SLVSGO0 October 2024 TPS25763-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Device Comparison Table
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Recommended Components
- 6.5 Thermal Information
- 6.6 Buck-Boost Regulator
- 6.7 CC Cable Detection Parameters
- 6.8 CC VCONN Parameters
- 6.9 CC PHY Parameters
- 6.10 Thermal Shutdown Characteristics
- 6.11 Oscillator Characteristics
- 6.12 ADC Characteristics
- 6.13 TVSP Parameters
- 6.14 Input/Output (I/O) Characteristics
- 6.15 BC1.2 Characteristics
- 6.16 I2C Requirements and Characteristics
- 6.17 Typical Characteristics
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Device Power Management and Supervisory Circuitry
- 8.3.2 TVSP Device Configuration and ESD Protection
- 8.3.3 External NFET and LSGD
- 8.3.4
Buck-Boost Regulator
- 8.3.4.1 Buck-Boost Regulator Operation
- 8.3.4.2 Switching Frequency, Frequency Dither, Phase-Shift and Synchronization
- 8.3.4.3 VIN Supply and VIN Over-Voltage Protection
- 8.3.4.4 Feedback Paths and Error Amplifiers
- 8.3.4.5 Transconductors and Compensation
- 8.3.4.6 Output Voltage DAC, Soft-Start and Cable Droop Compensation
- 8.3.4.7 VBUS Overvoltage Protection
- 8.3.4.8 VBUS Undervoltage Protection
- 8.3.4.9 Current Sense Resistor (RSNS) and Current Limit Operation
- 8.3.4.10 Buck-Boost Peak Current Limits
- 8.3.5 USB-PD Physical Layer
- 8.3.6 VCONN
- 8.3.7 Cable Plug and Orientation Detection
- 8.3.8 ADC
- 8.3.9 BC 1.2, Legacy and Fast Charging Modes (Px_DP, Px_DM)
- 8.3.10 DisplayPort Hot-Plug Detect (HPD)
- 8.3.11 USB2.0 Low-Speed Endpoint
- 8.3.12 Digital Interfaces
- 8.3.13 I2C Interface
- 8.3.14 Digital Core
- 8.3.15 NTC Input
- 8.3.16 Thermal Sensors and Thermal Shutdown
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Revision History
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RQL|29
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8.3.7.1 Configured as a Source
When Port A is configured as a Source, the device detects when a cable or a Sink is attached using the Px_CC1 and Px_CC2 pins. When in a disconnected state, the device monitors the voltages on these pins to determine what, if anything, is connected. See USB Type-C Specification for more information.
Table 8-5 shows the Cable Detect States for a Source.
| Px_CC1 | Px_CC2 | CONNECTION STATE | RESULTING ACTION |
|---|---|---|---|
| Open | Open | Nothing attached | Continue monitoring both Px_CCy pins for attach. Power is not applied to Px_VBUS or VCONN. |
| Rd | Open | Sink attached | Monitor Px_CC1 for detach. Power is applied to Px_VBUS but not to VCONN (Px_CC2). |
| Open | Rd | Sink attached | Monitor Px_CC2 for detach. Power is applied to Px_VBUS but not to VCONN (Px_CC1). |
| Ra | Open | Powered Cable-No UFP attached | Monitor Px_CC2 for a Sink attach and Px_CC1 for cable detach. Power is not applied to Px_VBUS or VCONN (Px_CC1). |
| Open | Ra | Powered Cable-No UFP attached | Monitor Px_CC1 for a Sink attach and Px_CC2 for cable detach. Power is not applied to Px_VBUS or VCONN (Px_CC2). |
| Ra | Rd | Powered Cable-UFP Attached | Provide power on Px_VBUS and VCONN (Px_CC1) then monitor Px_CC2 for a Sink detach. Px_CC1 is not monitored for a detach. |
| Rd | Ra | Powered Cable-UFP attached | Provide power on Px_VBUS and VCONN (Px_CC2) then monitor Px_CC1 for a Sink detach. Px_CC2 is not monitored for a detach. |
When a port is configured as a Source, a current IRp1.5A, is driven out of each Px_CCy pin and each pin is monitored for different states. When a Sink is attached to the port a pull-down resistance of Rd to GND exists. The current IRp1.5A is then forced across the resistance Rd generating a voltage at the Px_CCy pin. The device applies the configured IRp1.5A until the buck-boost regulator is enabled and operating at 5 V, at which time application firmware may remain at IRp1.5A or change to IRp3.0A.
When the Px_CCy pin is connected to an electronically marked cable VCONN input, the pull-down resistance is different (Ra). In this case the voltage on the Px_CCy pin pulls below VRDstd and the system recognizes the electronically marked cable.
The VDstd1.5 or VD3.0 threshold is monitored to detect a disconnection depending upon which Rp current source is active. When a connection has been recognized and the voltage on Px_CCy subsequently rises above the disconnect threshold for tCC, the system registers a disconnection.
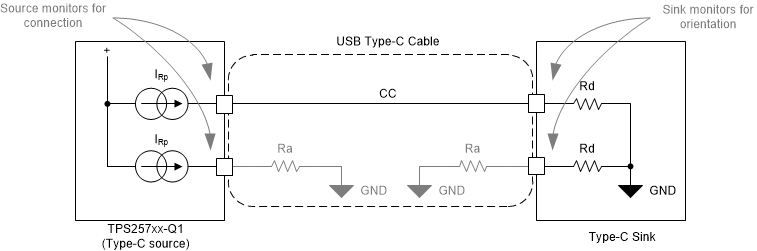 Figure 8-29 Type-C Cable
Figure 8-29 Type-C Cable