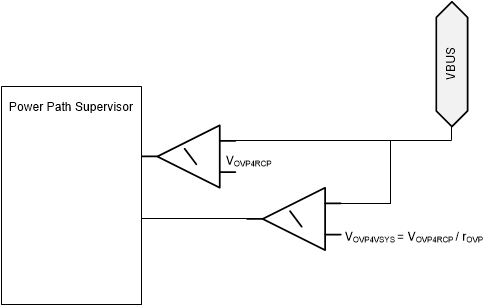 Figure 8-18 Diagram for OVP
Comparators
Figure 8-18 Diagram for OVP
Comparators